Welcome!
gget is a free, open-source command-line tool and Python package that enables efficient querying of genomic databases.
gget consists of a collection of separate but interoperable modules, each designed to facilitate one type of database querying in a single line of code.
Note: The databases queried by
ggetare continuously updated and may change structure.ggetmodules are automatically tested twice weekly and updated as needed. If you encounter an issue, first upgrade to the latest version with pip install --upgrade gget. If the issue persists, please report it.
Missing a database or functionality you’d love to see?
Request new feature
gget modules
These are the gget core modules. Click on any module to access detailed documentation.
| gget 8cube What is the expression of gene X across 8 different mouse strains and tissues? |
gget alphafold Predict 3D protein structure from an amino acid sequence. |
gget archs4 What is the expression of my gene in tissue X? |
| gget bgee Find all orthologs of a gene. |
gget blast BLAST a nucleotide or amino acid sequence. |
gget blat Find the genomic location of a nucleotide or amino acid sequence. |
| gget cbio Explore a gene's expression in the specified cancers. |
gget cellxgene Get ready-to-use single-cell RNA seq count matrices from certain tissues/ diseases/ etc. |
gget cosmic Search for genes, mutations, and other factors associated with certain cancers. |
| gget diamond Align amino acid sequences to a reference. |
gget elm Find protein interaction domains and functions in an amino acid sequence. |
gget enrichr Check if a list of genes is associated with a specific celltype/ pathway/ disease/ etc. |
| gget info Fetch all of the information associated with an Ensembl ID. |
gget muscle Align multiple nucleotide or amino acid sequences to each other. |
gget mutate Mutate nucleotide sequences based on specified mutations. |
| gget opentargets Explore which diseases and drugs a gene is associated with. |
gget pdb Fetch data from the Protein Data Bank (PDB) based on a PDB ID. |
gget ref Get reference genomes from Ensembl. |
| gget search Find Ensembl IDs associated with the specified search word. |
gget seq Fetch the nucleotide or amino acid sequence of a gene. |
gget virus Filter and fetch global viral sequences and extensive metadata. |
If you use gget in a publication, please cite*:
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
Read the article here: https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
✨ What's new
Version ≥ 0.30.2 (Feb 08, 2026):
gget virus: Metadata streaming optimization, improved protein filtering, and enhanced error handling and retry logic- Metadata now streams to disk during fetch to prevent memory exhaustion on large datasets (100,000+ records)
- Fixed metadata CSV mapping (camelCase → snake_case) for organism name, host, and collection date
- Enhanced protein filtering for segmented viruses with improved FASTA header parsing
- Added
annotated=Falseoption for filtering unannotated sequences - Added progress bars to batched sequence downloads
- Fixed collection date naming bug
- Improved error messages for invalid filter dates
- Added enhanced retry attempts for virus name resolution
- Added verbosity to influenza A and COVID-19 checking steps
Version ≥ 0.30.0 (Jan 19, 2026):
- NEW MODULES:
- SECURITY IMPROVEMENTS:
- Replaced
os.system()with f-strings containing URLs from external APIs ingget/main.py - Replaced
exec()withimportlib.import_module()ingget setupfor safer dynamic imports - Replaced
shell=Truesubprocess calls with list-based arguments ingget muscle,gget diamond, andgget setupto prevent command injection
- Replaced
Version ≥ 0.29.3 (Sep 11, 2025):
gget blat: Updated API request to new permissions.gget pdb: Added wwpdb mirror; falls back to rcsb if wwpdb fails.gget cellxgene: Improved argument handling; frontend unchanged. Fixes issue 181.gget setup/gget alphafold: Fixed pip_cmd bug in gget.setup("alphafold")
Version ≥ 0.29.2 (Jul 03, 2025):
- gget can now be installed using
uv pip install gget- All package metadata (version, author, description, etc.) is now managed in setup.cfg for full compatibility with modern tools like uv, pip, and PyPI
- gget now uses a minimal setup.py and is fully PEP 517/518 compatible
gget setupwill now try to useuv pip installfirst for speed and modern dependency resolution, and fall back ontopip installif uv fails or is not available- Users are informed at each step which installer is being used and if a retry is happening
- Note: Some scientific dependencies (e.g., cellxgene-census) may not yet support Python 3.12. If you encounter installation errors, try using Python 3.9 or 3.10. (The pip installation might also still succeed in these cases.)
- All required dependencies are now listed in setup.cfg under install_requires -> Installing gget with
pip install .oruv pip install .will automatically install all dependencies
Version ≥ 0.29.1 (Apr 21, 2025):
gget mutate:- gget mutate has been simplified to focus on taking as input a list of mutations and associated reference genome with corresponding annotation information, and produce as output the sequences with the mutation incorporated and a short region of surrounding context. For the full functionality of the previous version and how it integrates in the context of a novel variant screening pipeline, visit the varseek repository being developed by members of the gget team at https://github.com/pachterlab/varseek.git.
- Added additional information to returned data frames as described here: https://github.com/pachterlab/gget/pull/169
gget cosmic:- Major restructuring of the
gget cosmicmodule to adhere to new login requirements set by COSMIC - New arguments
emailandpasswordwere added to allow the user to manually enter their login credentials without required input for data download - Default changed:
gget_mutate=False - Deprecated argument:
entity - Argument
mutation_classis nowcosmic_project
- Major restructuring of the
gget bgee:type="orthologs"is now the default, removing the need to specify thetypeargument when calling orthologs- Allow querying multiple genes at once.
gget diamond:- Now supports translated alignment of nucleotide sequences to amino acid reference sequences using the
--translatedflag.
- Now supports translated alignment of nucleotide sequences to amino acid reference sequences using the
gget elm:- Improved server error handling.
Version ≥ 0.29.0 (Sep 25, 2024):
- New modules:
gget enrichrnow also supports species other than human and mouse (fly, yeast, worm, and fish) via modEnrichRgget mutate:
gget mutatewill now merge identical sequences in the final file by default. Mutation creation was vectorized to decrease runtime. Improved flanking sequence check for non-substitution mutations to make sure no wildtype kmer is retained in the mutation-containing sequence. Addition of several new arguments to customize sequence generation and output.gget cosmic:
Added support for targeted as well as gene screens. The CSV file created for gget mutate now also contains protein mutation info.gget ref:
Added out file option.gget infoandgget seq:
Switched to Ensembl POST API to increase speed (nothing changes in front end).- Other "behind the scenes" changes:
- Unit tests reorganized to increase speed and decrease code
- Requirements updated to allow newer mysql-connector versions
- Support Numpy>= 2.0
Version ≥ 0.28.6 (Jun 2, 2024):
- New module:
gget mutate gget cosmic: You can now download entire COSMIC databases using the argumentdownload_cosmicargumentgget ref: Can now fetch the GRCh37 genome assembly usingspecies='human_grch37'gget search: Adjust access of human data to the structure of Ensembl release 112 (fixes issue 129)
Version ≥ 0.28.5 (May 29, 2024):
- Yanked due to logging bug in
gget.setup("alphafold")+ inversion mutations ingget mutateonly reverse the string instead of also computing the complementary strand
Version ≥ 0.28.4 (January 31, 2024):
gget setup: Fix bug with filepath when runninggget.setup("elm")on Windows OS.
Version ≥ 0.28.3 (January 22, 2024):
gget searchandgget refnow also support fungi 🍄, protists 🌝, and invertebrate metazoa 🐝 🐜 🐌 🐙 (in addition to vertebrates and plants)- New module:
gget cosmic gget enrichr: Fix duplicate scatter dots in plot when pathway names are duplicatedgget elm:- Changed ortho results column name 'Ortholog_UniProt_ID' to 'Ortholog_UniProt_Acc' to correctly reflect the column contents, which are UniProt Accessions. 'UniProt ID' was changed to 'UniProt Acc' in the documentation for all
ggetmodules. - Changed ortho results column name 'motif_in_query' to 'motif_inside_subject_query_overlap'.
- Added interaction domain information to results (new columns: "InteractionDomainId", "InteractionDomainDescription", "InteractionDomainName").
- The regex string for regular expression matches was encapsulated as follows: "(?=(regex))" (instead of directly passing the regex string "regex") to enable capturing all occurrences of a motif when the motif length is variable and there are repeats in the sequence (https://regex101.com/r/HUWLlZ/1).
- Changed ortho results column name 'Ortholog_UniProt_ID' to 'Ortholog_UniProt_Acc' to correctly reflect the column contents, which are UniProt Accessions. 'UniProt ID' was changed to 'UniProt Acc' in the documentation for all
gget setup: Use theoutargument to specify a directory the ELM database will be downloaded into. Completes this feature request.gget diamond: The DIAMOND command is now run with--ignore-warningsflag, allowing niche sequences such as amino acid sequences that only contain nucleotide characters and repeated sequences. This is also true for DIAMOND alignments performed withingget elm.gget refandgget searchback-end change: the current Ensembl release is fetched from the new release file on the Ensembl FTP site to avoid errors during uploads of new releases.gget search:- FTP link results (
--ftp) are saved in txt file format instead of json. - Fix URL links to Ensembl gene summary for species with a subspecies name and invertebrates.
- FTP link results (
gget ref:- Back-end changes to increase speed
- New argument:
list_iv_speciesto list all available invertebrate species (can be combined with thereleaseargument to fetch all species available from a specific Ensembl release)
Version ≥ 0.28.2 (November 15, 2023):
gget info: Return a logging error message when the NCBI server fails for a reason other than a fetch fail (this is an error on the server side rather than an error withgget)- Replace deprecated 'text' argument to find()-type methods whenever used with dependency
BeautifulSoup gget elm: Remove false positive and true negative instances from returned resultsgget elm: Addexpandargument
Version ≥ 0.28.0 (November 5, 2023):
- Updated documentation of
gget muscleto add a tutorial on how to visualize sequences with varying sequence name lengths + slight change to returned visualization so it's a bit more robust to varying sequence names gget musclenow also allows a list of sequences as input (as an alternative to providing the path to a FASTA file)- Allow missing gene filter for
gget cellxgene(fixes bug) gget seq: Allow missing gene names (fixes https://github.com/pachterlab/gget/issues/107)gget enrichr: Use new argumentskegg_outandkegg_rankto create an image of the KEGG pathway with the genes from the enrichment analysis highlighted (thanks to this PR by Noriaki Sato)- New modules:
gget elmandgget diamond
Version ≥ 0.27.9 (August 7, 2023):
gget enrichr: Use new argumentbackground_listto provide a list of background genesgget searchnow also searches Ensembl synonyms (in addition to gene descriptions and names) to return more comprehensive search results (thanks to Samuel Klein for the suggestion)
Version ≥ 0.27.8 (July 12, 2023):
gget search: Specify the Ensembl release from which information is fetched with new argument-r--release- Fixed bug in
gget pdb(this bug was introduced in version 0.27.5)
Version ≥ 0.27.7 (May 15, 2023):
- Moved dependencies for modules
gget gptandgget cellxgenefrom automatically installed requirements togget setup. - Updated
gget alphafolddependencies for compatibility with Python >= 3.10. - Added
census_versionargument togget cellxgene.
Version ≥ 0.27.6 (May 1, 2023) (YANKED due to problems with dependencies -> replaced with version 0.27.7):
- Thanks to PR by Tomás Di Domenico:
gget searchcan now also query plant 🌱 Ensembl IDs. - New module:
gget cellxgene
Version ≥ 0.27.5 (April 6, 2023):
- Updated
gget searchto function correctly with new Pandas version 2.0.0 (released on April 3rd, 2023) as well as older versions of Pandas - Updated
gget infowith new flagsuniprotandncbiwhich allow turning off results from these databases independently to save runtime (note: flagensembl_onlywas deprecated) - All gget modules now feature a
-q / --quiet(Python:verbose=False) flag to turn off progress information
Version ≥ 0.27.4 (March 19, 2023):
- New module:
gget gpt
Version ≥ 0.27.3 (March 11, 2023):
gget infoexcludes PDB IDs by default to increase speed (PDB results can be included using flag--pdb/pdb=True).
Version ≥ 0.27.2 (January 1, 2023):
- Updated
gget alphafoldto DeepMind's AlphaFold v2.3.0 (including new argumentsmultimer_for_monomerandmultimer_recycles)
Version ≥ 0.27.0 (December 10, 2022):
- Updated
gget alphafoldto match recent changes by DeepMind - Updated version number to match gget's creator's age following a long-standing Pachter lab tradition
Version ≥ 0.3.13 (November 11, 2022):
- Reduced runtime for
gget enrichrandgget archs4when used with Ensembl IDs
Version ≥ 0.3.12 (November 10, 2022):
gget infonow also returns subcellular localisation data from UniProt- New
gget infoflagensembl_onlyreturns only Ensembl results - Reduced runtime for
gget infoandgget seq
Version ≥ 0.3.11 (September 7, 2022):
- New module:
gget pdb
Version ≥ 0.3.10 (September 2, 2022):
gget alphafoldnow also returns pLDDT values for generating plots from output without rerunning the program (also see the gget alphafold FAQ)
Version ≥ 0.3.9 (August 25, 2022):
- Updated openmm installation instructions for
gget alphafold
Version ≥ 0.3.8 (August 12, 2022):
- Fixed mysql-connector-python version requirements
Version ≥ 0.3.7 (August 9, 2022):
- NOTE: The Ensembl FTP site changed its structure on August 8, 2022. Please upgrade to
ggetversion ≥ 0.3.7 if you usegget ref
Version ≥ 0.3.5 (August 6, 2022):
- New module:
gget alphafold
Version ≥ 0.2.6 (July 7, 2022):
gget refnow supports plant genomes! 🌱
Version ≥ 0.2.5 (June 30, 2022):
- NOTE: UniProt changed the structure of their API on June 28, 2022. Please upgrade to
ggetversion ≥ 0.2.5 if you use any of the modules querying data from UniProt (gget infoandgget seq).
Version ≥ 0.2.3: (June 26, 2022):
- JSON is now the default output format for the command-line interface for modules that previously returned data frame (CSV) format by default (the output can be converted to data frame/CSV using flag
[-csv][--csv]). Data frame/CSV remains the default output for Jupyter Lab / Google Colab (and can be converted to JSON withjson=True). - For all modules, the first required argument was converted to a positional argument and should not be named anymore in the command-line, e.g.
gget ref -s human→gget ref human. gget info:[--expand]is deprecated. The module will now always return all of the available information.- Slight changes to the output returned by
gget info, including the return of versioned Ensembl IDs. gget infoandgget seqnow support 🪱 WormBase and 🪰 FlyBase IDs.gget archs4andgget enrichrnow also take Ensembl IDs as input with added flag[-e][--ensembl](ensembl=Truein Jupyter Lab / Google Colab).gget seqargumentseqtypewas replaced by flag[-t][--translate](translate=True/Falsein Jupyter Lab / Google Colab) which will return either nucleotide (False) or amino acid (True) sequences.gget searchargumentseqtypewas renamed toid_typefor clarity (still taking the same arguments 'gene' or 'transcript').
💡 Active users of this documentation website
Automatically updates every day at 16:00 UTC.
⬇️ Daily gget downloads

Automatically updates every Sunday at 23:55 UTC.
🧑🤝🧑 Dependent software
The following applications build on gget:
- gget-mcp
"MCP server providing a powerful bioinformatics toolkit for genomics queries and analysis, wrapping the popular
ggetlibrary."- Other tools using this or other
ggetMCP servers:
- Other tools using this or other
- Biomni
A General-Purpose Biomedical AI Scientist being developed at Stanford and Genentech. - PerTurboAgent
A Self-Planning Agent for Boosting Sequential Perturb-seq Experiments."We [...] use packages gget and blitzgsea for data enrichment analysis"
- Scientific skills for Claude by K-Dense-AI
" This repository contains 138 scientific skills organized across multiple domains. Each skill provides comprehensive documentation, code examples, and best practices for working with scientific libraries, databases, and tools.
🧬 Bioinformatics & Genomics
Genomic tools: gget, ..." - Therapeutics Data Commons (TDC)
Artificial intelligence foundation for therapeutic science (source code, Nat Chem Bio paper) by Harvard's Artificial Intelligence for Medicine and Science lab. - BioDiscoveryAgent
BioDiscoveryAgent is an LLM-based AI agent for closed-loop design of genetic perturbation experiments (preprint) by the Stanford Network Analysis Project. - DeepChopper
Language models to identify chimeric artificial reads in NanoPore direct-RNA sequencing data by the Yang lab at Northwestern. - BRAD
A LLM powered chatbot for bioinformatics (documentation, project main page). - scPRINT
scPRINT is a large transformer model built for the inference of gene networks (connections between genes explaining the cell's expression profile) from scRNAseq data (preprint). - AnoPrimer
AnoPrimer is a Python package for primer design in An. gambiae and An. funestus, whilst considering genetic variation in wild whole-genome sequenced specimens in malariagen_data. - AvaTaR
Optimizing LLM Agents for Tool-Assisted Knowledge Retrieval (NeurIPS 2024) by James Zou Lab at Stanford University. - GRLDrugProp
Graph representation learning for modelling drug properties. - MicrobioLink2
A computational tool that analyzes the impact of host-microbe interaction on downstream signaling in human cells and tissues. - Rust implementation of gget: https://github.com/noamteyssier/ggetrs
- https://github.com/Superbio-ai/getbio
- https://github.com/yonniejon/AchillesPrediction
- https://github.com/ELELAB/cancermuts
- https://github.com/Benoitdw/SNPrimer
- https://github.com/louisjoecodes/a16z-hackathon-project
- https://github.com/EvX57/BACE1-Drug-Discovery
- https://github.com/vecerkovakaterina/hidden-genes-msc
- https://github.com/vecerkovakaterina/llm_bioinfo_agent
- https://github.com/greedjar74/upstage_AI_Lab
- https://github.com/alphavector/all
See more: https://github.com/pachterlab/gget/network/dependents
📃 Featured publications using gget
- David Bradley et al., The fitness cost of spurious phosphorylation. The EMBO Journal (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00200-7
"Phosphosites matching to putative short linear motifs (SLiMs) were extracted using the gget elm resource"
- Mikael Nilsson et al., Resolving thyroid lineage cell trajectories merging into a dual endocrine gland in mammals. Nature Portfolio (under review) (2024). DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5278325/v1
"Enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes [...] was performed using gget enrichr"
- Avasthi P et al., Repeat expansions associated with human disease are present in diverse organisms. Arcadia (2024). DOI: 10.57844/arcadia-e367-8b55
"We used the gget package using the gget.blast command [...] to BLAST our proteins of interest against the non-redundant NCBI protein database"
- Ibrahim Al Rayyes et al., Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals the Molecular Logic Underlying Ca2+ Signaling Diversity in Human and Mouse Brain. bioRxiv (2024). DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.26.591400
"The gget package was used to perform the gene set enrichment analyses with databases Reactome_2022 and KEGG_2021_Mouse."
- Beatriz Beamud et al., Genetic determinants of host tropism in Klebsiella phages. Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112048
"Proteins with seemingly enzymatic activity were confirmed to have the characteristic β-helical domain using gget AlphaFold2"
- Kimberly Siletti et al., Transcriptomic diversity of cell types across the adult human brain. Science (2023). DOI: 10.1126/science.add7046
"The gget package (https://github.com/pachterlab/gget) was used to perform all gene ontologyenrichment analysis"
- David R. Blair & Neil Risch. Dissecting the Reduced Penetrance of Putative Loss-of-Function Variants in Population-Scale Biobanks. medRxiv (2024). DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.23.24314008
"Additional gene and transcript information (exon-intron boundaries, 5' and 3' UTRs, full coding and amino acid sequences) was downloaded using gget"
- Shanmugampillai Jeyarajaguru Kabilan et al., Molecular modelling approaches for the identification of potent Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 inhibitors from Boerhavia diffusa for the potential treatment of chronic kidney disease. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design (under review) (2024). DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4520611/v1
- Joseph M Rich et al., The impact of package selection and versioning on single-cell RNA-seq analysis. bioRxiv (2024). DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.04.588111
- Sanjay C. Nagi et al., AnoPrimer: Primer Design in malaria vectors informed by range-wide genomic variation. Wellcome Open Research (2024).
- Yasmin Makki Mohialden et al., A survey of the most recent Python packages for use in biology. NeuroQuantology (2023). DOI: 10.48047/NQ.2023.21.2.NQ23029
- Nicola A. Kearns et al., Generation and molecular characterization of human pluripotent stem cell-derived pharyngeal foregut endoderm. Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.08.024
- Jonathan Rosenski et al., Predicting gene knockout effects from expression data. BMC Medical Genomics (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s12920-023-01446-6
- Peter Overby et al., Pharmacological or genetic inhibition of Scn9a protects beta-cells while reducing insulin secretion in type 1 diabetes. bioRxiv (2023). DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.11.544521
- Mingze Dong et al., Deep identifiable modeling of single-cell atlases enables zero-shot query of cellular states. bioRxiv (2023). DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.11.566161
See more: Google Scholar
📰 gget in the news
- Oreate AI blog post: "Exploring AlphaFold2: A Guide to GitHub Repositories and Colab Resources"
gget opentargetsrelease blog post by the Open Targets platform- Documentary short film about gget: https://youtu.be/cVR0k6Mt97o
- Podcast episode for the Prototype Fund Public Interest Podcast about the importance of open-source software and its role in academic research (in German): https://public-interest-podcast.podigee.io/33-pips4e4
- Prototype Fund announcement: https://prototypefund.de/project/gget-genomische-datenbanken
🚂 gget code repository traffic
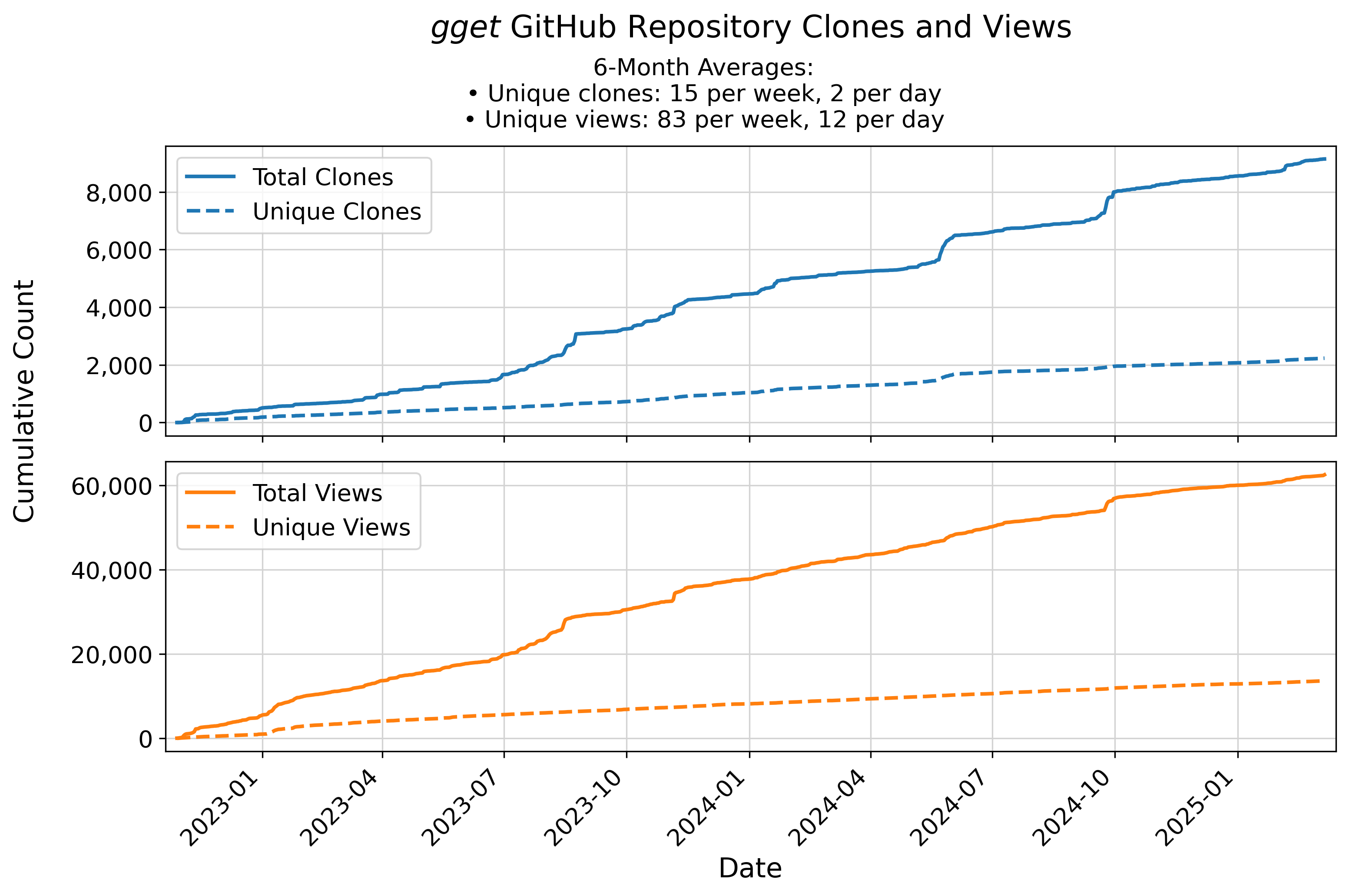 Updates automatically every week on Sunday at 23:55 (UTC).
Updates automatically every week on Sunday at 23:55 (UTC).
