Overview¶
seqspec, short for “sequence specification” (pronounced “seek-speck”), is a machine-readable specification for annotating sequencing libraries produced by genomics assays. Genomic library structure depends on both the assay and sequencer (and kits) used to generate and bind the assay-specific construct to the sequencing adapters to generate a sequencing library. seqspec is specific to both a genomics assay and sequencer and provides a standardized format for describing the structure of sequencing libraries and the resulting sequencing reads. Specifically, a seqspec file is a machine-readable YAML file that annotates the content of molecules in genomic libraries, the structure of reads generated from them, and how those are stored in files.
The primary goal of a seqspec file is to:
- Facilitate standardization of preprocessing steps across different assays
- Enable data management and tracking
- Simplify the interpretation and reuse of sequencing data
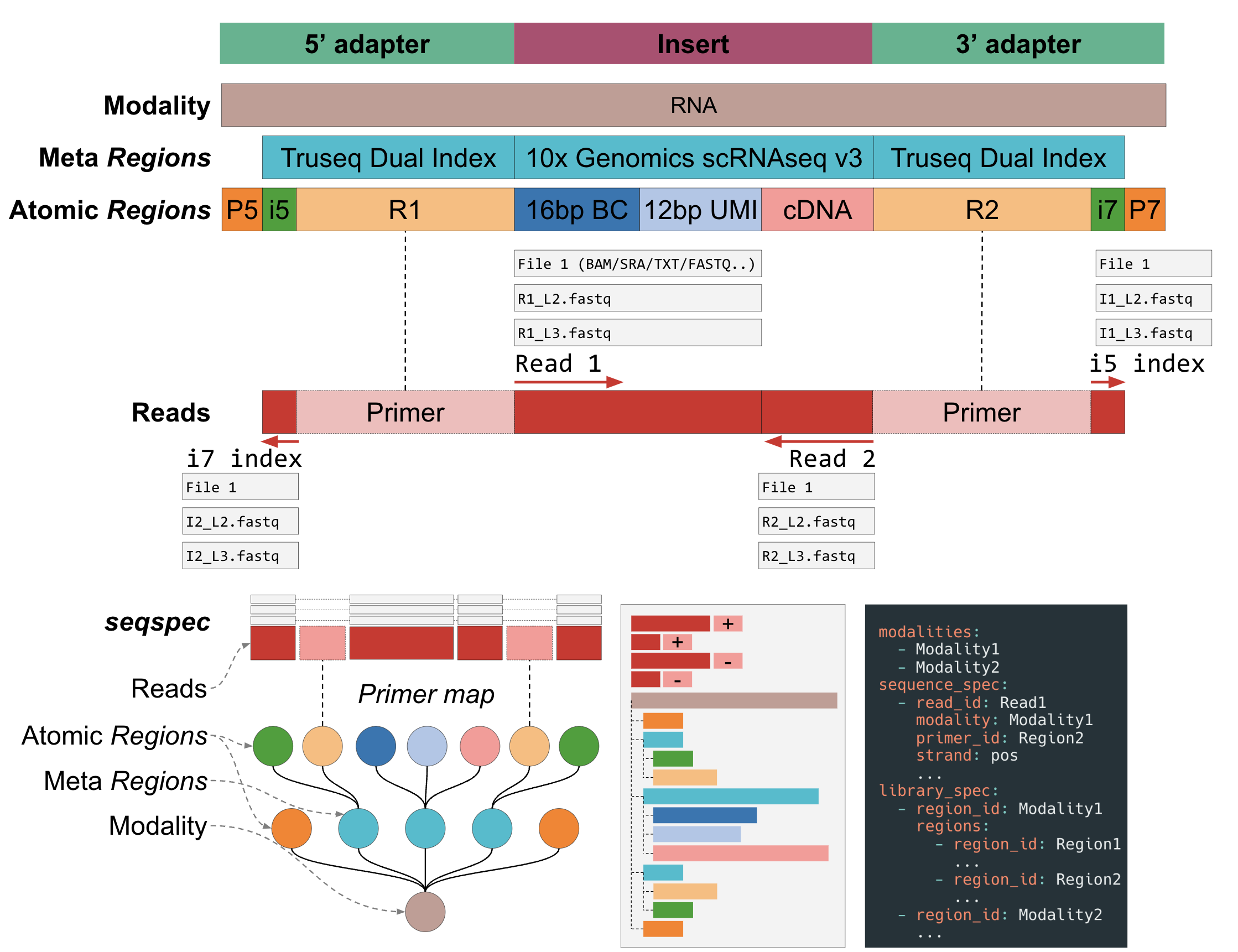 Figure 1: Detailed structure of a
Figure 1: Detailed structure of a seqspec file.
A seqspec file, Figure 1, contains
- Assay-level metadata such as library kit and sequencing machine,
- The 5’->3’ annotation and position of the elements in a library molecule (e.g. barcodes, UMIs),
- A list of the reads generated from sequencing the library molecule.