Installation
You can use uv or pip to install gget:
uv pip install gget
or
pip install --upgrade gget
Recommended: Install in a clean environment
We recommend using a virtual environment for a clean, conflict-free install. You can use uv, venv, or conda:
With uv:
pip install uv # if you don't have uv yet
uv venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install gget
With pip and venv:
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade gget
With conda:
conda create -n gget-env python=3.11
conda activate gget-env
pip install --upgrade gget
For use in Jupyter Lab / Google Colab:
import gget
Install from source
git clone https://github.com/pachterlab/gget.git
cd gget
uv pip install .
or
git clone https://github.com/pachterlab/gget.git
cd gget
pip install .
Troubleshooting
- If you see errors about missing dependencies, make sure you are using a clean environment and have the latest version of pip or uv.
- If you previously installed gget system-wide, uninstall it with:
or remove the executable from your system path.pip uninstall gget - If you continue to having trouble, please reach out.
🪄 Quick start guide
Command line:
# Fetch all Homo sapiens reference and annotation FTPs from the latest Ensembl release
$ gget ref homo_sapiens
# Get Ensembl IDs of human genes with "ace2" or "angiotensin converting enzyme 2" in their name/description
$ gget search -s homo_sapiens 'ace2' 'angiotensin converting enzyme 2'
# Look up gene ENSG00000130234 (ACE2) and its transcript ENST00000252519
$ gget info ENSG00000130234 ENST00000252519
# Fetch the amino acid sequence of the canonical transcript of gene ENSG00000130234
$ gget seq --translate ENSG00000130234
# Quickly find the genomic location of (the start of) that amino acid sequence
$ gget blat MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# BLAST (the start of) that amino acid sequence
$ gget blast MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# Align multiple nucleotide or amino acid sequences against each other (also accepts path to FASTA file)
$ gget muscle MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS
# Align one or more amino acid sequences against a reference (containing one or more sequences) (local BLAST) (also accepts paths to FASTA files)
$ gget diamond MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS -ref MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS
# Use Enrichr for an ontology analysis of a list of genes
$ gget enrichr -db ontology ACE2 AGT AGTR1 ACE AGTRAP AGTR2 ACE3P
# Get the human tissue expression of gene ACE2
$ gget archs4 -w tissue ACE2
# Get the protein structure (in PDB format) of ACE2 as stored in the Protein Data Bank (PDB ID returned by gget info)
$ gget pdb 1R42 -o 1R42.pdb
# Download virus genome datasets from NCBI Virus (e.g., Zika virus sequences)
$ gget virus "Zika virus" --host "Homo sapiens" --nuc_completeness complete
# Find Eukaryotic Linear Motifs (ELMs) in a protein sequence
$ gget setup elm # setup only needs to be run once
$ gget elm -o results MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# Fetch a scRNAseq count matrix (AnnData format) based on specified gene(s), tissue(s), and cell type(s) (default species: human)
$ gget setup cellxgene # setup only needs to be run once
$ gget cellxgene --gene ACE2 SLC5A1 --tissue lung --cell_type 'mucus secreting cell' -o example_adata.h5ad
# Predict the protein structure of GFP from its amino acid sequence
$ gget setup alphafold # setup only needs to be run once
$ gget alphafold MSKGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVSGEGEGDATYGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFSRYPDHMKQHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTIFFKDDGNYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNYNSHNVYIMADKQKNGIKVNFKIRHNIEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSALSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHGMDELYK
Python (Jupyter Lab / Google Colab):
import gget
gget.ref("homo_sapiens")
gget.search(["ace2", "angiotensin converting enzyme 2"], "homo_sapiens")
gget.info(["ENSG00000130234", "ENST00000252519"])
gget.seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=True)
gget.blat("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.blast("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.muscle(["MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", "MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS"])
gget.diamond("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", reference="MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS")
gget.enrichr(["ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1", "ACE", "AGTRAP", "AGTR2", "ACE3P"], database="ontology", plot=True)
gget.archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
gget.pdb("1R42", save=True)
gget.virus("Zika virus", host="Homo sapiens", nuc_completeness="complete")
gget.setup("elm") # setup only needs to be run once
ortho_df, regex_df = gget.elm("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.setup("cellxgene") # setup only needs to be run once
gget.cellxgene(gene = ["ACE2", "SLC5A1"], tissue = "lung", cell_type = "mucus secreting cell")
gget.setup("alphafold") # setup only needs to be run once
gget.alphafold("MSKGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVSGEGEGDATYGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFSRYPDHMKQHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTIFFKDDGNYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNYNSHNVYIMADKQKNGIKVNFKIRHNIEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSALSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHGMDELYK")
Call gget from R using reticulate:
system("pip install gget")
install.packages("reticulate")
library(reticulate)
gget <- import("gget")
gget$ref("homo_sapiens")
gget$search(list("ace2", "angiotensin converting enzyme 2"), "homo_sapiens")
gget$info(list("ENSG00000130234", "ENST00000252519"))
gget$seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=TRUE)
gget$blat("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget$blast("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget$muscle(list("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", "MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS"), out="out.afa")
gget$diamond("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", reference="MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS")
gget$enrichr(list("ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1", "ACE", "AGTRAP", "AGTR2", "ACE3P"), database="ontology")
gget$archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
gget$pdb("1R42", save=TRUE)
gget$virus("Zika virus", host="Homo sapiens", nuc_completeness="complete")
More examples
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget 8cube 🔬
Query 8cubeDB (snRNA-sequencing data of 8 different mouse strains, tissues, and individuals (four of each sex)) for gene-level specificity metrics and normalized expression values.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python).
This module was written by Nikhila Swarna.
gget 8cube specificity 🎯
Retrieve ψ and ζ specificity statistics for one or more genes.
gget 8cube specificity <GENES...>
Positional argument
genes
Gene symbols or Ensembl gene IDs. Multiple genes allowed.
Optional arguments
-csv --csv
Returns CSV instead of JSON (command-line only).
Python: Use json=False (default DataFrame) or json=True for JSON.
-o --out
Output file path (CSV or .json depending on --csv).
Python: save=True saves automatically to the current directory.
Flags
-q --quiet
Suppresses progress information.
Python: use verbose=False.
Example
gget 8cube specificity Acsm2 ENSMUSG00000046623.9
# Python
from gget.gget_8cube import specificity
specificity(["Acsm2", "ENSMUSG00000046623.9"])
→ Returns ψ and ζ specificity values for Acsm2.
gget 8cube psi_block 🧩
Retrieve ψ-block (block-level specificity) values for one or more genes.
gget 8cube psi_block <GENES...> --analysis_level <LEVEL> --analysis_type <TYPE>
Positional argument
genes
Gene symbols or Ensembl IDs.
Required arguments
-al --analysis_level
Biological analysis level (e.g., Kidney, Across_tissues).
-at --analysis_type
Partition type (e.g., Sex:Celltype, Sex:Strain).
Optional arguments
-csv --csv
Return CSV instead of JSON.
Python: use json=True for JSON.
-o --out
Output file location.
Flags
-q --quiet
Suppress progress printing.
Example
gget 8cube psi_block Acsm2 \
--analysis_level Kidney \
--analysis_type "Sex:Celltype"
# Python
from gget.gget_8cube import psi_block
psi_block(["Acsm2"], analysis_level="Kidney", analysis_type="Sex:Celltype")
→ Returns ψ-block partition-level specificity scores for Acsm2.
gget 8cube expression 📊
Retrieve mean and variance of normalized expression values for one or more genes.
gget 8cube expression <GENES...> --analysis_level <LEVEL> --analysis_type <TYPE>
Positional argument
genes
Gene symbols or Ensembl IDs. Multiple accepted.
Required arguments
-al --analysis_level
Biological grouping (e.g., Kidney, Across_tissues).
-at --analysis_type
Partition layout (e.g., Sex:Celltype).
Optional arguments
-csv --csv
Return CSV instead of JSON.
Python: use json=True.
-o --out
Output file path.
Flags
-q --quiet
Suppress progress messages.
Example
gget 8cube expression ENSMUSG00000046623.9 \
--analysis_level Across_tissues \
--analysis_type Strain
# Python
from gget.gget_8cube import gene_expression
gene_expression(["ENSMUSG00000046623.9"], analysis_level="Across_tissues", analysis_type="Strain")
→ Returns normalized expression values grouped by cell type and sex.
Example workflow
# Specificity
gget 8cube specificity Gjb4
# ψ-block specificity
gget 8cube psi_block Gjb4 --analysis_level Across_tissues --analysis_type Strain
# Expression values
gget 8cube expression Gjb4 --analysis_level Across_tissues --analysis_type Strain
Python API
from gget.gget_8cube import specificity, psi_block, gene_expression
or
from gget import specificity, psi_block, gene_expression
Notes
- Works with gene symbols and Ensembl IDs (with or without version numbers).
- All three functions accept multiple genes at once.
- Default Python output is a pandas DataFrame; use
json=Truefor JSON. - CLI defaults to JSON, unless
--csvis used.
References
If you use gget 8cube in a publication, please cite:
-
Swarna NP, et al. Determining gene specificity from multivariate single-cell RNA sequencing data (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.11.21.689845
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Rebboah E, et al. Systematic cell-type resolved transcriptomes of 8 tissues in 8 lab and wild-derived mouse strains captures global and local expression variation (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.21.649844
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget alphafold 🪢
Predict the 3D structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence using a simplified version of DeepMind’s AlphaFold2 originally released and benchmarked for AlphaFold Colab.
Returns: Predicted structure (PDB) and alignment error (json).
Before using gget alphafold for the first time:
-
Install the third-party dependency openmm by running the following command from the command line:
For Python versions < 3.10:
conda install -qy conda==4.13.0 && conda install -qy -c conda-forge openmm=7.5.1
For Python version 3.10:
conda install -qy conda==24.1.2 && conda install -qy -c conda-forge openmm=7.7.0
For Python version 3.11:
conda install -qy conda==24.11.1 && conda install -qy -c conda-forge openmm=8.0.0Recommendation: Follow with
conda update -qy condato update conda to the latest version afterwards. -
Run
gget setup alphafold/gget.setup("alphafold")once (also seegget setup). Runninggget setup alphafold/gget.setup("alphafold")will download and install the latest version of AlphaFold2 hosted on the AlphaFold GitHub Repo. You can rerun this command any time to update the software after a new AlphaFold release.
Positional argument
sequence
Amino acid sequence (str), or list of sequences (gget alphafold will automatically use the multimer model if multiple sequences are passed), or path to FASTA file.
Optional arguments
-mr --multimer_recycles
The multimer model will continue recycling until the predictions stop changing, up to the limit set here. Default: 3.
For higher accuracy, at the potential cost of longer inference times, set this to 20.
-o --out
Path to folder to save prediction results in (str). Default: "./[date_time]_gget_alphafold_prediction".
Flags
-mfm --multimer_for_monomer
Use multimer model for a monomer.
-r --relax
AMBER relax the best model.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
plot
Python only. plot=True provides an interactive, 3D graphical overview of the predicted structure and alignment quality using py3Dmol and matplotlib (default: True).
show_sidechains
Python only. show_sidechains=True includes side chains in the plot (default: True).
Example
# Generate new prediction from amino acid sequence
gget alphafold MAAHKGAEHHHKAAEHHEQAAKHHHAAAEHHEKGEHEQAAHHADTAYAHHKHAEEHAAQAAKHDAEHHAPKPH
# Find similar sequences deposited on the PDB for comparative analysis
gget blast --database pdbaa MAAHKGAEHHHKAAEHHEQAAKHHHAAAEHHEKGEHEQAAHHADTAYAHHKHAEEHAAQAAKHDAEHHAPKPH
# Fetch the PDB files of similar structures returned by gget blast for comparison, to get a measure for model quality
gget pdb 3UQ3 -o 3UQ3.pdb
gget pdb 2K42 -o 2K42.pdb
# Python
gget.alphafold("MAAHKGAEHHHKAAEHHEQAAKHHHAAAEHHEKGEHEQAAHHADTAYAHHKHAEEHAAQAAKHDAEHHAPKPH")
# Find similar sequences deposited on the PDB for comparative analysis
gget.blast("MAAHKGAEHHHKAAEHHEQAAKHHHAAAEHHEKGEHEQAAHHADTAYAHHKHAEEHAAQAAKHDAEHHAPKPH", database="pdbaa")
# Fetch the PDB files of similar structures returned by gget blast for comparison, to get a measure for model quality
gget.pdb("3UQ3", save=True)
gget.pdb("2K42", save=True)
→ gget alphafold returns the predicted structure (PDB) and predicted alignment error (.json) in a new folder ("./[date_time]_gget_alphafold_prediction"). The use case above exemplifies how to use gget blast and gget pdb for a comparative analysis of the new prediction. PDB files can be viewed interactively in 3D online, or using programs like PyMOL or Blender. To compare two PDB files, you can use this website. The Python interface also returns interactive plots, which can be generated from the PDB and JSON as described in the gget alphafold FAQ Q4.
Tutorials
🔗 Google Colab tutorial
🔗 Protein structure prediction with comparison to related crystal structures
🔗 gget alphafold FAQ
References
If you use gget alphafold in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Jumper, J., Evans, R., Pritzel, A. et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596, 583–589 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2
And, if applicable:
- Evans, R. et al. Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. bioRxiv 2021.10.04.463034; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.04.463034
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget archs4 🐁
Find the most correlated genes to a gene of interest or find the gene's tissue expression atlas using ARCHS4.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python).
Positional argument
gene
Short name (gene symbol) of gene of interest, e.g. STAT4.
Alternatively: use flag --ensembl to input an Ensembl gene IDs, e.g. ENSG00000138378.
Optional arguments
-w --which
'correlation' (default) or 'tissue'.
'correlation' returns a gene correlation table that contains the 100 most correlated genes to the gene of interest. The Pearson correlation is calculated over all samples and tissues in ARCHS4.
'tissue' returns a tissue expression atlas calculated from human or mouse samples (as defined by 'species') in ARCHS4.
-s --species
'human' (default) or 'mouse'.
Defines whether to use human or mouse samples from ARCHS4.
(Only for tissue expression atlas.)
-o --out
Path to the file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.csv (or .json). Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Flags
-e --ensembl
Add this flag if gene is given as an Ensembl gene ID.
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Examples
gget archs4 ACE2
# Python
gget.archs4("ACE2")
→ Returns the 100 most correlated genes to ACE2:
| gene_symbol | pearson_correlation |
|---|---|
| SLC5A1 | 0.579634 |
| CYP2C18 | 0.576577 |
| . . . | . . . |
gget archs4 -w tissue ACE2
# Python
gget.archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
→ Returns the tissue expression of ACE2 (by default, human data is used):
| id | min | q1 | median | q3 | max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System.Urogenital/Reproductive System.Kidney.RENAL CORTEX | 0.113644 | 8.274060 | 9.695840 | 10.51670 | 11.21970 |
| System.Digestive System.Intestine.INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELL | 0.113644 | 5.905560 | 9.570450 | 13.26470 | 13.83590 |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . |
Check out this tutorial by Dave Tang who wrote an R script to create this figure from the gget archs4 JSON output:
More examples
References
If you use gget archs4 in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Lachmann A, Torre D, Keenan AB, Jagodnik KM, Lee HJ, Wang L, Silverstein MC, Ma’ayan A. Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse. Nature Communications 9. Article number: 1366 (2018), doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03751-6
-
Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P and Pachter L, Near optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification, Nature Biotechnology 34, p 525--527 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3519
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget bgee 🐝
Fetch orthology and gene expression data from Bgee using Ensembl IDs.
Return format: JSON/CSV (command-line) or data frame (Python).
If you are specifically interested in human gene expression data, consider using gget opentargets or gget archs4 instead. gget bgee has less data, but supports more species.
This module was written by Sam Wagenaar with edits from Kateřina Večerková.
Positional argument
ens_id
Ensembl gene ID, e.g. ENSG00000169194 or ENSSSCG00000014725.
When type=expression you can also input a list of multiple Ensembl IDs.
NOTE: Some of the species in Bgee are not in Ensembl or Ensembl metazoa, and for those you can use NCBI gene IDs, e.g. 118215821 (a gene in Anguilla anguilla).
Optional arguments
-t --type
Type of data to fetch. Options: orthologs (default), expression.
-o --out
Path to the JSON file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.json. Default: Standard out.
Flags
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns the output in CSV format, instead of JSON format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Examples
Get orthologs for a gene
gget bgee ENSSSCG00000014725
import gget
gget.bgee("ENSSSCG00000014725")
→ Returns orthologs for the gene with Ensembl ID ENSSSCG00000014725.
| gene_id | gene_name | species_id | genus | species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 734881 | hbb1 | 8355 | Xenopus | laevis |
| ENSFCAG00000038029 | LOC101098159 | 9685 | Felis | catus |
| ENSBTAG00000047356 | LOC107131172 | 9913 | Bos | taurus |
| ENSOARG00000019163 | LOC101105437 | 9940 | Ovis | aries |
| ENSXETG00000025667 | hbg1 | 8364 | Xenopus | tropicalis |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Get gene expression data for a gene
gget bgee ENSSSCG00000014725 -t expression
import gget
gget.bgee("ENSSSCG00000014725", type="expression")
→ Returns gene expression data for the gene with Ensembl ID ENSSSCG00000014725.
| anat_entity_id | anat_entity_name | score | score_confidence | expression_state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBERON:0000178 | blood | 99.98 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0002106 | spleen | 99.96 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0002190 | subcutaneous adipose tissue | 99.70 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0005316 | endocardial endothelium | 99.61 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0002107 | liver | 99.27 | high | expressed |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Get gene expression data for multiple genes
gget bgee ENSBTAG00000047356 ENSBTAG00000018317 -t expression
import gget
gget.bgee(["ENSBTAG00000047356", "ENSBTAG00000018317"], type="expression")
→ Returns gene expression data for the genes ENSBTAG00000047356 and ENSBTAG00000018317.
| anat_entity_id | anat_entity_name | score | score_confidence | expression_state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBERON:0001017 | central nervous system | 92.15 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0002616 | regional part of brain | 79.01 | high | expressed |
| BGEE:0000000 | anatomical entity and cellular component | 89.12 | high | expressed |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
More examples
References
If you use gget bgee in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Frederic B Bastian, Julien Roux, Anne Niknejad, Aurélie Comte, Sara S Fonseca Costa, Tarcisio Mendes de Farias, Sébastien Moretti, Gilles Parmentier, Valentine Rech de Laval, Marta Rosikiewicz, Julien Wollbrett, Amina Echchiki, Angélique Escoriza, Walid H Gharib, Mar Gonzales-Porta, Yohan Jarosz, Balazs Laurenczy, Philippe Moret, Emilie Person, Patrick Roelli, Komal Sanjeev, Mathieu Seppey, Marc Robinson-Rechavi (2021). The Bgee suite: integrated curated expression atlas and comparative transcriptomics in animals. Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D831–D847, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa793
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget blast 💥
BLAST a nucleotide or amino acid sequence to any BLAST database.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python).
Positional argument
sequence
Nucleotide or amino acid sequence, or path to FASTA or .txt file.
Optional arguments
-p --program
'blastn', 'blastp', 'blastx', 'tblastn', or 'tblastx'.
Default: 'blastn' for nucleotide sequences; 'blastp' for amino acid sequences.
-db --database
'nt', 'nr', 'refseq_rna', 'refseq_protein', 'swissprot', 'pdbaa', or 'pdbnt'.
Default: 'nt' for nucleotide sequences; 'nr' for amino acid sequences.
More info on BLAST databases
-l --limit
Limits number of hits to return. Default: 50.
-e --expect
Defines the expect value cutoff. Default: 10.0.
-o --out
Path to the file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.csv (or .json). Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Flags
-lcf --low_comp_filt
Turns on low complexity filter.
-mbo --megablast_off
Turns off MegaBLAST algorithm. Default: MegaBLAST on (blastn only).
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
wrap_text
Python only. wrap_text=True displays data frame with wrapped text for easy reading (default: False).
Example
gget blast MKWMFKEDHSLEHRCVESAKIRAKYPDRVPVIVEKVSGSQIVDIDKRKYLVPSDITVAQFMWIIRKRIQLPSEKAIFLFVDKTVPQSR
# Python
gget.blast("MKWMFKEDHSLEHRCVESAKIRAKYPDRVPVIVEKVSGSQIVDIDKRKYLVPSDITVAQFMWIIRKRIQLPSEKAIFLFVDKTVPQSR")
→ Returns the BLAST result of the sequence of interest. gget blast automatically detects this sequence as an amino acid sequence and therefore sets the BLAST program to blastp with database nr.
| Description | Scientific Name | Common Name | Taxid | Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PREDICTED: gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-as... | Colobus angolensis palliatus | NaN | 336983 | 180 | 180 | 100% | ... |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | ... |
BLAST from .fa or .txt file:
gget blast fasta.fa
# Python
gget.blast("fasta.fa")
→ Returns the BLAST results of the first sequence contained in the fasta.fa file.
More examples
References
If you use gget blast in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403-10. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. PMID: 2231712.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget blat 🎯
Find the genomic location of a nucleotide or amino acid sequence using BLAT.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python).
Positional argument
sequence
Nucleotide or amino acid sequence, or path to FASTA or .txt file.
Optional arguments
-st --seqtype
'DNA', 'protein', 'translated%20RNA', or 'translated%20DNA'.
Default: 'DNA' for nucleotide sequences; 'protein' for amino acid sequences.
-a --assembly
'human' (hg38) (default), 'mouse' (mm39), 'zebrafinch' (taeGut2),
or any of the species assemblies available here (use short assembly name).
-o --out
Path to the file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.csv (or .json). Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Flags
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Example
gget blat -a taeGut2 MKWMFKEDHSLEHRCVESAKIRAKYPDRVPVIVEKVSGSQIVDIDKRKYLVPSDITVAQFMWIIRKRIQLPSEKAIFLFVDKTVPQSR
# Python
gget.blat("MKWMFKEDHSLEHRCVESAKIRAKYPDRVPVIVEKVSGSQIVDIDKRKYLVPSDITVAQFMWIIRKRIQLPSEKAIFLFVDKTVPQSR", assembly="taeGut2")
→ Returns BLAT results for assembly taeGut2 (zebra finch). In the above example, gget blat automatically detects this sequence as an amino acid sequence and therefore sets the BLAT seqtype to protein.
| genome | query_size | aligned_start | aligned_end | matches | mismatches | %_aligned | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| taeGut2 | 88 | 12 | 88 | 77 | 0 | 87.5 | ... |
More examples
References
If you use gget blat in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Kent WJ. BLAT--the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002 Apr;12(4):656-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.229202. PMID: 11932250; PMCID: PMC187518.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget cbio 📖
Plot cancer genomics heatmaps using data from cBioPortal using Ensembl IDs or gene names.
This module was written by Sam Wagenaar.
Positional argument
subcommand
Either search or plot
search subcommand (Python: gget.cbio_search)
Find cBioPortal study IDs by keyword.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or string list (Python).
Note: This does not return studies with mixed cancer types.
Positional argument
keywords
Space-separated list of keywords to search for, e.g. breast lung.
Python: Pass keywords as a list of strings.
plot subcommand (Python: gget.cbio_plot)
Plot cancer genomics heatmaps using data from cBioPortal. Return format: PNG (command-line and Python)
Required arguments
-s --study_ids
Space-separated list of cBioPortal study IDs, e.g. msk_impact_2017 egc_msk_2023.
-g --genes
Space-separated list of gene names or Ensembl IDs, e.g. NOTCH3 ENSG00000108375.
Optional arguments
-st --stratification
Column to stratify the data by. Default: tissue.
Options:
- tissue
- cancer_type
- cancer_type_detailed
- study_id
- sample
-vt --variation_type
Type of variation to plot. Default: mutation_occurrences.
Options:
- mutation_occurrences
- cna_nonbinary (Note:
stratificationmust be 'sample' for this option) - sv_occurrences
- cna_occurrences
- Consequence (Note:
stratificationmust be 'sample' for this option)
-f --filter
Filter the data by a specific value in a specific column, e.g. study_id:msk_impact_2017
Python: filter=(column, value)
-dd --data_dir
Directory to store data files. Default: ./gget_cbio_cache.
-fd --figure_dir
Directory to output figures. Default: ./gget_cbio_figures.
-fn --filename
Filename for the output figure, relative to figure_dir. Default: auto-generated
Python: figure_filename
-t --title
Title for the output figure. Default: auto-generated
Python: figure_title
-dpi --dpi
DPI of the output figure. Default: 100.
Flags
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
-nc --no_confirm
Command-line only. Skip download confirmation prompts.
Python: Use confirm_download=True to enable download confirmation prompts.
-sh --show
Show the plot in a window (automatic in Jupyter notebooks).
Examples
Find all cBioPortal studies with cancer types matching specific keywords:
gget cbio search esophag ovary ovarian
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_search(['esophag', 'ovary', 'ovarian'])
→ Returns a list of studies with cancer types matching the keywords esophag, ovary, or ovarian.
['egc_tmucih_2015', 'egc_msk_2017', ..., 'msk_spectrum_tme_2022']
Plot a heatmap of mutation occurrences for specific genes in a specific study:
gget cbio plot \
-s msk_impact_2017 \
-g AKT1 ALK FLT4 MAP3K1 MLL2 MLL3 NOTCH3 NOTCH4 PDCD1 RNF43 \
-st tissue \
-vt mutation_occurrences \
-dpi 200
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_plot(
['msk_impact_2017'],
['AKT1', 'ALK', 'FLT4', 'MAP3K1', 'MLL2', 'MLL3', 'NOTCH3', 'NOTCH4', 'PDCD1', 'RNF43'],
stratification='tissue',
variation_type='mutation_occurrences',
dpi=200
)
→ Saves a heatmap of mutation occurrences for the specified genes in the specified study to ./gget_cbio_figures/Heatmap_tissue.png.
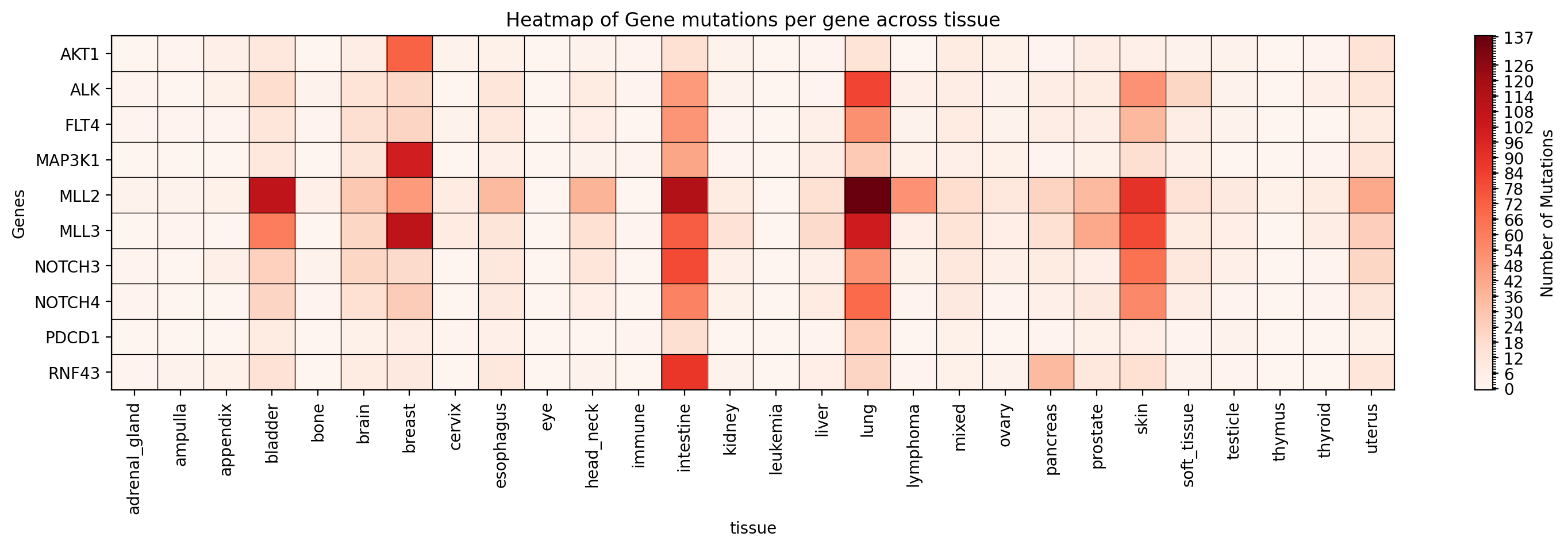
Plot a heatmap of mutation types for specific genes in a specific study:
gget cbio plot \
-s msk_impact_2017 \
-g AKT1 ALK FLT4 MAP3K1 MLL2 MLL3 NOTCH3 NOTCH4 PDCD1 RNF43 \
-st sample \
-vt Consequence \
-dpi 200
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_plot(
['msk_impact_2017'],
['AKT1', 'ALK', 'FLT4', 'MAP3K1', 'MLL2', 'MLL3', 'NOTCH3', 'NOTCH4', 'PDCD1', 'RNF43'],
stratification='sample',
variation_type='Consequence',
dpi=200,
)
→ Saves a heatmap of mutation types for the specified genes in the specified study to ./gget_cbio_figures/Heatmap_sample.png.
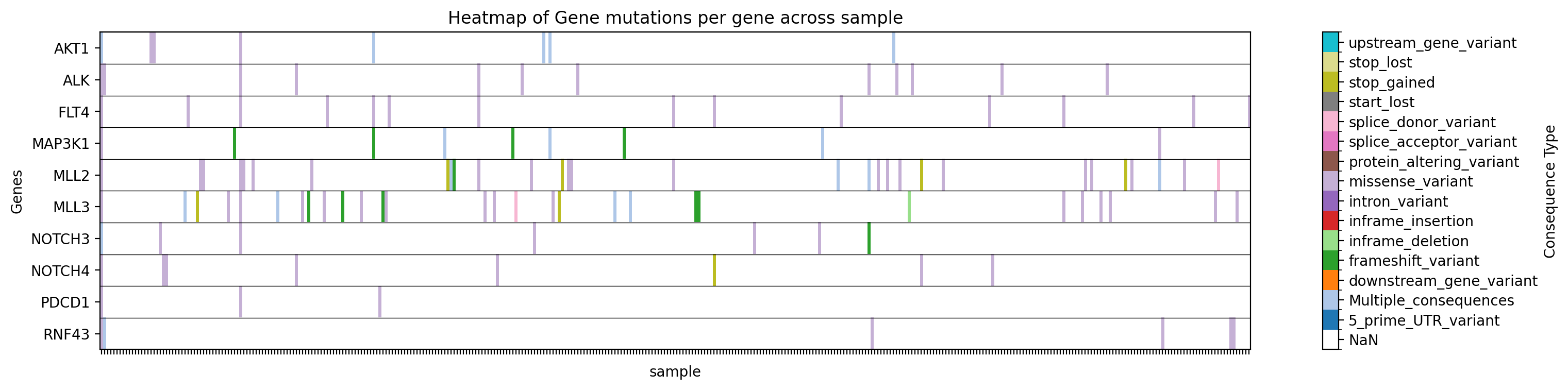
Plot a heatmap of mutation types for specific genes in a specific study, filtering by tissue:
gget cbio plot \
-s msk_impact_2017 \
-g AKT1 ALK FLT4 MAP3K1 MLL2 MLL3 NOTCH3 NOTCH4 PDCD1 RNF43 \
-st sample \
-vt Consequence \
-f tissue:intestine \
-dpi 200
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_plot(
['msk_impact_2017'],
['AKT1', 'ALK', 'FLT4', 'MAP3K1', 'MLL2', 'MLL3', 'NOTCH3', 'NOTCH4', 'PDCD1', 'RNF43'],
stratification='sample',
variation_type='Consequence',
filter=('tissue', 'intestine'),
dpi=200,
)
→ Saves a heatmap of mutation types for the specified genes in the specified study, filtered by tissue, to ./gget_cbio_figures/Heatmap_sample_intestine.png.
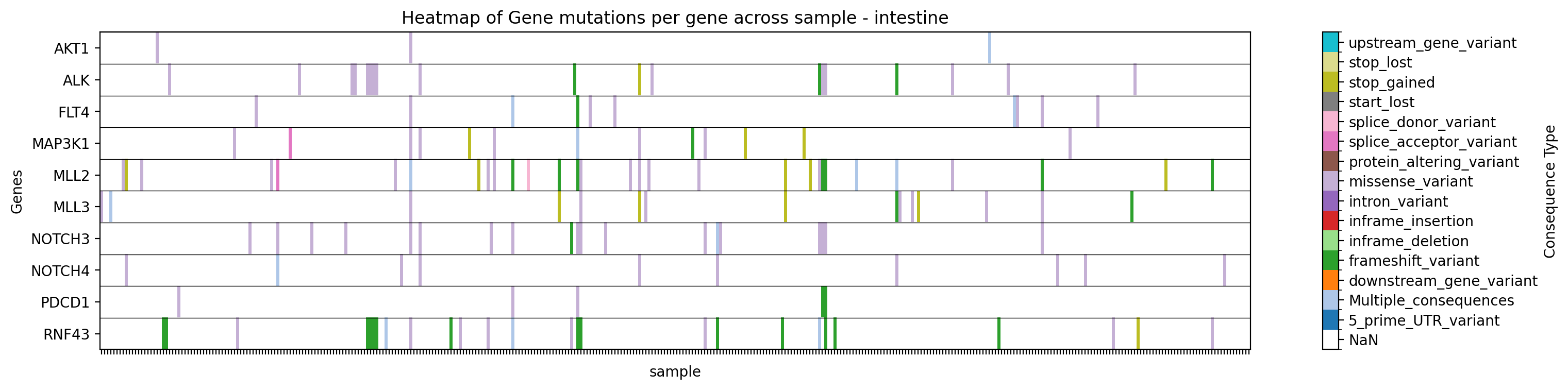
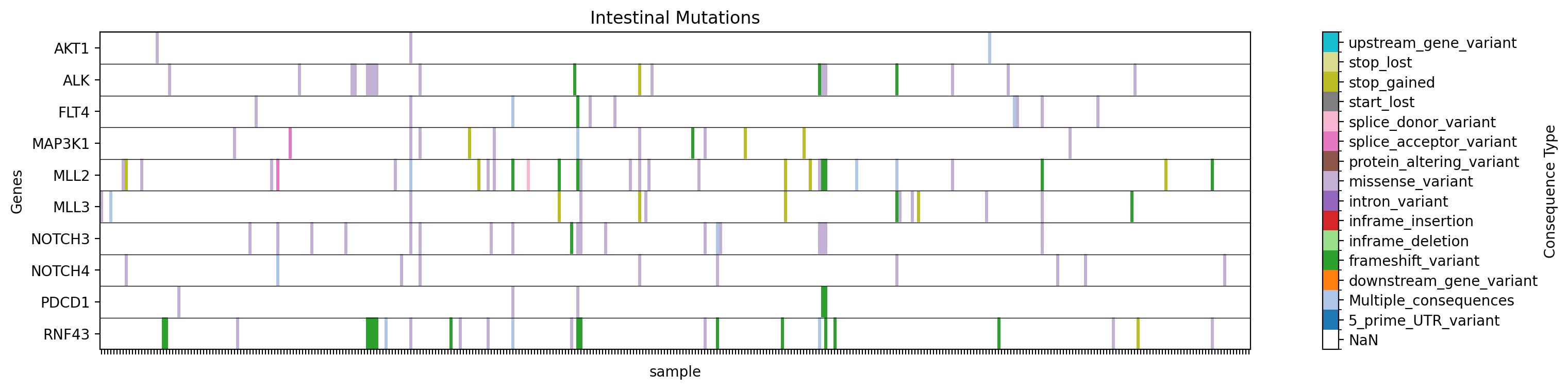
Plot a heatmap with a custom title and filename:
gget cbio plot \
-s msk_impact_2017 \
-g AKT1 ALK FLT4 MAP3K1 MLL2 MLL3 NOTCH3 NOTCH4 PDCD1 RNF43 \
-st sample \
-vt Consequence \
-f tissue:intestine \
-dpi 200 \
-t "Intestinal Mutations" \
-fn intestinal_mutations.png
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_plot(
['msk_impact_2017'],
['AKT1', 'ALK', 'FLT4', 'MAP3K1', 'MLL2', 'MLL3', 'NOTCH3', 'NOTCH4', 'PDCD1', 'RNF43'],
stratification='sample',
variation_type='Consequence',
filter=('tissue', 'intestine'),
dpi=200,
figure_title='Intestinal Mutations',
figure_filename='intestinal_mutations.png'
)
→ Saves a heatmap of mutation types for the specified genes in the specified study, filtered by tissue, with the title "Intestinal Mutations" to ./gget_cbio_figures/intestinal_mutations.png.
More examples
References
If you use gget cbio in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, Antipin Y, Reva B, Goldberg AP, Sander C, Schultz N. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012 May;2(5):401-4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095. Erratum in: Cancer Discov. 2012 Oct;2(10):960. PMID: 22588877; PMCID: PMC3956037.
-
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, Cerami E, Sander C, Schultz N. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013 Apr 2;6(269):pl1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004088. PMID: 23550210; PMCID: PMC4160307.
-
de Bruijn I, Kundra R, Mastrogiacomo B, Tran TN, Sikina L, Mazor T, Li X, Ochoa A, Zhao G, Lai B, Abeshouse A, Baiceanu D, Ciftci E, Dogrusoz U, Dufilie A, Erkoc Z, Garcia Lara E, Fu Z, Gross B, Haynes C, Heath A, Higgins D, Jagannathan P, Kalletla K, Kumari P, Lindsay J, Lisman A, Leenknegt B, Lukasse P, Madela D, Madupuri R, van Nierop P, Plantalech O, Quach J, Resnick AC, Rodenburg SYA, Satravada BA, Schaeffer F, Sheridan R, Singh J, Sirohi R, Sumer SO, van Hagen S, Wang A, Wilson M, Zhang H, Zhu K, Rusk N, Brown S, Lavery JA, Panageas KS, Rudolph JE, LeNoue-Newton ML, Warner JL, Guo X, Hunter-Zinck H, Yu TV, Pilai S, Nichols C, Gardos SM, Philip J; AACR Project GENIE BPC Core Team, AACR Project GENIE Consortium; Kehl KL, Riely GJ, Schrag D, Lee J, Fiandalo MV, Sweeney SM, Pugh TJ, Sander C, Cerami E, Gao J, Schultz N. Analysis and Visualization of Longitudinal Genomic and Clinical Data from the AACR Project GENIE Biopharma Collaborative in cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 1;83(23):3861-3867. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0816. PMID: 37668528; PMCID: PMC10690089.
-
Please also cite the source of the data if you are using a publicly available dataset.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget cellxgene 🍱
Query data from CZ CELLxGENE Discover using the CZ CELLxGENE Discover Census. CZ CELLxGENE Discover provides ready-to-use single-cell RNA sequencing count matrices for certain tissues/diseases/genes/etc.
Returns: An AnnData object containing the count matrix and metadata of single-cell RNA sequencing data from the defined tissues/genes/etc.
Before using gget cellxgene for the first time, run gget setup cellxgene / gget.setup("cellxgene") once (also see gget setup).
Optional arguments
-s --species
Choice of 'homo_sapiens' or 'mus_musculus'. Default: 'homo_sapiens'.
-g --gene
Str or list of gene name(s) or Ensembl ID(s). Default: None.
NOTE: Use -e / --ensembl (Python: ensembl=True) when providing Ensembl ID(s) instead of gene name(s).
NOTE: Gene symbols are case sensitive! Use canonical casing when passing gene symbols, e.g., 'PAX7' (human), 'Pax7' (mouse).
See https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/gene-expression for examples of available genes.
-cv --census_version
Str defining version of Census, e.g. "2023-05-15", or "latest" or "stable". Default: "stable".
-cn --column_names
List of metadata columns to return (stored in AnnData.obs).
Default: ['dataset_id', 'assay', 'suspension_type', 'sex', 'tissue_general', 'tissue', 'cell_type']
For more options, see: https://api.cellxgene.cziscience.com/curation/ui/#/ -> Schemas -> dataset
-o --out
Path to file to save generated AnnData .h5ad file (or .csv with -mo / --meta_only).
Required when using from command line!
Flags
-e --ensembl
Use when genes are provided as Ensembl IDs instead of gene names.
-mo --meta_only
Only returns metadata data frame (corresponds to AnnData.obs).
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Optional arguments corresponding to CZ CELLxGENE Discover metadata attributes
--tissue
Str or list of tissue(s), e.g. ['lung', 'blood']. Default: None.
See https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/gene-expression for examples of available tissues.
--cell_type
Str or list of cell type (s), e.g. ['mucus secreting cell', 'neuroendocrine cell']. Default: None.
See https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/gene-expression and select a tissue to see examples of available cell types.
--development_stage
Str or list of development stage(s). Default: None.
--disease
Str or list of disease(s). Default: None.
--sex
Str or list of sex(es), e.g. 'female'. Default: None.
--dataset_id
Str or list of CELLxGENE dataset ID(s). Default: None.
--tissue_general_ontology_term_id
Str or list of high-level tissue UBERON ID(s). Default: None.
Tissue labels and their corresponding UBERON IDs are listed here.
--tissue_general
Str or list of high-level tissue label(s). Default: None.
Tissue labels and their corresponding UBERON IDs are listed here.
--tissue_ontology_term_id
Str or list of tissue ontology term ID(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--assay_ontology_term_id
Str or list of assay ontology term ID(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--assay
Str or list of assay(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--cell_type_ontology_term_id
Str or list of cell type ontology term ID(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--development_stage_ontology_term_id
Str or list of development stage ontology term ID(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--disease_ontology_term_id
Str or list of disease ontology term ID(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--donor_id
Str or list of donor ID(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--self_reported_ethnicity_ontology_term_id
Str or list of self-reported ethnicity ontology ID(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--self_reported_ethnicity
Str or list of self-reported ethnicity as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--sex_ontology_term_id
Str or list of sex ontology ID(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
--suspension_type
Str or list of suspension type(s) as defined in the CELLxGENE dataset schema. Default: None.
Examples
gget cellxgene --gene ACE2 ABCA1 SLC5A1 --tissue lung --cell_type 'mucus secreting cell' 'neuroendocrine cell' -o example_adata.h5ad
# Python
adata = gget.cellxgene(
gene = ["ACE2", "ABCA1", "SLC5A1"],
tissue = "lung",
cell_type = ["mucus secreting cell", "neuroendocrine cell"]
)
adata
→ Returns an AnnData object containing the scRNAseq ACE2, ABCA1, and SLC5A1 count matrix of 3322 human lung mucus secreting and neuroendocrine cells from CZ CELLxGENE Discover and their corresponding metadata.
Fetch metadata (corresponds to AnnData.obs) only:
gget cellxgene --meta_only --gene ENSMUSG00000015405 --ensembl --tissue lung --species mus_musculus -o example_meta.csv
# Python
df = gget.cellxgene(
meta_only = True,
gene = "ENSMUSG00000015405",
ensembl = True,
tissue = "lung",
species = "mus_musculus"
)
df
→ Returns only the metadata from ENSMUSG00000015405 (ACE2) expression datasets corresponding to mouse lung cells.
Also see: https://chanzuckerberg.github.io/cellxgene-census/notebooks/api_demo/census_gget_demo.html
References
If you use gget cellxgene in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Chanzuckerberg Initiative. (n.d.). CZ CELLxGENE Discover. Retrieved [insert date here], from https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget cosmic 🪐
Search for genes, mutations, and other factors associated with cancer using the COSMIC (Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer) database.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python) when download_cosmic=False. When download_cosmic=True, downloads the requested database into the specified folder.
This module was originally written in part by @AubakirovArman (information querying) and @josephrich98 (database download).
NOTE: License fees apply for the commercial use of COSMIC. You can read more about licensing COSMIC data here.
NOTE: When using this module for the first time, first download a COSMIC database to obtain cosmic_tsv_path (see examples below).
Positional argument (for querying information)
searchterm
Search term, which can be a mutation, or gene name (or Ensembl ID), or sample, etc.
Examples: 'EGFR', 'ENST00000275493', 'c.650A>T', 'p.Q217L', 'COSV51765119', 'BT2012100223LNCTB' (sample ID)
NOTE: (Python only) Set to None when downloading COSMIC databases with download_cosmic=True.
Required argument (for querying information)
-ctp --cosmic_tsv_path
Path to the COSMIC database tsv file, e.g. 'path/to/CancerMutationCensus_AllData_v101_GRCh37.tsv'.
This file is downloaded when downloading COSMIC databases using the arguments described below.
NOTE: This is a required argument when download_cosmic=False.
Optional arguments (for querying information)
-l --limit
Limits number of hits to return. Default: 100.
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
Flags (for downloading COSMIC databases)
-d --download_cosmic
Switches into database download mode.
-gm --gget_mutate
Creates a modified version of the COSMIC database for use with gget mutate.
Optional arguments (for downloading COSMIC databases)
-cp --cosmic_project
'cancer' (default), 'cancer_example', 'census', 'resistance', 'cell_line', 'genome_screen', or 'targeted_screen'
Type of COSMIC database to download:
| cosmic_project | Description | Notes | Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| cancer | Cancer Mutation Census (CMC) (most commonly used COSMIC mutation set) | Only available for GRCh37. Most feature-rich schema (takes the longest to search). | 2 GB |
| cancer_example | Example CMC subset provided for testing and demonstration | Downloadable without a COSMIC account. Minimal dataset. | 2.5 MB |
| census | COSMIC census of curated somatic mutations in known cancer genes | Smaller curated set of known cancer drivers. | 630 MB |
| resistance | Mutations associated with drug resistance | Helpful for pharmacogenomics research. | 1.6 MB |
| cell_line | Cell Lines Project mutation data | Sample metadata often available. | 2.7 GB |
| genome_screen | Mutations from genome screening efforts | Includes less curated data, good for large-scale screens. | |
| targeted_screen | Mutations from targeted screening panels | Focused panel datasets, good for clinical settings. |
-cv --cosmic_version
Version of the COSMIC database. Default: None -> Defaults to latest version.
-gv --grch_version
Version of the human GRCh reference genome the COSMIC database was based on (37 or 38). Default: 37
--email
Email for COSMIC login. Helpful for avoiding required input upon running gget COSMIC. Default: None
--password
Password for COSMIC login. Helpful for avoiding required input upon running gget COSMIC, but password will be stored in plain text in the script. Default: None
Additional arguments for the --gget_mutate flag
--keep_genome_info
Whether to keep genome information in the modified database for use with gget mutate. Default: False
--remove_duplicates
Whether to remove duplicate rows from the modified database for use with gget mutate. Default: False
--seq_id_column
(str) Name of the seq_id column in the csv file created by gget_mutate. Default: "seq_ID"
--mutation_column
(str) Name of the mutation column in the csv file created by gget_mutate. Default: "mutation"
--mut_id_column
(str) Name of the mutation_id column in the csv file created by gget_mutate. Default: "mutation_id"
Optional arguments (general)
-o --out
Path to the file (or folder when downloading databases with the download_cosmic flag) the results will be saved in, e.g. 'path/to/results.json'.
Defaults:
-> When download_cosmic=False: Results will be returned to standard out
-> When download_cosmic=True: Database will be downloaded into current working directory
Flags (general)
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Examples
Download the COSMIC "cancer" database and query information
# The download_cosmic command will ask for your COSMIC email and password and only needs to be run once
gget cosmic --download_cosmic --cosmic_project cancer
gget cosmic EGFR --cosmic_tsv_path 'CancerMutationCensus_AllData_Tsv_v101_GRCh37/CancerMutationCensus_AllData_v101_GRCh37.tsv'
# Python
# The download_cosmic command will ask for your COSMIC email and password and only needs to be run once
gget.cosmic(searchterm=None, download_cosmic=True, cosmic_project="cancer")
gget.cosmic("EGFR", cosmic_tsv_path="CancerMutationCensus_AllData_Tsv_v101_GRCh37/CancerMutationCensus_AllData_v101_GRCh37.tsv")
→ The first command downloads the requested COSMIC database of the latest COSMIC release into the current working directory. The second command searches the database for mutations associated with the 'EGFR' gene and returns results in the following format:
| GENE_NAME | ACCESSION_NUMBER | ONC_TSG | Mutation_CDS | Mutation_AA | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | ENST00000275493.2 | oncogene | c.650A>T | p.Q217L | ... |
| EGFR | ENST00000275493.2 | oncogene | c.966C>T | p.G322= | ... |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Download the COSMIC "census" database and query information
# The download_cosmic command will ask for your COSMIC email and password and only needs to be run once
gget cosmic --download_cosmic --cosmic_project census
gget cosmic EGFR --cosmic_tsv_path 'Cosmic_MutantCensus_Tsv_v101_GRCh37/Cosmic_MutantCensus_v101_GRCh37.tsv'
# Python
# The download_cosmic command will ask for your COSMIC email and password and only needs to be run once
gget.cosmic(searchterm=None, download_cosmic=True, cosmic_project="cancer")
gget.cosmic("EGFR", cosmic_tsv_path="Cosmic_MutantCensus_Tsv_v101_GRCh37/Cosmic_MutantCensus_v101_GRCh37.tsv")
→ The first command downloads the requested COSMIC database of the latest COSMIC release into the current working directory. The second command searches the database for mutations associated with the 'EGFR' gene and returns results in the following format:
| GENE_SYMBOL | COSMIC_GENE_ID | MUTATION_DESCRIPTION | MUTATION_CDS | Mutation_AA | MUTATION_SOMATIC_STATUS | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | COSG35617 | inframe_deletion | c.2235_2249del | p.E746_A750del | Reported in another cancer sample as somatic | ... |
| EGFR | COSG35617 | missense_variant | c.2573T>G | p.L858R | Reported in another cancer sample as somatic | ... |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
References
If you use gget cosmic in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, Sondka Z, Beare DM, Bindal N, Boutselakis H, Cole CG, Creatore C, Dawson E, Fish P, Harsha B, Hathaway C, Jupe SC, Kok CY, Noble K, Ponting L, Ramshaw CC, Rye CE, Speedy HE, Stefancsik R, Thompson SL, Wang S, Ward S, Campbell PJ, Forbes SA. COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 8;47(D1):D941-D947. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1015. PMID: 30371878; PMCID: PMC6323903.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget diamond 💎
Align multiple protein or translated DNA sequences using DIAMOND (DIAMOND is similar to BLAST, but this is a local computation).
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python).
Positional argument
query
Sequences (str or list) or path to FASTA file containing sequences to be aligned against the reference.
Required arguments
-ref --reference
Reference sequences (str or list) or path to FASTA file containing reference sequences.
Add the --translated flag (Python: translated=True) if reference sequences are amino acid sequences and query sequences are nucleotide sequences.
Optional arguments
-db --diamond_db
Path to save DIAMOND database created from reference (str).
Default: None -> Temporary db file will be deleted after alignment or saved in out if out is provided.
-s --sensitivity
Sensitivity of alignment (str). Default: "very-sensitive".
One of the following: fast, mid-sensitive, sensitive, more-sensitive, very-sensitive, or ultra-sensitive.