Structure¶
A seqspec file consists of three main components:
- Assay Information: Metadata about the assay, including identifiers, protocols, and kits used.
- Library Structure: Description of the molecular components in the sequencing library.
- Read Structure: Description of the sequencing reads generated from the sequencing library.
seqspec files are written in YAML format and can be created and edited in a text editor like VSCode, TextEdit, Notepad, or Sublime. The basic structure includes:
seqspec_version: <version>
assay_id:
# + Assay metadata
modalities:
# List of modalities (e.g., RNA, DNA, ATAC)
library_spec:
# List of regions in the library
sequence_spec:
# List of reads generated from the libraryseqspec files can be manipulated and used with the seqspec command line tool.
Assay Information¶
The header of a seqspec file stores assay metadata including library preparation and sequencing kits and protocols.
modalities contains a list of strings describing the types of molecules assayed. They come from a controlled vocabulary. The first-level library_spec regions must have region_ids equal to these modalities.
Library structure¶
The library_spec describes the “regions”, or set of standard “blocks” such as a barcode, contained in the sequencing library. Each region is annotated with the following metadata:
region_id: Unique identifier for the regionregion_type: Type of region (e.g., barcode, UMI, cDNA). See the complete list in the technical specification.metais used as a modality placeholder byseqspec initfor the top-level regions.sequence_type: Nature of the sequence (fixed, random, onlist)sequence: Actual or representative sequencemin_lenandmax_len: Minimum and maximum length of the region
Each region can contain nested regions under the regions property. This means a valid library structure could look like:
region_1
|-region_2
|--region_3
|-region_4
region_5
|-region_6Regions are annotated in the 5’ -> 3’ order. The spec encodes relative ordering and bounds (min_len, max_len), not absolute coordinates.
This means that that the vertical ordering of the regions in the spec must correspond to their 5’ -> 3’ ordering of the element in the library molecule that is being annotated.
Sequence structure¶
The sequence_spec contains a list of sequencing reads generated from the library_spec. Each read is annotated with the following metadata:
read_id: Identifier for the readmodality: Associated modalityprimer_id: ID of the primer region in the library structurestrand: Orientation of the read (pos or neg)min_lenandmax_len: Minimum and maximum length of the read
Mapping Reads to Library Elements¶
The relationship between the sequence_spec and library_spec in seqspec is defined as follows:
- Each read in the
sequence_spechas aprimer_idthat corresponds to a uniqueregion_idin thelibrary_spec. - This
primer_idindicates the starting point of the read within the library molecule. - The
min_lenandmax_lenproperties of the read define how many bases are sequenced from this starting point. - The read encompasses all library elements that fall within its length, starting from the end of the
primer_idregion. - If the read is on the positive strand, it extends to the right of the primer; if on the negative strand, it extends to the left.
This mapping enables precise identification of library elements captured in each sequencing read using the seqspec index command.
Mapping Files to Reads¶
Each Read can contain a list of File objects. These correspond to real files that contain the sequences represented by the Read. Practically, multiple FASTQ files from different lanes but the same read are common. For example, a run with three lanes per read might look like:
Read 1
- R1_L001.fastq.gz
- R1_L002.fastq.gz
- R1_L003.fastq.gz
Read 2
- R2_L001.fastq.gz
- R2_L002.fastq.gz
- R2_L003.fastq.gz
And are sometimes represented as “pairs”
- R1_L001.fastq.gz, R2_L001.fastq.gz
- R1_L002.fastq.gz, R2_L002.fastq.gz
- R1_L003.fastq.gz, R2_L003.fastq.gz
The files entry for each Read must list files in a consistent order across reads (e.g., lane 3 of Read 1 aligns with lane 3 of Read 2).
sequence_spec:
- !Read
read_id: Read 1
...
- files:
- !File
file_id: R1_L001.fastq.gz
...
- !File
file_id: R1_L002.fastq.gz
...
- !File
file_id: R1_L003.fastq.gz
...
- !Read
read_id: Read 2
...
- files:
- !File
file_id: R2_L001.fastq.gz
...
- !File
file_id: R2_L002.fastq.gz
...
- !File
file_id: R2_L003.fastq.gz
...Sometimes reads are grouped together in a single file (e.g., paired-end reads in a BAM). seqspec supports this by repeating the same File under each corresponding Read.
sequence_spec:
- !Read
read_id: Read 1
...
- files:
- !File
file_id: reads.bam
...
- !Read
read_id: Read 2
...
- files:
- !File
file_id: reads.bam
...Format requirements¶
The following requirements are often sources of errors when writing a seqspec file.
- Each
region_idin the top-most level oflibrary_specmust correspond to one modality inmodalities. - The
primer_idof each read in thesequence_specmust exist as aregion_idin thelibrary_spec
Conclusion¶
seqspec provides a standardized way to describe complex genomics assays, facilitating data interpretation, preprocessing, and reanalysis. By clearly defining library structures and read configurations, it enables more efficient and accurate processing of sequencing data across different assays and platforms. For more information about the contents of a seqspec file, please see the technical specification.