-t --threads
Number of threads used (int). Default: 1.
-db --diamond_binary
Path to DIAMOND binary (str). Default: None -> Uses DIAMOND binary installed with gget.
-o --out
Path to the folder to save results in (str), e.g. "path/to/directory". Default: Standard out; temporary files are deleted.
Flags
-x --translated
Perform translated alignment of nucleotide sequences to amino acid reference sequences.
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Example
# !!! Make sure to list the positional argument first here so it is not added as a reference sequence
gget diamond GGETISAWESQME ELVISISALIVE LQVEFRANKLIN PACHTERLABRQCKS -ref GGETISAWESQMEELVISISALIVELQVEFRANKLIN PACHTERLABRQCKS
# Python
gget.diamond(["GGETISAWESQME", "ELVISISALIVE", "LQVEFRANKLIN", "PACHTERLABRQCKS"], reference=["GGETISAWESQMEELVISISALIVELQVEFRANKLIN", "PACHTERLABRQCKS"])
→ Returns results in JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python) format:
| query_accession | subject_accession | identity_percentage | query_seq_length | subject_seq_length | length | mismatches | gap_openings | query_start | query_end | subject_start | subject_end | e-value | bit_score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seq0 | Seq0 | 100 | 13 | 37 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 13 | 2.82e-09 | 30.8 |
| Seq2 | Seq0 | 100 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 26 | 37 | 4.35e-08 | 27.7 |
| Seq3 | Seq1 | 100 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 2.01e-11 | 36.2 |
More examples
References
If you use gget diamond in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Buchfink, B., Xie, C. & Huson, D. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12, 59–60 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3176
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget elm 🎭
Locally predict Eukaryotic Linear Motifs from an amino acid sequence or UniProt Acc using data from the ELM database.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python). This module returns two data frames (or JSON formatted files) (see examples).
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement.
Before using gget elm for the first time, run gget setup elm (bash) / gget.setup("elm") (Python) once (also see gget setup).
Positional argument
sequence
Amino acid sequence or Uniprot Acc (str).
When providing a Uniprot Acc, use flag --uniprot (Python: uniprot=True).
Optional arguments
-s --sensitivity
Sensitivity of DIAMOND alignment (str). Default: "very-sensitive".
One of the following: fast, mid-sensitive, sensitive, more-sensitive, very-sensitive, or ultra-sensitive.
-t --threads
Number of threads used in DIAMOND alignment (int). Default: 1.
-bin --diamond_binary
Path to DIAMOND binary (str). Default: None -> Uses DIAMOND binary installed with gget.
-o --out
Path to the folder to save results in (str), e.g. "path/to/directory". Default: Standard out; temporary files are deleted.
Flags
-u --uniprot
Set to True if sequence is a Uniprot Acc instead of an amino acid sequence.
-e --expand
Expand the information returned in the regex data frame to include the protein names, organisms, and references that the motif was orignally validated on.
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Examples
Find ELMs in an amino acid sequence:
gget setup elm # Downloads/updates local ELM database
gget elm -o gget_elm_results LIAQSIGQASFV
# Python
gget.setup(“elm”) # Downloads/updates local ELM database
ortholog_df, regex_df = gget.elm("LIAQSIGQASFV")
Find ELMs giving a UniProt Acc as input:
gget setup elm # Downloads/updates local ELM database
gget elm -o gget_elm_results --uniprot Q02410 -e
# Python
gget.setup(“elm”) # Downloads/updates local ELM database
ortholog_df, regex_df = gget.elm("Q02410", uniprot=True, expand=True)
→ Returns two data frames (or JSON formatted dictionaries for command line) containing extensive information about linear motifs associated with orthologous proteins and motifs found in the input sequence directly based on their regex expressions:
ortholog_df:
| Ortholog_UniProt_Acc | ProteinName | class_accession | ELMIdentifier | FunctionalSiteName | Description | Organism | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q02410 | APBA1_HUMAN | ELME000357 | LIG_CaMK_CASK_1 | CASK CaMK domain binding ligand motif | Motif that mediates binding to the calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) domain of the peripheral plasma membrane protein CASK/Lin2. | Homo sapiens | … |
| Q02410 | APBA1_HUMAN | ELME000091 | LIG_PDZ_Class_2 | PDZ domain ligands | The C-terminal class 2 PDZ-binding motif is classically represented by a pattern such as | Homo sapiens | … |
regex_df:
| Instance_accession | ELMIdentifier | FunctionalSiteName | ELMType | Description | Instances (Matched Sequence) | Organism | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELME000321 | CLV_C14_Caspase3-7 | Caspase cleavage motif | CLV | Caspase-3 and Caspase-7 cleavage site. | ERSDG | Mus musculus | … |
| ELME000102 | CLV_NRD_NRD_1 | NRD cleavage site | CLV | N-Arg dibasic convertase (NRD/Nardilysin) cleavage site. | RRA | Rattus norvegicus | … |
| ELME000100 | CLV_PCSK_PC1ET2_1 | PCSK cleavage site | CLV | NEC1/NEC2 cleavage site. | KRD | Mus musculus | … |
| ELME000146 | CLV_PCSK_SKI1_1 | PCSK cleavage site | CLV | Subtilisin/kexin isozyme-1 (SKI1) cleavage site. | RLLTA | Homo sapiens | … |
| ELME000231 | DEG_APCC_DBOX_1 | APCC-binding Destruction motifs | DEG | An RxxL-based motif that binds to the Cdh1 and Cdc20 components of APC/C thereby targeting the protein for destruction in a cell cycle dependent manner | SRVKLNIVR | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c | … |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
Tutorials
🔗 General gget elm demo
🔗 A point mutation in BRCA2 is carcinogenic due to the loss of a protein interaction motif
🔗 Filter gget elm results based on disordered protein regions
References
If you use gget elm in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Laura Luebbert, Chi Hoang, Manjeet Kumar, Lior Pachter, Fast and scalable querying of eukaryotic linear motifs with gget elm, Bioinformatics, 2024, btae095, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btae095
-
Manjeet Kumar, Sushama Michael, Jesús Alvarado-Valverde, Bálint Mészáros, Hugo Sámano‐Sánchez, András Zeke, Laszlo Dobson, Tamas Lazar, Mihkel Örd, Anurag Nagpal, Nazanin Farahi, Melanie Käser, Ramya Kraleti, Norman E Davey, Rita Pancsa, Lucía B Chemes, Toby J Gibson, The Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource: 2022 release, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 50, Issue D1, 7 January 2022, Pages D497–D508, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab975
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget enrichr 💰
Perform an enrichment analysis on a list of genes using Enrichr or modEnrichr.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python).
Positional argument
genes
Short names (gene symbols) of genes to perform enrichment analysis on, e.g. PHF14 RBM3 MSL1 PHF21A.
Alternatively: use flag --ensembl to input a list of Ensembl gene IDs, e.g. ENSG00000106443 ENSG00000102317 ENSG00000188895.
Other required arguments
-db --database
Database database to use as reference for the enrichment analysis.
Supports any database listed here under 'Gene-set Library' or one of the following shortcuts:
'pathway' (KEGG_2021_Human)
'transcription' (ChEA_2016)
'ontology' (GO_Biological_Process_2021)
'diseases_drugs' (GWAS_Catalog_2019)
'celltypes' (PanglaoDB_Augmented_2021)
'kinase_interactions' (KEA_2015)
NOTE: database shortcuts are not supported for species other than 'human' or 'mouse'. Click on the species databases listed below under species to view a list of databases available for each species.
Optional arguments
-s --species
Species to use as reference for the enrichment analysis. (Default: human)
Options:
| Species | Database list |
|---|---|
human | Enrichr |
mouse | Equivalent to human |
fly | FlyEnrichr |
yeast | YeastEnrichr |
worm | WormEnrichr |
fish | FishEnrichr |
-bkg_l --background_list
Short names (gene symbols) of background genes to perform enrichment analysis on, e.g. NSUN3 POLRMT NLRX1.
Alternatively: use flag --ensembl_background to input a list of Ensembl gene IDs.
See this Tweetorial to learn why you should use a background gene list when performing an enrichment analysis.
-o --out
Path to the file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.csv (or .json). (Default: Standard out.)
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
-ko --kegg_out
Path to the png file the marked KEGG pathway images will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/pathway.png. (Default: None)
-kr --kegg_rank
Rank of the KEGG pathway to be plotted. (Default: 1)
figsize
Python only. (width, height) of plot in inches. (Default: (10,10))
ax
Python only. Pass a matplotlib axes object for plot customization. (Default: None)
Flags
-e --ensembl
Add this flag if genes are given as Ensembl gene IDs.
-e_b --ensembl_bkg
Add this flag if background_list are given as Ensembl gene IDs.
-bkg --background
If True, use set of > 20,000 default background genes listed here.
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
plot
Python only. plot=True provides a graphical overview of the first 15 results (default: False).
Examples
gget enrichr -db ontology ACE2 AGT AGTR1
# Python
gget.enrichr(["ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1"], database="ontology", plot=True)
→ Returns pathways/functions involving genes ACE2, AGT, and AGTR1 from the GO Biological Process 2021 database. In Python, plot=True returns a graphical overview of the results:
Use gget enrichr with a background gene list:
See this Tweetorial to learn why you should use a background gene list when performing an enrichment analysis.
# Here, we are passing the input genes first (positional argument 'genes'), so they are not added to the background gene list behind the '-bkgr_l' argument
gget enrichr \
PHF14 RBM3 MSL1 PHF21A ARL10 INSR JADE2 P2RX7 LINC00662 CCDC101 PPM1B KANSL1L CRYZL1 ANAPC16 TMCC1 CDH8 RBM11 CNPY2 HSPA1L CUL2 PLBD2 LARP7 TECPR2 ZNF302 CUX1 MOB2 CYTH2 SEC22C EIF4E3 ROBO2 ADAMTS9-AS2 CXXC1 LINC01314 ATF7 ATP5F1 \
-db ChEA_2022 \
-bkg_l NSUN3 POLRMT NLRX1 SFXN5 ZC3H12C SLC25A39 ARSG DEFB29 PCMTD2 ACAA1A LRRC1 2810432D09RIK SEPHS2 SAC3D1 TMLHE LOC623451 TSR2 PLEKHA7 GYS2 ARHGEF12 HIBCH LYRM2 ZBTB44 ENTPD5 RAB11FIP2 LIPT1 INTU ANXA13 KLF12 SAT2 GAL3ST2 VAMP8 FKBPL AQP11 TRAP1 PMPCB TM7SF3 RBM39 BRI3 KDR ZFP748 NAP1L1 DHRS1 LRRC56 WDR20A STXBP2 KLF1 UFC1 CCDC16 9230114K14RIK RWDD3 2610528K11RIK ACO1 CABLES1 LOC100047214 YARS2 LYPLA1 KALRN GYK ZFP787 ZFP655 RABEPK ZFP650 4732466D17RIK EXOSC4 WDR42A GPHN 2610528J11RIK 1110003E01RIK MDH1 1200014M14RIK AW209491 MUT 1700123L14RIK 2610036D13RIK PHF14 RBM3 MSL1 PHF21A ARL10 INSR JADE2 P2RX7 LINC00662 CCDC101 PPM1B KANSL1L CRYZL1 ANAPC16 TMCC1 CDH8 RBM11 CNPY2 HSPA1L CUL2 PLBD2 LARP7 TECPR2 ZNF302 CUX1 MOB2 CYTH2 SEC22C EIF4E3 ROBO2 ADAMTS9-AS2 CXXC1 LINC01314 ATF7 ATP5F1COX15 TMEM30A NSMCE4A TM2D2 RHBDD3 ATXN2 NFS1 3110001I20RIK BC038156 C330002I19RIK ZFYVE20 POLI TOMM70A LOC100047782 2410012H22RIK RILP A230062G08RIK PTTG1IP RAB1 AFAP1L1 LYRM5 2310026E23RIK SLC7A6OS MAT2B 4932438A13RIK LRRC8A SMO NUPL2
# Python
gget.enrichr(
genes = [
"PHF14", "RBM3", "MSL1", "PHF21A", "ARL10", "INSR", "JADE2", "P2RX7",
"LINC00662", "CCDC101", "PPM1B", "KANSL1L", "CRYZL1", "ANAPC16", "TMCC1",
"CDH8", "RBM11", "CNPY2", "HSPA1L", "CUL2", "PLBD2", "LARP7", "TECPR2",
"ZNF302", "CUX1", "MOB2", "CYTH2", "SEC22C", "EIF4E3", "ROBO2",
"ADAMTS9-AS2", "CXXC1", "LINC01314", "ATF7", "ATP5F1"
],
database = "ChEA_2022",
background_list = [
"NSUN3","POLRMT","NLRX1","SFXN5","ZC3H12C","SLC25A39","ARSG",
"DEFB29","PCMTD2","ACAA1A","LRRC1","2810432D09RIK","SEPHS2",
"SAC3D1","TMLHE","LOC623451","TSR2","PLEKHA7","GYS2","ARHGEF12",
"HIBCH","LYRM2","ZBTB44","ENTPD5","RAB11FIP2","LIPT1",
"INTU","ANXA13","KLF12","SAT2","GAL3ST2","VAMP8","FKBPL",
"AQP11","TRAP1","PMPCB","TM7SF3","RBM39","BRI3","KDR","ZFP748",
"NAP1L1","DHRS1","LRRC56","WDR20A","STXBP2","KLF1","UFC1",
"CCDC16","9230114K14RIK","RWDD3","2610528K11RIK","ACO1",
"CABLES1", "LOC100047214","YARS2","LYPLA1","KALRN","GYK",
"ZFP787","ZFP655","RABEPK","ZFP650","4732466D17RIK","EXOSC4",
"WDR42A","GPHN","2610528J11RIK","1110003E01RIK","MDH1","1200014M14RIK",
"AW209491","MUT","1700123L14RIK","2610036D13RIK",
"PHF14", "RBM3", "MSL1", "PHF21A", "ARL10", "INSR", "JADE2",
"P2RX7", "LINC00662", "CCDC101", "PPM1B", "KANSL1L", "CRYZL1",
"ANAPC16", "TMCC1","CDH8", "RBM11", "CNPY2", "HSPA1L", "CUL2",
"PLBD2", "LARP7", "TECPR2", "ZNF302", "CUX1", "MOB2", "CYTH2",
"SEC22C", "EIF4E3", "ROBO2", "ADAMTS9-AS2", "CXXC1", "LINC01314", "ATF7",
"ATP5F1""COX15","TMEM30A","NSMCE4A","TM2D2","RHBDD3","ATXN2","NFS1",
"3110001I20RIK","BC038156","C330002I19RIK","ZFYVE20","POLI","TOMM70A",
"LOC100047782","2410012H22RIK","RILP","A230062G08RIK",
"PTTG1IP","RAB1","AFAP1L1", "LYRM5","2310026E23RIK",
"SLC7A6OS","MAT2B","4932438A13RIK","LRRC8A","SMO","NUPL2"
],
plot=True
)
→ Returns hits of the input gene list given the background gene list from the transcription factor/target library ChEA 2022. In Python, plot=True returns a graphical overview of the results:
Generate a KEGG pathway image with the genes from the enrichment analysis highlighted:
This feature is available thanks to a PR by Noriaki Sato.
gget enrichr -db pathway --kegg_out kegg.png --kegg_rank 1 ZBP1 IRF3 RIPK1
# Python
gget.enrichr(["ZBP1", "IRF3", "RIPK1"], database="pathway", kegg_out="kegg.png", kegg_rank=1)
→ In addition to the standard gget enrichr output, the kegg_out argument saves an image with the genes from the enrichment analysis highlighted in the KEGG pathway:
The following example was submitted by Dylan Lawless via PR:
Use gget enrichr in R and create a similar plot using ggplot.
NOTE the switch of axes compared to the Python plot.
system("pip install gget")
install.packages("reticulate")
library(reticulate)
gget <- import("gget")
# Perform enrichment analysis on a list of genes
df <- gget$enrichr(list("ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1"), database = "ontology")
# Count number of overlapping genes
df$overlapping_genes_count <- lapply(df$overlapping_genes, length) |> as.numeric()
# Only keep the top 15 results
df <- df[1:15, ]
# Plot
library(ggplot2)
df |>
ggplot() +
geom_bar(aes(
x = -log10(adj_p_val),
y = reorder(path_name, -adj_p_val)
),
stat = "identity",
fill = "lightgrey",
width = 0.5,
color = "black") +
geom_text(
aes(
y = path_name,
x = (-log10(adj_p_val)),
label = overlapping_genes_count
),
nudge_x = 0.75,
show.legend = NA,
color = "red"
) +
geom_text(
aes(
y = Inf,
x = Inf,
hjust = 1,
vjust = 1,
label = "# of overlapping genes"
),
show.legend = NA,
color = "red"
) +
geom_vline(linetype = "dotted", linewidth = 1, xintercept = -log10(0.05)) +
ylab("Pathway name") +
xlab("-log10(adjusted P value)")
Tutorials
Using gget enrichr with background genes
References
If you use gget enrichr in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z, Meirelles GV, Clark NR, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013; 128(14). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-128
-
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM, Lachmann A, McDermott MG, Monteiro CD, Gundersen GW, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016; gkw377. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw377
-
Xie Z, Bailey A, Kuleshov MV, Clarke DJB., Evangelista JE, Jenkins SL, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML, Kropiwnicki E, Jagodnik KM, Jeon M, & Ma’ayan A. Gene set knowledge discovery with Enrichr. Current Protocols, 1, e90. 2021. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.90.
If working with non-human/mouse datasets, please also cite:
- Kuleshov MV, Diaz JEL, Flamholz ZN, Keenan AB, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML, Cagan RL, Ma'ayan A. modEnrichr: a suite of gene set enrichment analysis tools for model organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 2;47(W1):W183-W190. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz347. PMID: 31069376; PMCID: PMC6602483.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget gpt 💬
Generates natural language text based on a given prompt using the OpenAI API's 'openai.ChatCompletion.create' endpoint. This module, including its source code, documentation and unit tests, were partly written by OpenAI's Chat-GTP3.
NOTE:
OpenAI API calls are only 'free' for the first three months after generating your OpenAI Account (OpenAI provides a $5 credit that expires).
You can define a hard monthly billing limit (e.g. $1) here.
See their pricing and FAQ here.
Get your OpenAI API key here.
Returns: A string containing the generated text.
Before using gget gpt for the first time, run gget setup gpt / gget.setup("gpt") once (also see gget setup).
Positional argument
prompt
The input prompt to generate text from (str).
api_key
Your OpenAI API key (str) (get your API key).
Optional arguments
-m --model
The name of the GPT model to use for generating the text (str). Default is "gpt-3.5-turbo".
See https://platform.openai.com/docs/models/gpt-4 for more information on the available models.
-temp --temperature
Value between 0 and 2 that controls the level of randomness and creativity in the generated text (float).
Higher values result in more creative and varied text. Default is 1.
-tp --top_p
Controls the diversity of the generated text as an alternative to sampling with temperature (float).
Higher values result in more diverse and unexpected text. Default is 1.
Note: OpenAI recommends altering this or temperature but not both.
-s --stop
A sequence of tokens to mark the end of the generated text (str). Default is None.
-mt --max_tokens
Controls the maximum length of the generated text, in tokens (int). Default is 200.
-pp --presence_penalty
Number between -2.0 and 2.0. Higher values result increase the model's likelihood to talk about new topics (float). Default is 0.
-fp --frequency_penalty
Number between -2.0 and 2.0. Higher values decrease the model's likelihood to repeat the same line verbatim (float). Default is 0.
-lb --logit_bias
A dictionary that specifies a bias towards certain tokens in the generated text (dict). Default is None.
-o --out
If provided, saves the generated text to a file with the specified path (str). Default: Standard out.
Example
gget gpt "How are you today GPT?" your_api_token
# Python
print(gget.gpt("How are you today GPT?", "your_api_token"))

Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget info 💡
Fetch extensive gene and transcript metadata from Ensembl, UniProt, and NCBI using Ensembl IDs.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python).
Positional argument
ens_ids
One or more Ensembl IDs (WormBase and Flybase IDs are also supported).
NOTE: Providing a list of more than 1,000 Ensembl IDs at once might result in a server error (to process more than 1,000 IDs, split the list of IDs into chunks of 1,000 IDs and run these separately).
Optional arguments
-o --out
Path to the file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.csv (or .json). Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Flags
-n --ncbi
TURN OFF results from NCBI.
Python: ncbi=False prevents data retrieval from NCBI (default: True).
-u --uniprot
TURN OFF results from UniProt.
Python: uniprot=False prevents data retrieval from UniProt (default: True).
-pdb --pdb
INCLUDE PDB IDs in output (might increase runtime).
Python: pdb=True includes PDB IDs in the results (default: False).
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
wrap_text
Python only. wrap_text=True displays data frame with wrapped text for easy reading (default: False).
Example
gget info ENSG00000034713 ENSG00000104853 ENSG00000170296
# Python
gget.info(["ENSG00000034713", "ENSG00000104853", "ENSG00000170296"])
→ Returns extensive information about each requested Ensembl ID:
| uniprot_id | ncbi_gene_id | primary_gene_name | synonyms | protein_names | ensembl_description | uniprot_description | ncbi_description | biotype | canonical_transcript | ... | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000034713 | P60520 | 11345 | GABARAPL2 | [ATG8, ATG8C, FLC3A, GABARAPL2, GATE-16, GATE16, GEF-2, GEF2] | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein like 2 (GABA(A) receptor-associated protein-like 2)... | GABA type A receptor associated protein like 2 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:13291] | FUNCTION: Ubiquitin-like modifier involved in intra- Golgi traffic (By similarity). Modulates intra-Golgi transport through coupling between NSF activity and ... | Enables ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process and protein... | protein_coding | ENST00000037243.7 | ... |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | ... |
More examples
References
If you use gget info in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
-
Sayers EW, Beck J, Bolton EE, Brister JR, Chan J, Comeau DC, Connor R, DiCuccio M, Farrell CM, Feldgarden M, Fine AM, Funk K, Hatcher E, Hoeppner M, Kane M, Kannan S, Katz KS, Kelly C, Klimke W, Kim S, Kimchi A, Landrum M, Lathrop S, Lu Z, Malheiro A, Marchler-Bauer A, Murphy TD, Phan L, Prasad AB, Pujar S, Sawyer A, Schmieder E, Schneider VA, Schoch CL, Sharma S, Thibaud-Nissen F, Trawick BW, Venkatapathi T, Wang J, Pruitt KD, Sherry ST. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D33-D43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1044. PMID: 37994677; PMCID: PMC10767890.
-
The UniProt Consortium , UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D523–D531, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1052
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget muscle 🦾
Align multiple nucleotide or amino acid sequences to each other using Muscle5.
Return format: ClustalW formatted standard out or aligned FASTA (.afa).
Positional argument
fasta
List of sequences or path to FASTA or .txt file containing the nucleotide or amino acid sequences to be aligned.
Optional arguments
-o --out
Path to the aligned FASTA file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.afa. Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Flags
-s5 --super5
Aligns input using the Super5 algorithm instead of the Parallel Perturbed Probcons (PPP) algorithm to decrease time and memory.
Use for large inputs (a few hundred sequences).
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Example
gget muscle MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS
# Python
gget.muscle(["MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", "MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS"])
gget muscle fasta.fa
# Python
gget.muscle("fasta.fa")
→ Returns an overview of the aligned sequences with ClustalW coloring. (To return an aligned FASTA (.afa) file, use --out argument (or save=True in Jupyter Lab/Google Colab).) In the above example, the 'fasta.fa' includes several sequences to be aligned (e.g. isoforms returned from gget seq).

You can also view aligned fasta files returned by gget.muscle using programs like alv, as shown below:
# Python
!pip install biopython
!pip install alv
from Bio import AlignIO
import alv
gget.muscle("fasta.fa", out="fasta_aligned.afa")
msa = AlignIO.read("fasta_aligned.afa", "fasta")
alv.view(msa)
More examples
References
If you use gget muscle in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Edgar RC (2021), MUSCLE v5 enables improved estimates of phylogenetic tree confidence by ensemble bootstrapping, bioRxiv 2021.06.20.449169. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.20.449169
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget mutate 🧟
Takes in nucleotide sequences and mutations (in standard mutation annotation and returns mutated versions of the input sequences according to the provided mutations.
Return format: Saves mutated sequences in FASTA format (or returns a list containing the mutated sequences if out=None).
This module was written by Joseph Rich.
** Update: The more complex functionality of gget mutate has been ported to https://github.com/pachterlab/kvar. kvar expands on this functionality in the context of screening for variants/mutations in sequencing data. If this sounds interesting to you, please check it out! **
Positional argument
sequences
Path to the FASTA file containing the sequences to be mutated, e.g., 'path/to/seqs.fa'.
Sequence identifiers following the '>' character must correspond to the identifiers in the seq_ID column of mutations.
Example format of the FASTA file:
>seq1 (or ENSG00000106443)
ACTGCGATAGACT
>seq2
AGATCGCTAG
Alternatively: Input sequence(s) as a string or list, e.g. 'AGCTAGCT'.
NOTE: Only the letters until the first space or dot will be used as sequence identifiers - Version numbers of Ensembl IDs will be ignored.
NOTE: When the sequences input is a genome fasta file, also see the gtf argument below.
Required arguments
-m --mutations
Path to the csv or tsv file (e.g., 'path/to/mutations.csv') or data frame (DataFrame object) containing information about the mutations in the following format (the 'notes' and 'mut_ID' columns are optional):
| mutation | mut_ID | seq_ID | notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| c.2C>T | mut1 | seq1 | -> Apply mutation 1 to sequence 1 |
| c.9_13inv | mut2 | seq2 | -> Apply mutation 2 to sequence 2 |
| c.9_13inv | mut2 | seq4 | -> Apply mutation 2 to sequence 4 |
| c.9_13delinsAAT | mut3 | seq4 | -> Apply mutation 3 to sequence 4 |
| ... | ... | ... |
'mutation' = Column containing the mutations to be performed written in standard mutation annotation
'mut_ID' = Column containing the identifier for each mutation
'seq_ID' = Column containing the identifiers of the sequences to be mutated (must correspond to the string following the '>' character in the 'sequences' FASTA file; do NOT include spaces or dots)
Alternatively: Input mutation(s) as a string or list, e.g., 'c.2C>T'.
If a list is provided, the number of mutations must equal the number of input sequences.
For use from the terminal (bash): Enclose individual mutation annotations in quotation marks to prevent parsing errors.
Optional input-related arguments
-mc --mut_column
Name of the column containing the mutations to be performed in mutations. Default: 'mutation'.
-sic --seq_id_column
Name of the column containing the IDs of the sequences to be mutated in mutations. Default: 'seq_ID'.
-mic --mut_id_column
Name of the column containing the IDs of each mutation in mutations. Default: Same as mut_column.
Optional mutant sequence generation/filtering arguments
-k --k
Length of sequences flanking the mutation. Default: 30.
If k > total length of the sequence, the entire sequence will be kept.
Optional general arguments
-o --out
Path to output FASTA file containing the mutated sequences, e.g., 'path/to/output_fasta.fa'.
Default: None -> returns a list of the mutated sequences to standard out.
The identifiers (following the '>') of the mutated sequences in the output FASTA will be '>[seq_ID]_[mut_ID]'.
Optional general flags
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Examples
gget mutate ATCGCTAAGCT -m 'c.4G>T'
# Python
gget.mutate("ATCGCTAAGCT", "c.4G>T")
→ Returns ATCTCTAAGCT.
List of sequences with a mutation for each sequence provided in a list:
gget mutate ATCGCTAAGCT TAGCTA -m 'c.4G>T' 'c.1_3inv' -o mut_fasta.fa
# Python
gget.mutate(["ATCGCTAAGCT", "TAGCTA"], ["c.4G>T", "c.1_3inv"], out="mut_fasta.fa")
→ Saves 'mut_fasta.fa' file containing:
>seq1_mut1
ATCTCTAAGCT
>seq2_mut2
GATCTA
One mutation applied to several sequences with adjusted k:
gget mutate ATCGCTAAGCT TAGCTA -m 'c.1_3inv' -k 3
# Python
gget.mutate(["ATCGCTAAGCT", "TAGCTA"], "c.1_3inv", k=3)
→ Returns ['CTAGCT', 'GATCTA'].
References
If you use gget mutate in a publication, please cite the following articles:
- Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget opentargets 🎯
Fetch associated diseases or drugs from OpenTargets using Ensembl IDs.
Return format: JSON/CSV (command-line) or data frame (Python).
This module was written by Sam Wagenaar.
Positional argument
ens_id
Ensembl gene ID, e.g ENSG00000169194.
Optional arguments
-r --resource
Defines the type of information to return in the output. Default: 'diseases'.
Possible resources are:
| Resource | Return Value | Valid Filters | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
diseases | Associated diseases | None | Various:etc. |
drugs | Associated drugs | disease_id | ChEMBL |
tractability | Tractability data | None | Open Targets |
pharmacogenetics | Pharmacogenetic responses | drug_id | PharmGKB |
expression | Gene expression data (by tissues, organs, and anatomical systems) | tissue_idanatomical_systemorgan | |
depmap | DepMap gene→disease-effect data. | tissue_id | DepMap Portal |
interactions | Protein⇄protein interactions | protein_a_idprotein_b_idgene_b_id |
-l --limit
Limit the number of results, e.g 10. Default: No limit.
Note: Not compatible with the tractability and depmap resources.
-o --out
Path to the JSON file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.json. Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Optional filter arguments
-fd --filter_disease disease_id
Filter by disease ID, e.g. 'EFO_0000274'. Only valid for the drugs resource.
-fc --filter_drug drug_id
Filter by drug ID, e.g. 'CHEMBL1743081'. Only valid for the pharmacogenetics resource.
-ft --filter_tissue tissue_id
Filter by tissue ID, e.g. 'UBERON_0000473'. Only valid for the expression and depmap resources.
-fa --filter_anat_sys
Filter by anatomical system, e.g. 'nervous system'. Only valid for the expression resource.
-fo --filter_organ anatomical_system
Filter by organ, e.g. 'brain'. Only valid for the expression resource.
-fpa --filter_protein_a protein_a_id
Filter by the protein ID of the first protein in the interaction, e.g. 'ENSP00000304915'. Only valid for the interactions resource.
-fpb --filter_protein_b protein_b_id
Filter by the protein ID of the second protein in the interaction, e.g. 'ENSP00000379111'. Only valid for the interactions resource.
-fgb --filter_gene_b gene_b_id
Filter by the gene ID of the second protein in the interaction, e.g. 'ENSG00000077238'. Only valid for the interactions resource.
filters
Python only. A dictionary of filters, e.g.
{'disease_id': ['EFO_0000274', 'HP_0000964']}
filter_mode
Python only. filter_mode='or' combines filters of different IDs with OR logic.
filter_mode='and' combines filters of different IDs with AND logic (default).
Flags
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns the output in CSV format, instead of JSON format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
-or --or
Command-line only. Filters are combined with OR logic. Default: AND logic.
wrap_text
Python only. wrap_text=True displays data frame with wrapped text for easy reading (default: False).
Examples
Get associated diseases for a specific gene:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r diseases -l 1
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='diseases', limit=1)
→ Returns the top disease associated with the gene ENSG00000169194.
| id | name | description | score |
|---|---|---|---|
| EFO_0000274 | atopic eczema | A chronic inflammatory genetically determined disease of the skin ... | 0.66364347241831 |
Get associated drugs for a specific gene:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r drugs -l 2
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='drugs', limit=2)
→ Returns the top 2 drugs associated with the gene ENSG00000169194.
| id | name | type | action_mechanism | description | synonyms | trade_names | disease_id | disease_name | trial_phase | trial_status | trial_ids | approved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHEMBL1743081 | TRALOKINUMAB | Antibody | Interleukin‑13 inhibitor | Antibody drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV ... | ['CAT-354', 'Tralokinumab'] | ['Adbry', 'Adtralza'] | EFO_0000274 | atopic eczema | 4 | [] | True | |
| CHEMBL4297864 | CENDAKIMAB | Antibody | Interleukin‑13 inhibitor | Antibody drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of III ... | [ABT-308, Abt-308, CC-93538, Cendakimab, RPC-4046] | [] | EFO_0004232 | eosinophilic esophagitis | 3 | Recruiting | [NCT04991935] | False |
Note: Returned trial_ids are ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers
Get tractability data for a specific gene:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r tractability
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='tractability')
→ Returns tractability data for the gene ENSG00000169194.
| label | modality |
|---|---|
| High-Quality Pocket | Small molecule |
| Approved Drug | Antibody |
| GO CC high conf | Antibody |
| UniProt loc med conf | Antibody |
| UniProt SigP or TMHMM | Antibody |
Get pharmacogenetic responses for a specific gene:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r pharmacogenetics -l 1
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='pharmacogenetics', limit=1)
→ Returns pharmacogenetic responses for the gene ENSG00000169194.
| rs_id | genotype_id | genotype | variant_consequence_id | variant_consequence_label | drugs | phenotype | genotype_annotation | response_category | direct_target | evidence_level | source | literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1295686 | 5_132660151_T_T,T | TT | SO:0002073 | no_sequence_alteration | id name 0 None hepatitis vaccines | increased risk for non‑immune response to the hepatitis B vaccine | Patients with the TT genotype may be at increased risk for non-immune response to the hepatitis B vaccine... | efficacy | False | 3 | pharmgkb | [21111021] |
Note: Returned literature ids are Europe PMC identifiers
Get tissues where a gene is most expressed:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r expression -l 2
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='expression', limit=2)
→ Returns the top 2 tissues where the gene ENSG00000169194 is most expressed.
| tissue_id | tissue_name | rna_zscore | rna_value | rna_unit | rna_level | anatomical_systems | organs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBERON_0000473 | testis | 5 | 1026 | 3 | [reproductive system] | [reproductive organ, reproductive structure] | |
| CL_0000542 | EBV‑transformed lymphocyte | 1 | 54 | 2 | [hemolymphoid system, immune system, lymphoid system] | [immune organ] |
Get DepMap gene-disease effect data for a specific gene:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r depmap
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='depmap')
→ Returns DepMap gene-disease effect data for the gene ENSG00000169194.
| depmap_id | expression | effect | tissue_id | tissue_name | cell_line_name | disease_cell_line_id | disease_name | mutation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACH‑001532 | 0.176323 | 0.054950 | UBERON_0002113 | kidney | JMU-RTK-2 | None | Rhabdoid Cancer | None |
Get protein-protein interactions for a specific gene:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r interactions -l 2
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='interactions', limit=2)
→ Returns the top 2 protein-protein interactions for the gene ENSG00000169194.
| evidence_score | evidence_count | source_db | protein_a_id | gene_a_id | gene_a_symbol | role_a | taxon_a | protein_b_id | gene_b_id | gene_b_symbol | role_b | taxon_b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.999 | 3 | string | ENSP00000304915 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | ENSP00000379111 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | unspecified role | 9606 |
| 0.999 | 3 | string | ENSP00000304915 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | ENSP00000360730 | ENSG00000131724 | IL13RA1 | unspecified role | 9606 |
Get protein-protein interactions for a specific gene, filtering by protein and gene IDs:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r interactions -fpa P35225 --filter_gene_b ENSG00000077238
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='interactions', filters={'protein_a_id': 'P35225', 'gene_b_id': 'ENSG00000077238'})
→ Returns protein-protein interactions for the gene ENSG00000169194, where the first protein is P35225 and the second gene is ENSG00000077238.
| evidence_score | evidence_count | source_db | protein_a_id | gene_a_id | gene_a_symbol | role_a | taxon_a | protein_b_id | gene_b_id | gene_b_symbol | role_b | taxon_b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 3 | reactome | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | P24394 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | unspecified role | 9606 |
| None | 2 | signor | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | regulator | 9606 | P24394 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | regulator target | 9606 |
Get protein-protein interactions for a specific gene, filtering by protein or gene IDs:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r interactions -fpa P35225 --filter_gene_b ENSG00000077238 ENSG00000111537 --or -l 5
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets(
'ENSG00000169194',
resource='interactions',
filters={'protein_a_id': 'P35225', 'gene_b_id': ['ENSG00000077238', 'ENSG00000111537']},
filter_mode='or',
limit=5
)
→ Returns protein-protein interactions for the gene ENSG00000169194, where the first protein is P35225 or the second gene is either ENSG00000077238 or ENSG00000111537.
| evidence_score | evidence_count | source_db | protein_a_id | gene_a_id | gene_a_symbol | role_a | taxon_a | protein_b_id | gene_b_id | gene_b_symbol | role_b | taxon_b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.999 | 3 | string | ENSP00000304915 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | ENSP00000379111 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | unspecified role | 9606 |
| 0.961 | 2 | string | ENSP00000304915 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | ENSP00000229135 | ENSG00000111537 | IFNG | unspecified role | 9606 |
| 0.800 | 9 | intact | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | Q14627 | ENSG00000123496 | IL13RA2 | unspecified role | 9606 |
| 0.740 | 6 | intact | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | P78552 | ENSG00000131724 | IL13RA1 | unspecified role | 9606 |
| 0.400 | 1 | intact | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | Q86XT9 | ENSG00000149932 | TMEM219 | stimulator | 9606 |
More examples
References
If you use gget opentargets in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Ochoa D, Hercules A, Carmona M, Suveges D, Baker J, Malangone C, Lopez I, Miranda A, Cruz-Castillo C, Fumis L, Bernal-Llinares M, Tsukanov K, Cornu H, Tsirigos K, Razuvayevskaya O, Buniello A, Schwartzentruber J, Karim M, Ariano B, Martinez Osorio RE, Ferrer J, Ge X, Machlitt-Northen S, Gonzalez-Uriarte A, Saha S, Tirunagari S, Mehta C, Roldán-Romero JM, Horswell S, Young S, Ghoussaini M, Hulcoop DG, Dunham I, McDonagh EM. The next-generation Open Targets Platform: reimagined, redesigned, rebuilt. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D1353-D1359. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1046. PMID: 36399499; PMCID: PMC9825572.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget pdb 🔮
Query RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB) for the protein structure/metadata of a given PDB ID.
Return format: Resource 'pdb' is returned in PDB format. All other resources are returned in JSON format.
Positional argument
pdb_id
PDB ID to be queried, e.g. '7S7U'.
Optional arguments
-r --resource
Defines type of information to be returned. One of the following:
'pdb': Returns the protein structure in PDB format (default).
'entry': Information about PDB structures at the top level of PDB structure hierarchical data organization.
'pubmed': Get PubMed annotations (data integrated from PubMed) for a given entry's primary citation.
'assembly': Information about PDB structures at the quaternary structure level.
'branched_entity': Get branched entity description (define entity ID as 'identifier').
'nonpolymer_entity': Get non-polymer entity data (define entity ID as 'identifier').
'polymer_entity': Get polymer entity data (define entity ID as 'identifier').
'uniprot': Get UniProt annotations for a given macromolecular entity (define entity ID as 'identifier').
'branched_entity_instance': Get branched entity instance description (define chain ID as 'identifier').
'polymer_entity_instance': Get polymer entity instance (a.k.a chain) data (define chain ID as 'identifier').
'nonpolymer_entity_instance': Get non-polymer entity instance description (define chain ID as 'identifier').
-i --identifier
Can be used to define assembly, entity or chain ID (default: None). Assembly/entity IDs are numbers (e.g. 1), and chain IDs are letters (e.g. 'A').
-o --out
Path to the file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/7S7U.pdb or path/to/directory/7S7U_entry.json. Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Examples
gget pdb 7S7U -o 7S7U.pdb
# Python
gget.pdb("7S7U", save=True)
→ Saves the structure of 7S7U in PDB format as '7S7U.pdb' in the current working directory.
Find PDB crystal structures for a comparative analysis of protein structure:
# Find PDB IDs associated with an Ensembl ID
gget info ENSG00000130234
# Alternatively: Since many entries in the PDB do not have linked Ensembl IDs,
# you will likely find more PDB entries by BLASTing the sequence agains the PDB.
# Get the amino acid sequence of a transcript from an Ensembl ID
gget seq --translate ENSG00000130234 -o gget_seq_results.fa
# BLAST an amino acid sequence to find similar structures in the PDB
gget blast --database pdbaa gget_seq_results.fa
# Get PDB files from the PDB IDs returned by gget blast for comparative analysis
gget pdb 7DQA -o 7DQA.pdb
gget pdb 7CT5 -o 7CT5.pdb
# Find PDB IDs associated with an Ensembl ID
gget.info("ENSG00000130234")
# Alternatively: Since many entries in the PDB do not have linked Ensembl IDs,
# you will likely find more PDB entries by BLASTing the sequence agains the PDB.
# Get the amino acid sequence of a transcript from an Ensembl ID
gget.seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=True, save=True)
# BLAST an amino acid sequence to find similar structures in the PDB
gget.blast("gget_seq_results.fa", database="pdbaa")
# Get PDB files from the PDB IDs returned by gget blast for comparative analysis
gget.pdb("7DQA", save=True)
gget.pdb("7CT5", save=True)
→ The use case above exemplifies how to find PDB files for comparative analysis of protein structure starting with Ensembl IDs or amino acid sequences. The fetched PDB files can also be compared to predicted structures generated by gget alphafold. PDB files can be viewed interactively in 3D online, or using programs like PyMOL or Blender. To compare two PDB files, you can use this website.
More examples
References
If you use gget pdb in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.235. PMID: 10592235; PMCID: PMC102472.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget ref 📖
Fetch download links and metadata for Ensembl reference genomes.
Return format: dictionary/JSON.
Positional argument
species
Species for which the FTPs will be fetched in the format genus_species, e.g. homo_sapiens.
Supports all available vertebrate and invertebrate (plants, fungi, protists, and invertebrate metazoa) genomes from Ensembl, except bacteria.
Note: Not required when using flags --list_species or --list_iv_species.
Supported shortcuts: 'human', 'mouse', 'human_grch37' (accesses the GRCh37 genome assembly)
Optional arguments
-w --which
Defines which results to return. Default: 'all' -> Returns all available results.
Possible entries are one or a combination (as comma-separated list) of the following:
'gtf' - Returns the annotation (GTF).
'cdna' - Returns the trancriptome (cDNA).
'dna' - Returns the genome (DNA).
'cds' - Returns the coding sequences corresponding to Ensembl genes. (Does not contain UTR or intronic sequence.)
'cdrna' - Returns transcript sequences corresponding to non-coding RNA genes (ncRNA).
'pep' - Returns the protein translations of Ensembl genes.
-r --release
Defines the Ensembl release number from which the files are fetched, e.g. 104. Default: latest Ensembl release.
-od --out_dir
Path to the directory where the FTPs will be saved, e.g. path/to/directory/. Default: Current working directory.
-o --out
Path to the JSON file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.json. Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Flags
-l --list_species
Lists all available vertebrate species. (Python: combine with species=None.)
-liv --list_iv_species
Lists all available invertebrate species. (Python: combine with species=None.)
-ftp --ftp
Returns only the requested FTP links.
-d --download
Command-line only. Downloads the requested FTPs to the directory specified by out_dir (requires curl to be installed).
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Examples
Get the genome reference for a specific species:
gget ref -w gtf,dna homo_sapiens
# Python
gget.ref("homo_sapiens", which=["gtf", "dna"])
→ Returns a JSON with the latest human GTF and FASTA FTPs, and their respective metadata, in the format:
{
"homo_sapiens": {
"annotation_gtf": {
"ftp": "http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-106/gtf/homo_sapiens/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.106.gtf.gz",
"ensembl_release": 106,
"release_date": "28-Feb-2022",
"release_time": "23:27",
"bytes": "51379459"
},
"genome_dna": {
"ftp": "http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-106/fasta/homo_sapiens/dna/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.gz",
"ensembl_release": 106,
"release_date": "21-Feb-2022",
"release_time": "09:35",
"bytes": "881211416"
}
}
}
List all available genomes from Ensembl release 103:
gget ref --list_species -r 103
# Python
gget.ref(species=None, list_species=True, release=103)
→ Returns a list with all available genomes (checks if GTF and FASTAs are available) from Ensembl release 103.
(If no release is specified, gget ref will always return information from the latest Ensembl release.)
Use gget ref in combination with kallisto | bustools to build a reference index:
kb ref \
-i index.idx \
-g t2g.txt \
-f1 fasta.fa \
$(gget ref --ftp -w dna,gtf homo_sapiens)
→ kb ref builds a reference index using the latest DNA and GTF files of species Homo sapiens passed to it by gget ref.
More examples
References
If you use gget ref in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget search 🔎
Fetch genes and transcripts from Ensembl using free-form search terms.
Results are matched based on the "gene name" and "description" sections in the Ensembl database. gget version >= 0.27.9 also includes results that match the Ensembl "synonym" section.
Return format: JSON (command-line) or data frame/CSV (Python).
Positional argument
searchwords
One or more free form search words, e.g. gaba nmda. (Note: Search is not case-sensitive.)
Other required arguments
-s --species
Species or database to be searched.
A species can be passed in the format 'genus_species', e.g. 'homo_sapiens' or 'arabidopsis_thaliana'.
To pass a specific database, pass the name of the CORE database, e.g. 'mus_musculus_dba2j_core_105_1'.
All available core databases can be found here:
Vertebrates: http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/current/mysql/
Invertebrates: http://ftp.ensemblgenomes.org/pub/current/ + select kingdom + go to mysql/
Supported shortcuts: 'human', 'mouse'
Optional arguments
-r --release
Defines the Ensembl release number from which the files are fetched, e.g. 104. Default: None -> latest Ensembl release is used.
Note: The release argument does not apply to invertebrate species (you can pass a specific core database (which includes a release number) to the species argument instead). For invertebrate species, Ensembl only stores databases from 10 releases prior to the current release.
This argument is overwritten if a specific database (which includes a release number) is passed to the species argument.
-t --id_type
'gene' (default) or 'transcript'
Returns genes or transcripts, respectively.
-ao --andor
'or' (default) or 'and'
'or': Returns all genes that INCLUDE AT LEAST ONE of the searchwords in their name/description.
'and': Returns only genes that INCLUDE ALL of the searchwords in their name/description.
-l --limit
Limits the number of search results, e.g. 10. Default: None.
-o --out
Path to the csv the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.csv (or .json). Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Flags
-csv --csv
Command-line only. Returns results in CSV format.
Python: Use json=True to return output in JSON format.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
wrap_text
Python only. wrap_text=True displays data frame with wrapped text for easy reading (default: False).
Example
gget search -s human gaba gamma-aminobutyric
# Python
gget.search(["gaba", "gamma-aminobutyric"], "homo_sapiens")
→ Returns all genes that contain at least one of the search words in their name or Ensembl/external reference description:
| ensembl_id | gene_name | ensembl_description | ext_ref_description | biotype | url |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000034713 | GABARAPL2 | GABA type A receptor associated protein like 2 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:13291] | GABA type A receptor associated protein like 2 | protein_coding | https://uswest.ensembl.org/homo_sapiens/Gene/Summary?g=ENSG00000034713 |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . |
More examples
References
If you use gget search in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget setup 🔧
Function to install/download third-party dependencies for a specified gget module.
Note: Some dependencies (e.g.,
cellxgene-census) may not support the latest Python versions. If you encounter installation errors try using an environment with an earlier Python version.
Positional argument
module
gget module for which dependencies should be installed.
Optional arguments
-o --out
Path to the folder downloaded files will be saved in (currently only applies to module = 'elm').
NOTE: Do NOT use this argument when downloading the files for use with gget.elm.
Default: None (downloaded files are saved inside the gget package installation folder).
Flags
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Example
gget setup alphafold
# Python
gget.setup("alphafold")
→ Installs all (modified) third-party dependencies and downloads model parameters (~4GB) required to run gget alphafold.
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget seq 🧬
Fetch nucleotide or amino acid sequence(s) of a gene (and all its isoforms) or a transcript by Ensembl ID.
Return format: FASTA.
Positional argument
ens_ids
One or more Ensembl IDs.
Optional arguments
-o --out
Path to the file the results will be saved in, e.g. path/to/directory/results.fa. Default: Standard out.
Python: save=True will save the output in the current working directory.
Flags
-t --translate
Returns amino acid (instead of nucleotide) sequences.
Nucleotide sequences are fetched from Ensembl.
Amino acid sequences are fetched from UniProt.
-iso --isoforms
Returns the sequences of all known transcripts.
(Only for gene IDs.)
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Examples
gget seq ENSG00000034713 ENSG00000104853 ENSG00000170296
# Python
gget.seq(["ENSG00000034713", "ENSG00000104853", "ENSG00000170296"])
→ Returns the nucleotide sequences of ENSG00000034713, ENSG00000104853, and ENSG00000170296 in FASTA format.
gget seq -t -iso ENSG00000034713
# Python
gget.seq("ENSG00000034713", translate=True, isoforms=True)
→ Returns the amino acid sequences of all known transcripts of ENSG00000034713 in FASTA format.
More examples
References
If you use gget seq in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606
-
The UniProt Consortium , UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D523–D531, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1052
Python arguments are equivalent to long-option arguments (
--arg), unless otherwise specified. Flags are True/False arguments in Python. The manual for any gget tool can be called from the command-line using the-h--helpflag.
gget virus 🦠
Download viral nucleotide sequences, along with rich, linked metadata, from across the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC), including NCBI, ENA, and DDBJ (accessed via NCBI Virus), with the option to further enrich results using metadata from NCBI GenBank (e.g. gene and protein annotations, amino acid sequences, and more). gget virus applies sequential server-side and local filters to efficiently download customized datasets.
Return format: FASTA, CSV, and JSONL files saved to an output folder.
This module was written by Ferdous Nasri.
Note: For SARS-CoV-2 and Alphainfluenza (Influenza A) queries, gget virus uses NCBI's optimized cached data packages via the NCBI datasets CLI. The datasets CLI binary is bundled with gget for all major platforms—no additional installation required. If you already have the NCBI datasets CLI installed on your system, gget will automatically use your existing installation.
Positional argument
virus
Virus taxon name (e.g. 'Zika virus'), taxon ID (e.g. '2697049'), NCBI accession number (e.g. 'NC_045512.2'), space-separated list of accessions (e.g. 'NC_045512.2 MN908947.3 MT020781.1'), or path to a text file containing accession numbers (one per line) (e.g. 'path/to/text.txt').
Add --is_accession when passing an NCBI accession number. Add --is_sars_cov2 or is_alphainfluenza for optimized download of SARS-CoV2 or Alphainfluenza sequences, respectively.
Use flag --download_all_accessions to apply filters without searching for a specific virus.
Optional arguments
Host filters
--host
Filter by host organism name or NCBI Taxonomy ID (e.g., 'human', 'Aedes aegypti', 1335626).
--lab_passaged
'true' or 'false'. Filter for or against lab-passaged samples.
Command line: --lab_passaged true to fetch only lab-passaged samples, or --lab_passaged false to exclude them.
Python: lab_passaged=True or lab_passaged=False (lab_passaged=None for no filter).
Sequence & Gene filters
--nuc_completeness
Filter by nucleotide completeness. One of: 'complete' or 'partial'.
Set to 'complete' to only return nucleotide sequences marked as complete; set to 'partial' to only return sequences that are marked as partial.
--min_seq_length
Filter by minimum sequence length.
--max_seq_length
Filter by maximum sequence length.
--min_gene_count
Filter by minimum number of genes.
--max_gene_count
Filter by maximum number of genes.
--min_protein_count
Filter by minimum number of proteins.
--max_protein_count
Filter by maximum number of proteins.
--min_mature_peptide_count
Filter by minimum number of mature peptides.
--max_mature_peptide_count
Filter by maximum number of mature peptides.
--max_ambiguous_chars
Filter by maximum number of ambiguous nucleotide characters (N's).
--has_proteins
Filter for sequences containing specific proteins or genes (e.g., 'spike', 'ORF1ab'). Can be a single protein name or a list of protein names.
Python: has_proteins="spike" or has_proteins=["spike", "ORF1ab"]
--annotated
'true' or 'false'. Filter for sequences that have been annotated with gene/protein information.
Command line: --annotated true to fetch only that have been annotated with gene/protein information, or --annotated false to exclude them.
Python: annotated=True or annotated=False (annotated=None for no filter).
Date filters
--min_collection_date
Filter by minimum sample collection date (YYYY-MM-DD).
--max_collection_date
Filter by maximum sample collection date (YYYY-MM-DD).
--min_release_date
Filter by minimum sequence release date (YYYY-MM-DD).
--max_release_date
Filter by maximum sequence release date (YYYY-MM-DD).
Location & Submitter filters
--geographic_location
Filter by geographic location of sample collection (e.g., 'USA', 'Asia').
--submitter_country
Filter by the country of the sequence submitter.
SARS-CoV-2 specific filters
--lineage
Filter by SARS-CoV-2 lineage (e.g. 'B.1.1.7', 'P.1').
Workflow configurations
--genbank_batch_size
Batch size for GenBank metadata API requests. Default: 200. Larger batches are faster but may be more prone to timeouts.
-o --out
Path to the folder where results will be saved. Default: current working directory.
Python: outfolder="path/to/folder"
Flags
-a --is_accession
Flag to indicate that the virus positional argument is an accession number, a space-separated list of accessions, or a path to a text file containing accession numbers (one per line). For SARS-CoV-2 and Alphainfluenza cached downloads, supports:
- Single accession:
NC_045512.2 - Space-separated list:
NC_045512.2 MN908947.3 MT020781.1 - Text file path:
accessions.txt(one accession per line)
--download_all_accessions
Use this flag when applying filters without searching for a specific virus (leave virus argument empty).
⚠️ WARNING: If you do not specify additional filters, this flag downloads ALL available viral sequences from NCBI (entire Viruses taxonomy, taxon ID 10239). This is an extremely large dataset that can take many hours to download and require significant disk space. Use with caution and ensure you have adequate storage and bandwidth. When this flag is set, the virus argument is ignored.
--refseq_only
Flag to limit search to RefSeq genomes only (higher quality, curated sequences).
--is_sars_cov2
Use NCBI's optimized cached data packages for a SARS-CoV-2 query. This provides faster and more reliable downloads. The system can auto-detect SARS-CoV-2 taxon-name queries, but for accession-based queries, you must set this flag explicitly.
--is_alphainfluenza
Use NCBI's optimized cached data packages for an Alphainfluenza (Influenza A virus) query. This provides faster and more reliable downloads for large Influenza A datasets. The system can auto-detect Alphainfluenza taxon-name queries, but for accession-based queries, you must set this flag explicitly.
-g --genbank_metadata
Fetch and save additional detailed metadata from GenBank, including collection dates, host details, and publication references, in a separate {virus}_genbank_metadata.csv file (plus full XML/CSV dumps).
--proteins_complete
Flag to only include sequences where all annotated proteins are complete.
-kt --keep_temp
Flag to keep all intermediate/temporary files generated during processing. By default, only final output files are retained.
-q --quiet
Command-line only. Prevents progress information from being displayed.
Python: Use verbose=False to prevent progress information from being displayed.
Example
gget virus "Zika virus" --nuc_completeness complete --host human --out zika_data
# Python
import gget
gget.virus(
"Zika virus",
nuc_completeness="complete",
host="human",
outfolder="zika_data"
)
→ Downloads complete Zika virus genomes from human hosts. Results are saved in the zika_data folder as Zika_virus_sequences.fasta, Zika_virus_metadata.csv, Zika_virus_metadata.jsonl, and command_summary.txt.
The metadata CSV file will look like this:
| accession | Organism Name | GenBank/RefSeq | Release date | Length | Nuc Completeness | Geographic Location | Host | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KX198135.1 | Zika virus | GenBank | 2016-05-18 | 10807 | complete | Americas:Haiti | Homo sapiens | ... |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | ... |
The command summary file (command_summary.txt) will contain, for example:
================================================================================
GGET VIRUS COMMAND SUMMARY
================================================================================
Execution Date: 2025-12-15 13:33:39
Output Folder: zika_data
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
COMMAND LINE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
gget virus "Zika virus" --nuc_completeness complete --host human --out zika_data
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EXECUTION STATUS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
✓ Command completed successfully
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SEQUENCE STATISTICS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total records from API: 234
After metadata filtering: 234
Final sequences (after all filters): 234
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DETAILED STATISTICS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Unique hosts: 1
- Homo sapiens
Unique geographic locations: 15
- Americas:Brazil
- Americas:Colombia
- ... (showing top 20)
Sequence length range: 10272 - 11155 bp
Average sequence length: 10742 bp
Completeness breakdown:
- complete: 234
Source database breakdown:
- GenBank: 233
- RefSeq: 1
Unique submitter countries: 12
- USA
- Brazil
- ... (showing top 20)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OUTPUT FILES
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FASTA Sequences: Zika_virus_sequences.fasta (2.45 MB)
JSONL Metadata: Zika_virus_metadata.jsonl (0.53 MB)
CSV Metadata: Zika_virus_metadata.csv (0.42 MB)
================================================================================
END OF SUMMARY
================================================================================
Note: If any operations fail during execution (API timeouts, sequence download failures, GenBank metadata failures), the summary will include a "FAILED OPERATIONS - RETRY COMMANDS" section with exact commands and URLs that can be run manually to retry the failed operations. For example:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FAILED OPERATIONS - RETRY COMMANDS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Some operations failed during execution. You can retry them manually:
[Failed Sequence Download Batches]
Total failed batches: 2
Batch 15: 200 sequences
Error: HTTPError: 500 Server Error
Accessions: NC_045512.2, MN908947.3, MT020781.1 ... and 197 more
Retry URL: https://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/efetch.fcgi?db=nucleotide&id=NC_045512.2,MN908947.3,...&rettype=fasta&retmode=text
[Failed GenBank Metadata Batches]
Total failed batches: 1
See detailed log file: genbank_failed_batches.log
Accessions: NC_045512.2, MN908947.3, MT020781.1 ... and 2 more
Retry URL: https://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/efetch.fcgi?db=nucleotide&id=NC_045512.2,MN908947.3,...&rettype=gb&retmode=xml
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Download a specific SARS-CoV-2 reference genome using its accession number:
gget virus NC_045512.2 --is_accession --is_sars_cov2
# Python
import gget
gget.virus("NC_045512.2", is_accession=True, is_sars_cov2=True)
→ Uses the optimized download method for SARS-CoV-2 to fetch the reference genome and its metadata.
Download SARS-CoV-2 sequences with cached optimization AND GenBank metadata:
gget virus "SARS-CoV-2" --host human --nuc_completeness complete --min_seq_length 29000 --genbank_metadata
# Python
import gget
gget.virus(
"SARS-CoV-2",
host="human",
nuc_completeness="complete",
min_seq_length=29000,
genbank_metadata=True,
is_sars_cov2=True,
outfolder="covid_data"
)
→ Uses cached download for speed (via NCBI's SARS-CoV-2 data packages when available), applies the sequence length filter post-download, and fetches detailed GenBank metadata for all filtered sequences.
Download Influenza A virus sequences with optimized caching and post-download filtering:
gget virus "Influenza A virus" --host human --nuc_completeness complete --max_seq_length 15000 --genbank_metadata --is_alphainfluenza
# Python
import gget
gget.virus(
"Influenza A virus",
host="human",
nuc_completeness="complete",
max_seq_length=15000,
genbank_metadata=True,
is_alphainfluenza=True,
outfolder="influenza_a_data"
)
→ Uses NCBI's cached data packages for Alphainfluenza to download complete Influenza A genomes from human hosts much faster than the standard API method, then applies the sequence length filter and fetches GenBank metadata.
References
If you use gget virus in a publication, please cite the following articles:
-
Nasri, F. et al (2026). Coming soon.
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
O’Leary, N.A., Cox, E., Holmes, J.B. et al (2024). Exploring and retrieving sequence and metadata for species across the tree of life with NCBI Datasets. Sci Data 11, 732. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03571-y
Additional Details: Virus Retrieval Workflow
Overview
The gget.virus() function implements an optimized 10-step workflow for retrieving virus sequences and associated metadata from NCBI. The system is designed to minimize download overhead by filtering metadata first, then downloading only the sequences that pass initial filters, with optional detailed GenBank metadata retrieval. For SARS-CoV-2 and Alphainfluenza queries, the workflow can use optimized cached data packages while still applying all filters and fetching GenBank metadata.
Architecture
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Users │
│ │
│ • Virus Query (Taxon/Acc) │
│ • Filter Criteria │
│ (Host, Dates, Length...) │
│ • Output Flags │
│ (`--genbank_metadata`) │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Cached Download Check │
│ (SARS-CoV-2/Alphainfluenza)│
│ │
│ • Auto-detect or use flags │
│ • Download cached packages │
│ • Apply basic filters │
│ (host, complete, lineage)│
│ • Store for pipeline use │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ API & Pre-Filtering │
│ (or use cached metadata) │
│ │
│ • Calls NCBI Datasets API │
│ OR uses cached metadata │
│ • Applies server-side │
│ filters (host, refseq) │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Local Metadata Filtering & │
│ Sequence Handling │
│ │
│ • Applies ALL remaining │
│ local filters (dates, │
│ gene counts, etc.) │
│ • Generates final list of │
│ accession numbers │
│ • Uses cached sequences OR │
│ downloads via E-utilities│
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
┌───────────┴──────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐ ┌───────────────────────────────────┐
│ Final Processing │ │ GenBank Metadata (Optional) │
│ │ │ │
│ • Applies sequence-level │ │ • Fetched even for cached │
│ filters (e.g., max N's) │ │ downloads when requested │
│ • Formats standard metadata│ │ • Uses final accession list │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘ │ • Fetches via E-utilities API │
│ └──────────────────┬────────────────┘
│ │
└──────────────────┬─────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ Save Final Output Files │
│ │
│ • _sequences.fasta │
│ • _metadata.csv & .jsonl │
│ • _genbank_metadata.csv │
│ (if requested) │
└──────────────┬────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ Summary & Cleanup │
│ │
│ • command_summary.txt │
│ • Display results to user │
│ • Clean temp files │
└───────────────────────────────┘
Workflow Steps
Step 1: Input Validation & Setup
- Function:
virus()main function - Purpose: Validate all user parameters and configure logging
- Key Operations:
- Validate virus taxon/accession format
- Check filter parameter ranges and formats
- Set up output directory structure
- Configure logging based on verbosity level
- Check for SARS-CoV-2 or Alphainfluenza optimization opportunities
Step 2: Optimized Cached Download (SARS-CoV-2 & Alphainfluenza)
- Functions:
download_sars_cov2_optimized(),download_alphainfluenza_optimized() - Purpose: Use NCBI's pre-computed cached data packages for faster downloads
- NCBI datasets CLI: gget bundles the NCBI datasets CLI binary for all major platforms (macOS, Linux, Windows). If you already have the
datasetsCLI installed on your system, gget will automatically use your system installation instead. - Key Operations:
- Auto-detect or use explicit flags for SARS-CoV-2/Alphainfluenza queries
- Download compressed cached packages via NCBI datasets CLI
- Apply basic filters supported by cached downloads (host, complete_only, annotated, lineage)
- Extract sequences and basic metadata
- Store data for pipeline continuation (does not return early)
- Hierarchical fallback to standard API if cached download fails
- Filters Applied:
- ✅
host- Applied during download - ✅
complete_only- Applied during download - ✅
annotated- Applied during download - ✅
lineage(COVID only) - Applied during download - ⏭️ All other filters applied in subsequent steps
- ✅
Step 3: Metadata Retrieval
- Function:
fetch_virus_metadata() - Purpose: Retrieve metadata from NCBI Datasets API with server-side filtering, or use cached metadata
- Key Operations:
- If using cached download: Skip API call, use cached metadata
- Otherwise: Call NCBI Datasets API with server-side filters
- Apply server-side filters (host, geographic location, release date, completeness)
- Handle API pagination with connection pooling
- Implement exponential backoff with jitter for retries
- Parse JSON responses with streaming for large datasets
- Store metadata in structured format with validation
Step 4: Metadata-Only Filtering
- Function:
filter_metadata_only() - Purpose: Apply ALL local filters that don't require sequence data
- Key Operations:
- Filter by date ranges with smart date parsing
- Filter by genome completeness and quality indicators
- Apply numeric range filters (gene/protein counts, sequence length)
- Handle missing or malformed metadata gracefully
- Generate optimized accession list for targeted processing
- Note: Filters not applied during cached download are applied here
Step 5: Sequence Handling
- Function:
download_sequences_by_accessions() - Purpose: Use cached sequences or download FASTA sequences for filtered accessions
- Key Operations:
- If using cached download: Filter cached sequences by accession list from Step 4
- Otherwise: Download via E-utilities API with batch optimization
- Implement configurable batch sizes (default: 200)
- Stream large responses to manage memory
- Handle download retries with exponential backoff
- Return path to FASTA file for processing
Step 6: Sequence-Dependent Filtering
- Function:
filter_sequences() - Purpose: Apply final filters requiring sequence analysis
- Key Operations:
- Parse FASTA sequences and calculate sequence metrics
- Filter by ambiguous character count (
max_ambiguous_chars) - Filter by protein/gene presence (
has_proteins) - Filter by protein completeness indicators (
proteins_complete) - Return filtered sequences and updated metadata
Step 7: Saving Final Output Files
- Functions:
save_metadata_to_csv(),FastaIO.write() - Purpose: Save filtered sequences and metadata to output files
- Key Operations:
- Write filtered sequences to FASTA file
- Save metadata to CSV and JSONL formats
- Track output file sizes for summary
- Validate file creation success
Step 8: GenBank Metadata Retrieval (Optional)
- Function:
fetch_genbank_metadata() - Purpose: Fetch detailed GenBank records for final sequence set
- Key Operations:
- Available for both cached and non-cached downloads
- Retrieve comprehensive GenBank records
- Extract 23+ metadata fields per record
- Process in configurable batch sizes
- Implement rate limiting and retries
- Parse and validate GenBank XML
- Merge with existing metadata
Step 9: Final Summary & Command Summary Generation
- Function:
save_command_summary() - Purpose: Create detailed summary of execution and display results
- Key Operations:
- Record command line and parameters
- Track filtering statistics at each stage
- List output files with sizes
- Document any failed operations with retry commands
- Display comprehensive results summary to user
Step 10: Cleanup
- Purpose: Clean up temporary files and finalize execution
- Key Operations:
- Remove temporary processing directory (unless
keep_temp=True) - Remove intermediate metadata files
- Preserve GenBank metadata CSV when successfully retrieved
- Log completion status
- Remove temporary processing directory (unless
Function Dependencies
virus()
├── check_min_max() [Step 1: Input validation]
│ └── Validates min/max parameter pairs
├── is_sars_cov2_query() [Step 2: SARS-CoV-2 detection]
│ └── Auto-detects SARS-CoV-2 queries
├── download_sars_cov2_optimized() [Step 2: Cached download]
│ ├── _get_datasets_path()
│ ├── NCBI datasets CLI calls
│ └── Cached package downloads
├── is_alphainfluenza_query() [Step 2b: Alphainfluenza detection]
│ └── Auto-detects Alphainfluenza queries
├── download_alphainfluenza_optimized() [Step 2b: Cached download]
│ ├── _get_datasets_path()
│ ├── NCBI datasets CLI calls
│ └── Cached package downloads
├── unzip_file() [Step 2/2b: Extract cached data]
│ └── ZIP extraction utilities
├── fetch_virus_metadata() [Step 3: API metadata retrieval]
│ ├── NCBI Datasets API client
│ ├── Pagination handling
│ ├── Retry logic with backoff
│ └── _get_modified_virus_name() for retry
├── fetch_virus_metadata_chunked() [Step 3: Fallback for large datasets]
│ └── Date-chunked download strategy
├── load_metadata_from_api_reports() [Step 3: Metadata conversion]
│ └── Converts API format to internal format
├── filter_metadata_only() [Step 4: Metadata filtering]
│ ├── parse_date() for date comparisons
│ ├── Numeric validation
│ └── Missing data handling
├── download_sequences_by_accessions() [Step 5: Sequence download]
│ ├── E-utilities API client
│ ├── Batch processing (default: 200)
│ └── Stream handling
├── filter_sequences() [Step 6: Sequence filtering]
│ ├── FastaIO parser
│ └── Sequence validation
├── save_metadata_to_csv() [Step 7: Save outputs]
│ └── CSV formatting and writing
├── fetch_genbank_metadata() [Step 8: Optional GenBank data]
│ ├── _fetch_genbank_batch()
│ ├── _clean_xml_declarations()
│ ├── XML parsing utilities
│ └── Rate limiting
├── save_genbank_metadata_to_csv() [Step 8: Save GenBank data]
│ └── Merges with virus metadata
└── save_command_summary() [Step 9: Execution summary]
└── Failed operations tracking
Optimization Features
1. Server-Side Filtering
- Applies filters at the NCBI API level to reduce data transfer
- Supported filters: host, geographic location, release date, genome completeness
- Automatic validation of filter compatibility and values
2. Multi-Stage Filtering
- Stage 1: Metadata-only filters (fast, no sequence download)
- Stage 2: Sequence-dependent filters (pre-filtered set)
- Stage 3: GenBank metadata integration and filtering
- Stage 4: Final validation and quality checks
3. Optimized Downloads
- Configurable batch sizes for different data types
- Connection pooling for improved performance
- Stream handling for large downloads
- Rate limiting and retry mechanisms
4. Optimized Cached Downloads
- Special handling for SARS-CoV-2 and Alphainfluenza queries using NCBI's cached data packages
- Automatic detection or explicit flags (
--is_sars_cov2,--is_alphainfluenza) - Hierarchical fallback strategies to standard API if cached download fails
- Significantly faster downloads for large datasets
- Pipeline continuation: Cached downloads now continue through all workflow steps
- Post-download filtering: Filters not applied during cached download are applied afterward
- GenBank metadata: Available for cached downloads when
--genbank_metadataflag is used - Filter categories:
- Applied during download:
host,complete_only,annotated,lineage(COVID) - Applied post-download: All other filters (sequence length, gene counts, dates, etc.)
- Applied during download:
5. Efficient Data Structures
- Accession-based dictionaries for O(1) lookups
- Streaming parsers for JSON and XML
- Memory-efficient FASTA handling
- Optimized metadata merging
Output Files
1. FASTA Sequences ({virus}_sequences.fasta)
- Contains nucleotide sequences for filtered results
- Standard FASTA format with detailed headers
- Original orientation from NCBI preserved
- Optional protein/segment annotations in headers
2. CSV Metadata ({virus}_metadata.csv)
- Tabular format for spreadsheet analysis
- Standardized column structure
- Geographic and taxonomic information
- Collection and submission details
- Quality metrics and annotations
3. GenBank Metadata ({virus}_genbank_metadata.csv) [Optional]
- 23+ detailed metadata columns
- Publication references
- Feature annotations
- Cross-references to other databases
- Strain and isolate details
4. JSONL Metadata ({virus}_metadata.jsonl)
- JSON Lines format for virus metadata after metadata-only filtering
- Streaming-friendly format for programmatic access
- One JSON object per sequence with the same fields as the CSV metadata
- GenBank-specific fields are stored separately in
{virus}_genbank_metadata.csvwhen--genbank_metadatais used
5. Command Summary (command_summary.txt)
- Automatically generated summary of the command execution
- Records the exact command line that was run
- Execution status (success/failure with error messages)
- Filtering statistics at each stage:
- Total records from API
- Records after metadata filtering
- Final sequences after all filters
- Detailed statistics:
- Unique hosts with counts (up to top 20 listed)
- Unique geographic locations with counts (up to top 20 listed)
- Sequence length range and average
- Completeness breakdown (complete vs partial)
- Source database breakdown (GenBank vs RefSeq)
- Unique submitter countries with counts (up to top 20 listed)
- List of all generated output files with sizes
- Failed Operations Tracking (when applicable):
- API timeout failures: Exact URL that timed out with alternative command suggestions
- Failed sequence download batches: Batch numbers, accession lists, and retry URLs
- Failed GenBank metadata batches: Accession lists with individual retry URLs
- All failed operations include exact commands/URLs that can be run manually for retry
Usage Examples
Command Line Examples
# Get help and see all available parameters
$ gget virus --help
$ gget virus "Nipah virus"
# Download Zika virus sequences with basic filtering (API + metadata filtering)
$ gget virus "Zika virus" --host human --min_seq_length 10000 --max_seq_length 11000
# Download with metadata and sequence filtering
$ gget virus "Ebolavirus" --max_seq_length 20000 --genbank_metadata -o ./ebola_data
# Download SARS-CoV-2 with cached optimization
$ gget virus "SARS-CoV-2" --host dog --nuc_completeness complete
# Download Influenza A with post-download sequence filtering (warning: big data size)
$ gget virus "Influenza A virus" --host human --max_ambiguous_chars 50 --has_proteins spike
# Using accession ID to get data
$ gget virus -a "MK947457" --host deer --min_collection_date "2020-01-01"
Python Examples
import gget
import pandas as pd
from Bio import SeqIO
# Basic download with GenBank metadata
gget.virus(
"Zika virus",
host="human",
genbank_metadata=True,
outfolder="zika_data"
)
# Access different data types from output files
sequences = list(SeqIO.parse("zika_data/Zika_virus_sequences.fasta", "fasta"))
virus_metadata = pd.read_csv("zika_data/Zika_virus_metadata.csv")
genbank_metadata = pd.read_csv("zika_data/Zika_virus_genbank_metadata.csv")
# Print GenBank metadata summary
for _, row in genbank_metadata.head().iterrows():
print(f"Sequence: {row['accession']}")
print(f" Length: {row['sequence_length']} bp")
print(f" Host: {row.get('host', 'Unknown')}")
print(f" Location: {row.get('geographic_location', 'Unknown')}")
print(f" Collection date: {row.get('collection_date', 'Unknown')}")
# Advanced filtering with GenBank data
gget.virus(
"SARS-CoV-2",
host="human",
min_seq_length=29000,
max_seq_length=30000,
min_collection_date="2020-03-01",
max_collection_date="2020-03-31",
geographic_location="North America",
genbank_metadata=True,
genbank_batch_size=200,
outfolder="covid_march2020"
)
# Process and analyze results
# Read virus metadata
virus_df = pd.read_csv("covid_march2020/SARS-CoV-2_metadata.csv")
print(f"Total sequences: {len(virus_df)}")
print(f"Unique hosts: {virus_df['Host'].nunique()}")
print(f"Date range: {virus_df['Collection Date'].min()} to {virus_df['Collection Date'].max()}")
# Read GenBank metadata for detailed analysis
genbank_df = pd.read_csv("covid_march2020/SARS-CoV-2_genbank_metadata.csv")
print(f"Sequences with GenBank data: {len(genbank_df)}")
print("\nPublication summary:")
print(genbank_df['reference_count'].describe())
# Custom sequence analysis
sequences = list(SeqIO.parse("covid_march2020/SARS-CoV-2_sequences.fasta", "fasta"))
for record in sequences:
gc_content = (str(record.seq).count('G') + str(record.seq).count('C')) / len(record.seq)
print(f"{record.id}: GC content = {gc_content:.2%}")
# Merge metadata sources
merged_df = pd.merge(
virus_df,
genbank_df,
on='accession',
how='left',
suffixes=('_virus', '_genbank')
)
# Save merged analysis
merged_df.to_csv("covid_march2020/combined_analysis.csv", index=False)
Analysis Strategy Examples
The examples above demonstrate different analysis approaches:
- Basic GenBank Integration: Fetch sequences with GenBank metadata for comprehensive analysis
- Advanced Filtering: Combine virus metadata and GenBank data with custom filters
- Custom Analysis: Process sequences and metadata using BioPython and Pandas
- Data Integration: Merge virus and GenBank metadata for detailed analysis
Programmatic Access
# Access filtered metadata and sequences
metadata_file = "covid_data/SARS-CoV-2_metadata.jsonl"
sequences_file = "covid_data/SARS-CoV-2_sequences.fasta"
# Process results with custom analysis
import json
with open(metadata_file) as f:
for line in f:
record = json.loads(line)
# Custom analysis here
Welcome to gget's contributing guide
Thank you for investing your time in contributing to our project! Any contribution you make will be reflected on the gget repo. ✨
Read our Code of Conduct to keep our community approachable and respectable.
In this guide you will get an overview of the contribution workflow from opening an issue or creating a pull request (PR) to reviewing and merging a PR.
Issues
Create a new issue
If you spot a problem with gget or you have an idea for a new feature, check if an issue already exists. If a related issue doesn't exist, you can open a new issue using the relevant issue form.
Solve an issue
Scan through our existing issues to find one that interests you. You can narrow down the search using labels as filters. If you find an issue to work on, you are welcome to open a PR with a fix.
Contribute through pull requests
Getting started
- Fork the repository.
-
Using GitHub Desktop:
- Getting started with GitHub Desktop will guide you through setting up Desktop.
- Once Desktop is set up, you can use it to fork the repo!
-
Using the command line:
- Fork the repo so that you can make your changes without affecting the original project until you're ready to merge them.
- Create a working branch and start with your changes!
Commit your update
Commit the changes once you are happy with them.
‼️ Self-review the following before creating a Pull Request ‼️
- Review the content for technical accuracy.
- Copy-edit the changes/comments for grammar, spelling, and adherence to the general style of existing gget code.
- Format your code using black.
- Make sure the unit tests pass:
- Developer dependencies can be installed with
pip install -r dev-requirements.txt - Run existing unit tests from the gget repository root with
coverage run -m pytest -ra -v tests && coverage report --omit=main.py,tests*
- Developer dependencies can be installed with
- Add new unit tests if applicable:
- Arguments and expected results are stored in json files in ./tests/fixtures/
- Unit tests can be added to ./tests/test_*.py and will be automatically detected
- Make sure the edits are compatible with both the Python and the command line interface
- The command line interface and arguments are defined in ./gget/main.py
- Add new modules/arguments to the documentation if applicable:
- The manual for each module can be edited/added as ./docs/src/*.md
If you have any questions, feel free to start a discussion or create an issue as described above.
Pull Request
When you're finished with the changes, create a pull request, also known as a PR.
‼️ Please make all PRs against the dev branch of the gget repository.
- Don't forget to link PR to issue if you are solving one.
- Enable the checkbox to allow maintainer edits so the branch can be updated for a merge.
- If you run into any merge issues, checkout this git tutorial to help you resolve merge conflicts and other issues.
Once you submit your PR, a gget team member will review your proposal. We may ask questions or request additional information.
Your PR is merged!
Congratulations! 🎉 The gget team thanks you. ✨
Once your PR is merged, your contributions will be publicly visible on the gget repo.
Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
Our Pledge
We as members, contributors, and leaders pledge to make participation in our community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body size, visible or invisible disability, ethnicity, sex characteristics, gender identity and expression, level of experience, education, socio-economic status, nationality, personal appearance, race, religion, or sexual identity and orientation.
We pledge to act and interact in ways that contribute to an open, welcoming, diverse, inclusive, and healthy community.
Our Standards
Examples of behavior that contributes to a positive environment for our community include:
- Demonstrating empathy and kindness toward other people
- Being respectful of differing opinions, viewpoints, and experiences
- Giving and gracefully accepting constructive feedback
- Accepting responsibility and apologizing to those affected by our mistakes, and learning from the experience
- Focusing on what is best not just for us as individuals, but for the overall community
Examples of unacceptable behavior include:
- The use of sexualized language or imagery, and sexual attention or advances of any kind
- Trolling, insulting or derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
- Public or private harassment
- Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or email address, without their explicit permission
- Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a professional setting
Enforcement Responsibilities
Community leaders are responsible for clarifying and enforcing our standards of acceptable behavior and will take appropriate and fair corrective action in response to any behavior that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive, or harmful.
Community leaders have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are not aligned to this Code of Conduct, and will communicate reasons for moderation decisions when appropriate.
Scope
This Code of Conduct applies within all community spaces, and also applies when an individual is officially representing the community in public spaces. Examples of representing our community include using an official e-mail address, posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed representative at an online or offline event.
Enforcement
Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be reported to the community leaders responsible for enforcement at lpachter@caltech.edu. All complaints will be reviewed and investigated promptly and fairly.
All community leaders are obligated to respect the privacy and security of the reporter of any incident.
Enforcement Guidelines
Community leaders will follow these Community Impact Guidelines in determining the consequences for any action they deem in violation of this Code of Conduct:
1. Correction
Community Impact: Use of inappropriate language or other behavior deemed unprofessional or unwelcome in the community.
Consequence: A private, written warning from community leaders, providing clarity around the nature of the violation and an explanation of why the behavior was inappropriate. A public apology may be requested.
2. Warning
Community Impact: A violation through a single incident or series of actions.
Consequence: A warning with consequences for continued behavior. No interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, for a specified period of time. This includes avoiding interactions in community spaces as well as external channels like social media. Violating these terms may lead to a temporary or permanent ban.
3. Temporary Ban
Community Impact: A serious violation of community standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior.
Consequence: A temporary ban from any sort of interaction or public communication with the community for a specified period of time. No public or private interaction with the people involved, including unsolicited interaction with those enforcing the Code of Conduct, is allowed during this period. Violating these terms may lead to a permanent ban.
4. Permanent Ban
Community Impact: Demonstrating a pattern of violation of community standards, including sustained inappropriate behavior, harassment of an individual, or aggression toward or disparagement of classes of individuals.
Consequence: A permanent ban from any sort of public interaction within the community.
Attribution
This Code of Conduct is adapted from the Contributor Covenant, version 2.0, available at https://www.contributor-covenant.org/version/2/0/code_of_conduct.html.
Community Impact Guidelines were inspired by Mozilla's code of conduct enforcement ladder.
For answers to common questions about this code of conduct, see the FAQ at https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq. Translations are available at https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations.
Citation
If you use gget in a publication, please cite:
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
If using
gget alphafold, please also cite:- Jumper, J., Evans, R., Pritzel, A. et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596, 583–589 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2
And, if applicable:
- Evans, R. et al. Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. bioRxiv 2021.10.04.463034; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.04.463034
-
If using
gget archs4, please also cite:-
Lachmann A, Torre D, Keenan AB, Jagodnik KM, Lee HJ, Wang L, Silverstein MC, Ma’ayan A. Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse. Nature Communications 9. Article number: 1366 (2018), doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03751-6
-
Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P and Pachter L, Near optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification, Nature Biotechnology 34, p 525--527 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3519
-
-
If using
gget bgee, please also cite:- Frederic B Bastian, Julien Roux, Anne Niknejad, Aurélie Comte, Sara S Fonseca Costa, Tarcisio Mendes de Farias, Sébastien Moretti, Gilles Parmentier, Valentine Rech de Laval, Marta Rosikiewicz, Julien Wollbrett, Amina Echchiki, Angélique Escoriza, Walid H Gharib, Mar Gonzales-Porta, Yohan Jarosz, Balazs Laurenczy, Philippe Moret, Emilie Person, Patrick Roelli, Komal Sanjeev, Mathieu Seppey, Marc Robinson-Rechavi (2021). The Bgee suite: integrated curated expression atlas and comparative transcriptomics in animals. Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D831–D847, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa793
-
If using
gget blast, please also cite:- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403-10. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. PMID: 2231712.
-
If using
gget blat, please also cite:- Kent WJ. BLAT--the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002 Apr;12(4):656-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.229202. PMID: 11932250; PMCID: PMC187518.
-
If using
gget cbio, please also cite:-
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, Antipin Y, Reva B, Goldberg AP, Sander C, Schultz N. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012 May;2(5):401-4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095. Erratum in: Cancer Discov. 2012 Oct;2(10):960. PMID: 22588877; PMCID: PMC3956037.
-
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, Cerami E, Sander C, Schultz N. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013 Apr 2;6(269):pl1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004088. PMID: 23550210; PMCID: PMC4160307.
-
de Bruijn I, Kundra R, Mastrogiacomo B, Tran TN, Sikina L, Mazor T, Li X, Ochoa A, Zhao G, Lai B, Abeshouse A, Baiceanu D, Ciftci E, Dogrusoz U, Dufilie A, Erkoc Z, Garcia Lara E, Fu Z, Gross B, Haynes C, Heath A, Higgins D, Jagannathan P, Kalletla K, Kumari P, Lindsay J, Lisman A, Leenknegt B, Lukasse P, Madela D, Madupuri R, van Nierop P, Plantalech O, Quach J, Resnick AC, Rodenburg SYA, Satravada BA, Schaeffer F, Sheridan R, Singh J, Sirohi R, Sumer SO, van Hagen S, Wang A, Wilson M, Zhang H, Zhu K, Rusk N, Brown S, Lavery JA, Panageas KS, Rudolph JE, LeNoue-Newton ML, Warner JL, Guo X, Hunter-Zinck H, Yu TV, Pilai S, Nichols C, Gardos SM, Philip J; AACR Project GENIE BPC Core Team, AACR Project GENIE Consortium; Kehl KL, Riely GJ, Schrag D, Lee J, Fiandalo MV, Sweeney SM, Pugh TJ, Sander C, Cerami E, Gao J, Schultz N. Analysis and Visualization of Longitudinal Genomic and Clinical Data from the AACR Project GENIE Biopharma Collaborative in cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 1;83(23):3861-3867. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0816. PMID: 37668528; PMCID: PMC10690089.
-
Please also cite the source of the data if you are using a publicly available dataset.
-
-
If using
gget cellxgene, please also cite:- Chanzuckerberg Initiative. (n.d.). CZ CELLxGENE Discover. Retrieved [insert date here], from https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/
-
If using
gget cosmic, please also cite:- Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, Sondka Z, Beare DM, Bindal N, Boutselakis H, Cole CG, Creatore C, Dawson E, Fish P, Harsha B, Hathaway C, Jupe SC, Kok CY, Noble K, Ponting L, Ramshaw CC, Rye CE, Speedy HE, Stefancsik R, Thompson SL, Wang S, Ward S, Campbell PJ, Forbes SA. COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 8;47(D1):D941-D947. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1015. PMID: 30371878; PMCID: PMC6323903.
-
If using
gget diamond, please also cite:- Buchfink, B., Xie, C. & Huson, D. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12, 59–60 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3176
-
If using
gget elm, please also cite:-
Laura Luebbert, Chi Hoang, Manjeet Kumar, Lior Pachter, Fast and scalable querying of eukaryotic linear motifs with gget elm, Bioinformatics, 2024, btae095, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btae095
-
Manjeet Kumar, Sushama Michael, Jesús Alvarado-Valverde, Bálint Mészáros, Hugo Sámano‐Sánchez, András Zeke, Laszlo Dobson, Tamas Lazar, Mihkel Örd, Anurag Nagpal, Nazanin Farahi, Melanie Käser, Ramya Kraleti, Norman E Davey, Rita Pancsa, Lucía B Chemes, Toby J Gibson, The Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource: 2022 release, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 50, Issue D1, 7 January 2022, Pages D497–D508, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab975
-
-
If using
gget enrichr, please also cite:-
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z, Meirelles GV, Clark NR, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013; 128(14). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-128
-
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM, Lachmann A, McDermott MG, Monteiro CD, Gundersen GW, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016; gkw377. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw377
-
Xie Z, Bailey A, Kuleshov MV, Clarke DJB., Evangelista JE, Jenkins SL, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML, Kropiwnicki E, Jagodnik KM, Jeon M, & Ma’ayan A. Gene set knowledge discovery with Enrichr. Current Protocols, 1, e90. 2021. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.90.
If working with non-human/mouse datasets, please also cite:
- Kuleshov MV, Diaz JEL, Flamholz ZN, Keenan AB, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML, Cagan RL, Ma'ayan A. modEnrichr: a suite of gene set enrichment analysis tools for model organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 2;47(W1):W183-W190. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz347. PMID: 31069376; PMCID: PMC6602483.
-
-
If using
gget info, please also cite:-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
-
Sayers EW, Beck J, Bolton EE, Brister JR, Chan J, Comeau DC, Connor R, DiCuccio M, Farrell CM, Feldgarden M, Fine AM, Funk K, Hatcher E, Hoeppner M, Kane M, Kannan S, Katz KS, Kelly C, Klimke W, Kim S, Kimchi A, Landrum M, Lathrop S, Lu Z, Malheiro A, Marchler-Bauer A, Murphy TD, Phan L, Prasad AB, Pujar S, Sawyer A, Schmieder E, Schneider VA, Schoch CL, Sharma S, Thibaud-Nissen F, Trawick BW, Venkatapathi T, Wang J, Pruitt KD, Sherry ST. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D33-D43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1044. PMID: 37994677; PMCID: PMC10767890.
-
The UniProt Consortium , UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D523–D531, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1052
-
-
If using
gget muscle, please also cite:- Edgar RC (2021), MUSCLE v5 enables improved estimates of phylogenetic tree confidence by ensemble bootstrapping, bioRxiv 2021.06.20.449169. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.20.449169
-
If using
gget opentargets, please also cite:- Ochoa D, Hercules A, Carmona M, Suveges D, Baker J, Malangone C, Lopez I, Miranda A, Cruz-Castillo C, Fumis L, Bernal-Llinares M, Tsukanov K, Cornu H, Tsirigos K, Razuvayevskaya O, Buniello A, Schwartzentruber J, Karim M, Ariano B, Martinez Osorio RE, Ferrer J, Ge X, Machlitt-Northen S, Gonzalez-Uriarte A, Saha S, Tirunagari S, Mehta C, Roldán-Romero JM, Horswell S, Young S, Ghoussaini M, Hulcoop DG, Dunham I, McDonagh EM. The next-generation Open Targets Platform: reimagined, redesigned, rebuilt. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D1353-D1359. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1046. PMID: 36399499; PMCID: PMC9825572.
-
If using
gget pdb, please also cite:- Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.235. PMID: 10592235; PMCID: PMC102472.
-
If using
gget reforgget search, please also cite:- Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
-
If using
gget seq, please also cite:-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
-
The UniProt Consortium , UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D523–D531, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1052
-
Disclaimer
gget is only as accurate as the databases/servers/APIs it queries from. The accuracy or reliability of the data is not guaranteed or warranted in any way and the providers disclaim liability of any kind whatsoever, including, without limitation, liability for quality, performance, merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose arising out of the use, or inability to use the data.
¡Bienvenidos!
gget es un programa gratuito de código fuente abierta de Terminal y Python que permite la consulta eficiente de bases de datos genómicas.
gget consiste en un conjunto de módulos separados pero interoperables, cada uno diseñado para facilitar un tipo de consulta de base de datos en una sola línea de código.
Nota: Las bases de datos consultadas por
ggetse actualizan continuamente y pueden cambiar su estructura. Los módulos deggetse prueban automáticamente dos veces por semana y se actualizan cuando es necesario. Si encuentras un problema, primero actualiza a la versión más reciente conpip install --upgrade gget. Si el problema persiste, por favor repórtalo.
¿Falta alguna base de datos o funcionalidad que te gustaría ver?
Solicitar una nueva función
Módulos gget
Estos son los módulos principales de gget. Haga clic en cualquier módulo para acceder a la documentación detallada.
| gget 8cube ¿Cuál es la expresión del gen X en 8 cepas y tejidos diferentes de ratón?. |
gget alphafold Predecir la estructura 3D de una proteína a partir de una secuencia de aminoácidos. |
gget archs4 ¿Cuál es la expresión de mi gen en el tejido X? |
| gget bgee Encontrar todos los ortólogos de un gen. |
gget blast Realizar un BLAST de una secuencia de nucleótidos o aminoácidos. |
gget blat Encontrar la ubicación genómica de una secuencia de nucleótidos o aminoácidos. |
| gget cbio Explorar la expresión de un gen en los cánceres especificados. |
gget cellxgene Obtener matrices de conteo de ARN de células individuales listas para usar para ciertos tejidos/enfermedades/etc. |
gget cosmic Buscar genes, mutaciones y otros factores asociados con ciertos cánceres. |
| gget diamond Alinear secuencias de aminoácidos a una referencia. |
gget elm Encontrar dominios y funciones de interacción de proteínas en una secuencia de aminoácidos. |
gget enrichr Verificar si una lista de genes está asociada con un tipo celular específico/ vía/ enfermedad/ etc. |
| gget info Recuperar toda la información asociada con un ID de Ensembl. |
gget muscle Alinear múltiples secuencias de nucleótidos o aminoácidos entre sí. |
gget mutate Mutar secuencias de nucleótidos según mutaciones específicas. |
| gget opentargets Explorar qué enfermedades y medicamentos están asociados con un gen. |
gget pdb Recuperar datos de la Base de Datos de Proteínas (PDB) según un ID de PDB. |
gget ref Obtener genomas de referencia de Ensembl. |
| gget search Encontrar IDs de Ensembl asociados con la palabra de búsqueda especificada. |
gget seq Recuperar la secuencia de nucleótidos o aminoácidos de un gen. |
gget virus Filtrar y obtener secuencias virales globales y metadatos extensos. |
Si usa gget en una publicación, por favor cite*:
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
Lea el artículo aquí: https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
Gracias a Victor Garcia-Ruiz y Anna Karen Orta por su ayuda con la traduccion del sitio web.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
✨ ¡Lo más reciente!
Versión ≥ 0.30.2 (08 de febrero de 2026):
gget virus: Optimización del streaming de metadatos, mejora del filtrado de proteínas y manejo de errores y lógica de reintentos mejorados- Los metadatos ahora se escriben en disco durante la descarga para evitar el agotamiento de memoria en conjuntos de datos grandes (100.000+ registros)
- Corrección del mapeo del CSV de metadatos (camelCase → snake_case) para nombre del organismo, hospedador y fecha de recolección
- Mejora del filtrado de proteínas para virus segmentados con un parseo más robusto de los encabezados FASTA
- Se añadió la opción
annotated=Falsepara filtrar secuencias no anotadas - Se añadieron barras de progreso para descargas de secuencias por lotes
- Corrección de un error en el nombre del campo de fecha de recolección
- Mejora de los mensajes de error para fechas de filtrado inválidas
- Se añadieron reintentos mejorados para la resolución de nombres de virus
- Se añadió mayor verbosidad en los pasos de verificación de influenza A y COVID-19
Versión ≥ 0.30.0 (19 de enero de 2026):
- NUEVOS MÓDULOS:
- MEJORAS DE SEGURIDAD:
- Se reemplazó
os.system()con f-strings que contienen URLs de APIs externas engget/main.py - Se reemplazó
exec()porimportlib.import_module()engget setuppara importaciones dinámicas más seguras - Se reemplazaron llamadas a subprocess con
shell=Truepor argumentos basados en listas engget muscle,gget diamondygget setuppara prevenir la inyección de comandos
- Se reemplazó
Versión ≥ 0.29.3 (11 de septiembre de 2025):
gget blat: Actualiza la solicitud a la API para los nuevos permisos.gget pdb: Agregado el sitio web dewwpdb, retrocede arcsbsi las solicitudes fallan.gget cellxgene: Mejora el manejo de argumentos; el frontend no cambia.gget setup/gget alphafold: Corrige el error pip_cmd engget.setup("alphafold").
Versión ≥ 0.29.2 (03 de julio de 2025):
- Ahora se puede instalar
ggetusandouv pip install gget- Toda la metadata del paquete (versión, autor, descripción, etc.) ahora se gestiona en
setup.cfgpara una compatibilidad total con herramientas modernas comouv,pipy PyPI ggetahora utiliza unsetup.pymínimo y es completamente compatible con PEP 517/518
- Toda la metadata del paquete (versión, autor, descripción, etc.) ahora se gestiona en
gget setupintentará usar primerouv pip installpor su velocidad y resolución moderna de dependencias, y recurrirá apip installsiuvfalla o no está disponible- Se informa a los usuarios en cada paso qué instalador se está utilizando y si se realiza un reintento
- Nota: Algunas dependencias científicas (por ejemplo,
cellxgene-census) pueden no ser compatibles todavía con Python 3.12. Si encuentras errores de instalación, prueba usar Python 3.9 o 3.10. (La instalación conpiptambién podría funcionar en estos casos.)
- Todas las dependencias requeridas ahora están listadas en
setup.cfgbajoinstall_requires→ Instalar gget conpip install .ouv pip install .instalará automáticamente todas las dependencias
Versión ≥ 0.29.1 (21 de abril de 2025):
gget mutate:- gget mutate se ha simplificado para enfocarse en recibir como entrada una lista de mutaciones y el genoma de referencia correspondiente con información de anotación asociada, y producir como salida las secuencias con la mutación incorporada y una región corta de contexto circundante. Para la funcionalidad completa de la versión anterior y cómo se integra en el contexto de un pipeline de análisis de variantes novedosas, visita el repositorio varseek que está siendo desarrollado por miembros del equipo de gget en https://github.com/pachterlab/varseek.git.
- Se añadió información adicional a los data frames retornados, como se describe aquí: https://github.com/pachterlab/gget/pull/169
gget cosmic:- Reestructuración importante del módulo
gget cosmicpara cumplir con los nuevos requisitos de inicio de sesión establecidos por COSMIC - Se añadieron nuevos argumentos
emailypasswordpara permitir que el usuario introduzca manualmente sus credenciales sin necesidad de input adicional para la descarga de datos - Cambio por defecto:
gget_mutate=False - Argumento en desuso:
entity - Argumento
mutation_classahora escosmic_project
- Reestructuración importante del módulo
gget bgee:type="orthologs"ahora es el valor por defecto, eliminando la necesidad de especificar el argumentotypeal consultar ortólogos- Se permite la consulta de múltiples genes a la vez.
gget diamond:- Ahora soporta alineamiento traducido de secuencias nucleotídicas contra secuencias de referencia de aminoácidos usando la opción
--translated.
- Ahora soporta alineamiento traducido de secuencias nucleotídicas contra secuencias de referencia de aminoácidos usando la opción
gget elm:- Mejorado el manejo de errores del servidor.
Versión ≥ 0.29.0 (25 de septiembre de 2024):
- Nuevos módulos:
gget enrichrahora también soporta especies además de humano y ratón (mosca, levadura, gusano y pez) a través de modEnrichRgget mutate:
gget mutateahora fusionará secuencias idénticas en el archivo final por defecto. La creación de mutaciones fue vectorizada para disminuir el tiempo de ejecución. Se mejoró la verificación de la secuencia flanqueante para mutaciones no sustitutivas para asegurarse de que no se retenga ningún kmer silvestre en la secuencia que contiene la mutación. Se agregó varios nuevos argumentos para personalizar la generación de secuencias y la salida.gget cosmic:
Se agregó soporte para pantallas de genes así como dirigidas. El archivo CSV creado para gget mutate ahora también contiene información sobre mutaciones de proteínas.gget ref:
Se agregó opción de archivo de salida.gget infoygget seq:
Se cambió a la API POST de Ensembl para aumentar la velocidad (nada cambia en el front end).- Otros cambios "detrás de escena":
- Pruebas unitarias reorganizadas para aumentar la velocidad y disminuir el código
- Requisitos actualizados para permitir versiones más nuevas de mysql-connector
- Soporte para Numpy>= 2.0
Versión ≥ 0.28.6 (2 de junio de 2024):
- Nuevo módulo:
gget mutate gget cosmic: Ahora puedes descargar bases de datos completas de COSMIC utilizando el argumentodownload_cosmicgget ref: Ahora puede obtener la ensambladura del genoma GRCh27 usandospecies='human_grch37'gget search: Ajusta el acceso a los datos humanos a la estructura de la versión 112 de Ensembl (corrige issue 129)
Version ≥ 0.28.5 (May 29, 2024):
- Retirado debido a un error con 'logging' en
gget.setup("alphafold")+ mutaciones de inversión engget mutatesolo invierten la cadena en lugar de también calcular la hebra complementaria
Versión ≥ 0.28.4 (31 de enero de 2024):
gget setup: soluciona el error con la ruta del archivo al ejecutargget.setup("elm")en el sistema operativo Windows.
Versión ≥ 0.28.3 (22 de enero de 2024):
gget searchygget refahora también admiten hongos 🍄, protistas 🌝 y metazoos de invertebrados 🐝 🐜 🐌 🐙 (además de vertebrados y plantas)- Nuevo módulo:
gget cosmic gget enrichr: corrige puntos de dispersión duplicados en el gráfico cuando los nombres de las rutas están duplicadosgget elm:- Se cambió el nombre de la columna de resultados orto 'Ortholog_UniProt_ID' a 'Ortholog_UniProt_Acc' para reflejar correctamente el contenido de la columna, que son accesos de UniProt. 'UniProt ID' se cambió a 'UniProt Acc' en la documentación para todos los módulos
gget. - Se cambió el nombre de la columna de resultados ortogonales 'motif_in_query' a 'motif_inside_subject_query_overlap'.
- Se agregó información del dominio de interacción a los resultados (nuevas columnas: "InteractionDomainId", "InteractionDomainDescription", "InteractionDomainName").
- La cadena de expresiones regulares para coincidencias de expresiones regulares se encapsuló de la siguiente manera: "(?=(regex))" (en lugar de pasar directamente la cadena de expresiones regulares "regex") para permitir capturar todas las apariciones de un motivo cuando la longitud del motivo es variable y hay son repeticiones en la secuencia (https://regex101.com/r/HUWLlZ/1).
- Se cambió el nombre de la columna de resultados orto 'Ortholog_UniProt_ID' a 'Ortholog_UniProt_Acc' para reflejar correctamente el contenido de la columna, que son accesos de UniProt. 'UniProt ID' se cambió a 'UniProt Acc' en la documentación para todos los módulos
gget setup: utilice el argumentooutpara especificar un directorio en el que se descargará la base de datos ELM. Completa esta solicitud de función.gget Diamond: El comando DIAMOND ahora se ejecuta con el indicador--ignore-warnings, lo que permite secuencias de nicho, como secuencias de aminoácidos que solo contienen caracteres de nucleótidos y secuencias repetidas. Esto también es válido para las alineaciones DIAMOND realizadas dentro degget elm.- Cambio de back-end de
gget refygget search: la versión actual de Ensembl se obtiene del nuevo archivo de versión en el sitio FTP de Ensembl para evitar errores durante la carga de nuevos lanzamientos. gget search:- Los resultados del enlace FTP (
--ftp) se guardan en formato de archivo txt en lugar de json. - Se corrigieron enlaces URL al resumen de genes de Ensembl para especies con un nombre de subespecie e invertebrados.
- Los resultados del enlace FTP (
gget ref:- Cambios de back-end para aumentar la velocidad.
- Nuevo argumento:
list_iv_speciespara enumerar todas las especies de invertebrados disponibles (se puede combinar con el argumentoreleasepara obtener todas las especies disponibles de una liberación específica de Ensembl)
Versión ≥ 0.28.2 (15 de noviembre de 2023):
gget info: devuelve un mensaje de error cuando el servidor NCBI falla por un motivo distinto a un error de recuperación (esto es un error en el lado del servidor en lugar de un error congget)- Reemplace el argumento obsoleto 'texto' para los métodos de tipo find() siempre que se usen con la dependencia
BeautifulSoup gget elm: Elimina instancias de falsos positivos y verdaderos negativos de los resultados devueltos.gget elm: agrega el argumentoexpand
Versión ≥ 0.28.0 (5 de noviembre de 2023):
- Documentación actualizada de
gget musclepara agregar un tutorial sobre cómo visualizar secuencias con diferentes longitudes de nombres de secuencia + ligero cambio en la visualización devuelta para que sea un poco más sólida ante diferentes nombres de secuencia gget muscleahora también permite una lista de secuencias como entrada (como alternativa a proporcionar la ruta a un archivo FASTA)- Permitir filtro de genes faltante para
gget cellxgene(corrige error) gget seq: permite nombres de genes faltantes (correccione [https://github.com/pachterlab/gget/issues/107](https://github.com/pachterlab/gget /números/107))- Nuevos argumentos para
gget enrichr: use el argumentokegg_outykegg_rankpara crear una imagen de la vía KEGG con los genes del análisis de enriquecimiento resaltados (gracias a [este PR](https ://github.com/pachterlab/gget/pull/106) por Noriaki Sato) - Nuevos módulos:
gget elmygget Diamond
Versión ≥ 0.27.9 (7 de agosto de 2023):
- Nuevos argumentos para
gget enrichr: use el argumentobackground_listpara proporcionar una lista de genes 'background' gget searchahora también busca sinónimos Ensembl (además de nombres y descripciones de genes) para obtener resultados de búsqueda más completos (gracias a Samuel Klein por la sugerencia)
Versión ≥ 0.27.8 (12 de julio de 2023):
- Nuevo argumento para
gget search: especifique la versión de Ensembl desde la cual se obtiene la información con-r--release - Se corrigió un error en
gget pdb(este error se introdujo en la versión 0.27.5)
Versión ≥ 0.27.7 (15 de mayo de 2023):
- Se movieron las dependencias para los módulos
gget gptygget cellxgenede los requisitos instalados automáticamente agget setup - Dependencias
gget alphafoldactualizadas para compatibilidad con Python >= 3.10 - Se agregó el argumento
census_versionagget cellxgene
Versión ≥ 0.27.6 (1 de mayo de 2023) (TIRO debido a problemas con las dependencias -> reemplazada por la versión 0.27.7):
- Gracias a el PR de Tomás Di Domenico:
gget searchahora también puede consultar los ID de plantas 🌱 Ensembl - Nuevo módulo:
gget cellxgene
Versión ≥ 0.27.5 (6 de abril de 2023):
- Se actualizó
gget searchpara que funcione correctamente con la nueva versión de Pandas 2.0.0 (lanzado el 3 de abril de 2023), además de versiones anteriores de Pandas - Se actualizó
gget infocon nuevos banderasuniprotyncbique permiten desactivar los resultados de estas bases de datos de forma independiente para ahorrar tiempo de ejecución (nota: el indicadorensembl_onlyquedó obsoleto) - Todos los módulos gget ahora tienen una bandera
-q / --quiet(para Python:verbose=False) para desactivar la información de progreso
Versión ≥ 0.27.4 (19 de marzo de 2023):
- Nuevo módulo:
gget gpt
Versión ≥ 0.27.3 (11 de marzo de 2023):
gget infoexcluye los ID de PDB de forma predeterminada para aumentar la velocidad (los resultados de PDB se pueden incluir usando la marca--pdb/pdb=True).
Versión ≥ 0.27.2 (1 de enero de 2023):
- Se actualizó
gget alphafolda DeepMind's AlphaFold v2.3.0 (incluidos los nuevos argumentosmultimer_for_monomerymultimer_recycles)
Versión ≥ 0.27.0 (10 de diciembre de 2022):
- Se actualizó
gget alphafoldpara que coincida con los cambios recientes de DeepMind - Número de versión actualizado para que coincida con la edad de el creador de gget siguiendo una larga tradición de laboratorio de Pachter
Versión ≥ 0.3.13 (11 de noviembre de 2022):
- Tiempo de ejecución reducido para
gget enrichrygget archs4cuando se usa con ID de Ensembl
Versión ≥ 0.3.12 (10 de noviembre de 2022):
gget infoahora también devuelve datos de localización subcelular de UniProt- El nuevo indicador
gget infoensembl_onlydevuelve solo los resultados de Ensembl - Tiempo de ejecución reducido para
gget infoygget seq
Versión ≥ 0.3.11 (7 de septiembre de 2022):
- Nuevo módulo:
gget pdb
Versión ≥ 0.3.10 (2 de septiembre de 2022):
gget alphafoldahora también devuelve valores pLDDT para generar gráficos sin volver a ejecutar el programa (consulte también las preguntas frecuentes de gget alphafold)
Versión ≥ 0.3.9 (25 de agosto de 2022):
- Instrucciones de instalación de openmm actualizadas para
gget alphafold
Versión ≥ 0.3.8 (12 de agosto de 2022):
- Se corrigieron los requisitos de versión de mysql-connector-python
Versión ≥ 0.3.7 (9 de agosto de 2022):
- NOTA: El sitio FTP de Ensembl cambió su estructura el 8 de agosto de 2022. Actualice a la versión
gget≥ 0.3.7 si usaobtener ref
Versión ≥ 0.3.5 (6 de agosto de 2022):
- Nuevo módulo:
gget alphafold
Versión ≥ 0.2.6 (7 de julio de 2022):
- ¡
gget refahora admite genomas de plantas! 🌱
Versión ≥ 0.2.5 (30 de junio de 2022):
- NOTA: UniProt cambió la estructura de su API el 28 de junio de 2022. Actualice a la versión
gget≥ 0.2.5 si usa alguno de los módulos que consultan datos de UniProt (gget infoygget seq).
Versión ≥ 0.2.3: (26 de junio de 2022):
- JSON ahora es el formato de regreso predeterminado para la Terminal para los módulos que anteriormente devolvían el formato de data frame (CSV) (el formato se puede convertir a data frame/CSV usando la bandera
[-csv][--csv]). El formato data frame/CSV sigue siendo el formato de regreso predeterminada para Python (Jupyter Lab/Google Colab) (y se puede convertir a JSON conjson=True). - Para todos los módulos, el primer parámetro requerido se convirtió en un parámetro posicional y ya no debe nombrarse en la línea de comandos, p. ej.
gget ref -s human→gget ref human. gget info:[--expand]está en desuso. El módulo ahora siempre devolverá toda la información disponible.- Ligeros cambios en la salida devuelta por
gget info, incluida la devolución de los ID de Ensembl versionados. gget infoygget seqahora son compatibles con las IDs de WormBase y FlyBase.- Ahora también se pueden ingresar IDs de tipo Ensembl a
gget archs4ygget enrichrcon la bandera[-e][--ensembl](ensembl=Truepara Python (Jupyter Lab / Google Colab)). - El parámetro
seqtypedegget seqfue reemplazado por la bandera[-t][--translate](translate=True/Falsepara Python (Jupyter Lab / Google Colab)) que devolverá secuencias de nucleótidos (False) o aminoácidos (True). - El parámetro
seqtypedegget searchse renombró aid_type(aún tomando los mismos parámetros 'gene' o 'transcript').
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
💡 Usuarios activos de este sitio web
Este mapa se actualiza automáticamente todos los días a las 16:00 UTC.
⬇️ Descargas diarias de gget
Este mapa se actualiza automáticamente todos los domingos a las 23:55 UTC.
🧑🤝🧑 Programas dependientes
Las siguientes aplicaciones usan gget:
- gget-mcp
- Otras proyectos que utilizan este u otros servidores MCP de
gget:
- Otras proyectos que utilizan este u otros servidores MCP de
- Biomni
Un agente de inteligencia artificial biomédica de propósito general que se está desarrollando en Stanford y Genentech. - PerTurboAgent
Un agente de auto-planificación para potenciar experimentos secuenciales de Perturb-seq. - Habilidades científicas para Claude, desarrolladas por K-Dense-AI
- Therapeutics Data Commons (TDC)
Base de inteligencia artificial para la ciencia terapéutica (código fuente, artículo en Nat Chem Bio) del laboratorio de Inteligencia Artificial para Medicina y Ciencia de Harvard. - BioDiscoveryAgent
BioDiscoveryAgent es un agente de IA basado en modelos de lenguaje para el diseño en bucle cerrado de experimentos de perturbación genética (preprint) del Proyecto de Análisis de Redes de Stanford. - DeepChopper
Modelos de lenguaje para identificar lecturas artificiales quiméricas en datos de secuenciación directa de ARN de NanoPore por el laboratorio de Yang en Northwestern. - BRAD
Un chatbot impulsado por un modelo de lenguaje para bioinformática (documentación, página principal del proyecto). - scPRINT
scPRINT es un modelo transformer grande diseñado para inferir redes génicas (conexiones entre genes que explican el perfil de expresión de la célula) a partir de datos de scRNAseq (preprint). - AnoPrimer
AnoPrimer es un paquete de Python para el diseño de cebadores en An. gambiae y An. funestus, teniendo en cuenta la variación genética en especímenes de genomas completos secuenciados de la naturaleza en datos de malariagen. - AvaTaR
Optimización de Agentes de LLM para Recuperación de Conocimiento Asistida por Herramientas (NeurIPS 2024) por el laboratorio de James Zou en la Universidad de Stanford. - GRLDrugProp
Aprendizaje de representación de grafos para modelar propiedades de fármacos. - MicrobioLink2
Analiza el impacto de la interacción huésped-microbio en la señalización posterior en células y tejidos humanos. - Implementación en Rust de gget: https://github.com/noamteyssier/ggetrs
- https://github.com/Superbio-ai/getbio
- https://github.com/yonniejon/AchillesPrediction
- https://github.com/ELELAB/cancermuts
- https://github.com/Benoitdw/SNPrimer
- https://github.com/louisjoecodes/a16z-hackathon-project
- https://github.com/EvX57/BACE1-Drug-Discovery
- https://github.com/vecerkovakaterina/hidden-genes-msc
- https://github.com/vecerkovakaterina/llm_bioinfo_agent
- https://github.com/greedjar74/upstage_AI_Lab
- https://github.com/alphavector/all
Ver también: https://github.com/pachterlab/gget/network/dependents
📃 Publicaciones selectas
- David Bradley et al., The fitness cost of spurious phosphorylation. The EMBO Journal (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s44318-024-00200-7
- Mikael Nilsson et al., Resolving thyroid lineage cell trajectories merging into a dual endocrine gland in mammals. Nature Portfolio (en revisión) (2024). DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-5278325/v1
- Avasthi P et al., Repeat expansions associated with human disease are present in diverse organisms. Arcadia (2024). DOI: 10.57844/arcadia-e367-8b55
- Ibrahim Al Rayyes et al., Single-Cell Transcriptomics Reveals the Molecular Logic Underlying Ca2+ Signaling Diversity in Human and Mouse Brain. bioRxiv (2024). DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.26.591400
- David R. Blair & Neil Risch. Dissecting the Reduced Penetrance of Putative Loss-of-Function Variants in Population-Scale Biobanks. medRxiv (2024). DOI: 10.1101/2024.09.23.24314008
- Shanmugampillai Jeyarajaguru Kabilan et al., Molecular modelling approaches for the identification of potent Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 inhibitors from Boerhavia diffusa for the potential treatment of chronic kidney disease. Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design (en revisión) (2024). DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4520611/v1
- Joseph M Rich et al., The impact of package selection and versioning on single-cell RNA-seq analysis. bioRxiv (2024). DOI: 10.1101/2024.04.04.588111
- Sanjay C. Nagi et al., AnoPrimer: Primer Design in malaria vectors informed by range-wide genomic variation. Wellcome Open Research (2024).
- Yasmin Makki Mohialden et al., A survey of the most recent Python packages for use in biology. NeuroQuantology (2023). DOI: 10.48047/NQ.2023.21.2.NQ23029
- Kimberly Siletti et al., Transcriptomic diversity of cell types across the adult human brain. Science (2023). DOI: 10.1126/science.add7046
- Beatriz Beamud et al., Genetic determinants of host tropism in Klebsiella phages. Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112048
- Nicola A. Kearns et al., Generation and molecular characterization of human pluripotent stem cell-derived pharyngeal foregut endoderm. Cell Reports (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2023.08.024
- Jonathan Rosenski et al., Predicting gene knockout effects from expression data. BMC Medical Genomics (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s12920-023-01446-6
- Peter Overby et al., Pharmacological or genetic inhibition of Scn9a protects beta-cells while reducing insulin secretion in type 1 diabetes. bioRxiv (2023). DOI: 10.1101/2023.06.11.544521
- Mingze Dong et al., Deep identifiable modeling of single-cell atlases enables zero-shot query of cellular states. bioRxiv (2023). DOI: 10.1101/2023.11.11.566161
📰 Noticias
- Oreate AI publicación de blog: "Exploring AlphaFold2: A Guide to GitHub Repositories and Colab Resources"
gget opentargetspublicación de la plataforma Open Targets- Documental corto sobre gget: https://youtu.be/cVR0k6Mt97o
- Episodio de podcast para el Prototype Fund Public Interest Podcast sobre la importancia del software de código abierto y su papel en la investigación académica (en alemán): https://public-interest-podcast.podigee.io/33-pips4e4
- Anuncio del Prototype Fund: https://prototypefund.de/project/gget-genomische-datenbanken
🚂 Tráfico del repositorio de gget

Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Instalación
Puedes usar uv o pip para instalar gget:
uv pip install gget
or
pip install --upgrade gget
Recomendado: Instalar en un entorno limpio
Recomendamos usar un entorno virtual para una instalación limpia y sin conflictos. Puedes usar uv, venv, or conda:
Con uv:
pip install uv # if you don't have uv yet
uv venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
uv pip install gget
Con pip y venv:
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate
pip install --upgrade gget
Con conda:
conda create -n gget-env python=3.11
conda activate gget-env
pip install --upgrade gget
Para uso en Jupyter Lab / Google Colab:
import gget
Instalar desde el código fuente
git clone https://github.com/pachterlab/gget.git
cd gget
uv pip install .
or
git clone https://github.com/pachterlab/gget.git
cd gget
pip install .
Solución de problemas
- Si ves errores sobre dependencias faltantes, asegúrate de estar usando un entorno limpio y tener la última versión de
pipouv. - Si instalaste gget previamente de forma global, desinstálalo con:
o elimina el ejecutable de tupip uninstall ggetPATHdel sistema. - Si sigues teniendo problemas, por favor contáctanos.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
🪄 Guía de inicio rápido
Terminal:
# Obtenga todos los FTP de anotaciones y referencias de Homo sapiens de la última versión de Ensembl
$ gget ref homo_sapiens
# Obtenga IDs de Ensembl de genes humanos con "ace2" o "angiotensin converting enzyme 2" en su nombre/descripción
$ gget search -s homo_sapiens 'ace2' 'angiotensin converting enzyme 2'
# Busque el gen ENSG00000130234 (ACE2) y su transcripción ENST00000252519
$ gget info ENSG00000130234 ENST00000252519
# Obtenga la secuencia de aminoácidos de la transcripción canónica del gen ENSG00000130234
$ gget seq --translate ENSG00000130234
# Rápidamente encuentra la ubicación genómica de la secuencia de aminoácidos
$ gget blat MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# BLAST la secuencia de aminoácidos
$ gget blast MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# Alinee múltiples secuencias de nucleótidos o aminoácidos entre sí (también acepta la ruta al archivo FASTA)
$ gget muscle MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS
# Alinee una o más secuencias de aminoácidos con una referencia (que contiene una o más secuencias) (BLAST local) (también acepta rutas a archivos FASTA)
$ gget diamond MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS -ref MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS
# Alinea secuencias de nucleótidos o aminoácidos en un archivo FASTA
$ gget muscle path/to/file.fa
# Use Enrichr para un análisis de ontología de una lista de genes
$ gget enrichr -db ontology ACE2 AGT AGTR1 ACE AGTRAP AGTR2 ACE3P
# Obtene la expresión en tejido humano del gen ACE2
$ gget archs4 -w tissue ACE2
# Obtenga la estructura de la proteína (en formato PDB) de ACE2 (ID de PDB devuelta por gget info)
$ gget pdb 1R42 -o 1R42.pdb
# Descargar conjuntos de datos del genoma de virus de NCBI Virus (por ejemplo, secuencias del virus del Zika).
$ gget virus "Zika virus" --host "Homo sapiens" --nuc_completeness complete
# Encuentre motivos lineales eucarióticos (ELM) en una secuencia de aminoácidos
$ gget setup elm # solo debe ejecutarse una vez
$ gget elm -o results MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS
# Obtene una matriz de recuento de scRNAseq (formato AnnData) basada en genes, tejidos y tipos de células especificados (especie predeterminada: humano)
$ gget setup cellxgene # solo debe ejecutarse una vez
$ gget cellxgene --gene ACE2 SLC5A1 --tissue lung --cell_type 'mucus secreting cell' -o example_adata.h5ad
# Predice la estructura proteica de GFP a partir de su secuencia de aminoácidos
$ gget setup alphafold # solo debe ejecutarse una vez
$ gget alphafold MSKGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVSGEGEGDATYGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFSRYPDHMKQHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTIFFKDDGNYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNYNSHNVYIMADKQKNGIKVNFKIRHNIEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSALSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHGMDELYK
Python (Jupyter Lab / Google Colab):
import gget
gget.ref("homo_sapiens")
gget.search(["ace2", "angiotensin converting enzyme 2"], "homo_sapiens")
gget.info(["ENSG00000130234", "ENST00000252519"])
gget.seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=True)
gget.blat("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.blast("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.muscle(["MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", "MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS"])
gget.diamond("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", reference="MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS")
gget.enrichr(["ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1", "ACE", "AGTRAP", "AGTR2", "ACE3P"], database="ontology", plot=True)
gget.archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
gget.pdb("1R42", save=True)
gget.virus("Zika virus", host="Homo sapiens", nuc_completeness="complete")
gget.setup("elm") # solo debe ejecutarse una vez
ortho_df, regex_df = gget.elm("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget.setup("cellxgene") # solo debe ejecutarse una vez
gget.cellxgene(gene = ["ACE2", "SLC5A1"], tissue = "lung", cell_type = "mucus secreting cell")
gget.setup("alphafold") # solo debe ejecutarse una vez
gget.alphafold("MSKGEELFTGVVPILVELDGDVNGHKFSVSGEGEGDATYGKLTLKFICTTGKLPVPWPTLVTTFSYGVQCFSRYPDHMKQHDFFKSAMPEGYVQERTIFFKDDGNYKTRAEVKFEGDTLVNRIELKGIDFKEDGNILGHKLEYNYNSHNVYIMADKQKNGIKVNFKIRHNIEDGSVQLADHYQQNTPIGDGPVLLPDNHYLSTQSALSKDPNEKRDHMVLLEFVTAAGITHGMDELYK")
Use a gget con R usando reticulate:
system("pip install gget")
install.packages("reticulate")
library(reticulate)
gget <- import("gget")
gget$ref("homo_sapiens")
gget$search(list("ace2", "angiotensin converting enzyme 2"), "homo_sapiens")
gget$info(list("ENSG00000130234", "ENST00000252519"))
gget$seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=TRUE)
gget$blat("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget$blast("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS")
gget$muscle(list("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", "MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS"), out="out.afa")
gget$diamond("MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", reference="MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS")
gget$enrichr(list("ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1", "ACE", "AGTRAP", "AGTR2", "ACE3P"), database="ontology")
gget$archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
gget$pdb("1R42", save=TRUE)
gget$virus("Zika virus", host="Homo sapiens", nuc_completeness="complete")
Más ejemplos
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget 8cube 🔬
Consulta 8cubeDB (datos de secuenciación de snRNA de 8 cepas, tejidos e individuos diferentes de ratón (cuatro de cada sexo)) para métricas de especificidad a nivel génico y valores de expresión normalizados.
Formato de salida: JSON (línea de comandos) o data frame/CSV (Python).
Este módulo fue escrito por Nikhila Swarna.
gget 8cube specificity 🎯
Recupera estadísticas de especificidad ψ y ζ para uno o más genes.
gget 8cube specificity <GENES...>
Argumento posicional
genes
Símbolos génicos o IDs de genes Ensembl. Se permiten múltiples genes.
Argumentos opcionales
-csv --csv
Devuelve CSV en lugar de JSON (solo línea de comandos).
Python: usar json=False (DataFrame por defecto) o json=True para JSON.
-o --out
Ruta del archivo de salida (CSV o .json según --csv).
Python: save=True guarda automáticamente en el directorio actual.
Banderas
-q --quiet
Suprime la información de progreso.
Python: usar verbose=False.
Ejemplo
gget 8cube specificity Acsm2 ENSMUSG00000046623.9
# Python
from gget.gget_8cube import specificity
specificity(["Acsm2", "ENSMUSG00000046623.9"])
→ Devuelve los valores de especificidad ψ y ζ para Acsm2.
gget 8cube psi_block 🧩
Recupera valores de ψ-block (especificidad a nivel de bloque) para uno o más genes.
gget 8cube psi_block <GENES...> --analysis_level <LEVEL> --analysis_type <TYPE>
Argumento posicional
genes
Símbolos génicos o IDs Ensembl.
Argumentos requeridos
-al --analysis_level
Nivel de análisis biológico (p. ej., Kidney, Across_tissues).
-at --analysis_type
Tipo de partición (p. ej., Sex:Celltype, Sex:Strain).
Argumentos opcionales
-csv --csv
Devuelve CSV en lugar de JSON.
Python: usar json=True para JSON.
-o --out
Ubicación del archivo de salida.
Banderas
-q --quiet
Suprime la impresión del progreso.
Ejemplo
gget 8cube psi_block Acsm2 \
--analysis_level Kidney \
--analysis_type "Sex:Celltype"
# Python
from gget.gget_8cube import psi_block
psi_block(["Acsm2"], analysis_level="Kidney", analysis_type="Sex:Celltype")
→ Devuelve puntuaciones de especificidad ψ-block a nivel de partición para Acsm2.
gget 8cube expression 📊
Recupera la media y varianza de los valores de expresión normalizados para uno o más genes.
gget 8cube expression <GENES...> --analysis_level <LEVEL> --analysis_type <TYPE>
Argumento posicional
genes
Símbolos génicos o IDs Ensembl. Se aceptan múltiples.
Argumentos requeridos
-al --analysis_level
Agrupación biológica (p. ej., Kidney, Across_tissues).
-at --analysis_type
Diseño de partición (p. ej., Sex:Celltype).
Argumentos opcionales
-csv --csv
Devuelve CSV en lugar de JSON.
Python: usar json=True.
-o --out
Ruta del archivo de salida.
Banderas
-q --quiet
Suprime los mensajes de progreso.
Ejemplo
gget 8cube expression ENSMUSG00000046623.9 \
--analysis_level Across_tissues \
--analysis_type Strain
# Python
from gget.gget_8cube import gene_expression
gene_expression(["ENSMUSG00000046623.9"], analysis_level="Across_tissues", analysis_type="Strain")
→ Devuelve valores de expresión normalizados agrupados por tipo celular y sexo.
Ejemplo de flujo de trabajo
# Especificidad
gget 8cube specificity Gjb4
# Especificidad ψ-block
gget 8cube psi_block Gjb4 --analysis_level Across_tissues --analysis_type Strain
# Valores de expresión
gget 8cube expression Gjb4 --analysis_level Across_tissues --analysis_type Strain
API de Python
from gget.gget_8cube import specificity, psi_block, gene_expression
o
from gget import specificity, psi_block, gene_expression
Notas
- Funciona con símbolos génicos y IDs Ensembl (con o sin números de versión).
- Las tres funciones aceptan múltiples genes a la vez.
- La salida por defecto en Python es un DataFrame de pandas; use
json=Truepara JSON. - La CLI usa JSON por defecto, a menos que se utilice
--csv.
Citar
Si utiliza gget 8cube en una publicación, por favor cite:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Rebboah E, et al. Systematic cell-type resolved transcriptomes of 8 tissues in 8 lab and wild-derived mouse strains captures global and local expression variation (2025). https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.04.21.649844
-
Swarna NP, et al. Determining gene specificity from multivariate single-cell RNA sequencing data (2025). DOI próximamente.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget alphafold 🪢
Predice la estructura en 3D de cualquier proteína derivada de su secuencia de aminoácidos usando una versión simplificada del algoritmo AlphaFold2 de DeepMind, originalmente producido y publicado para AlphaFold Colab.
Resultado: Predicción de la estructura (en formato PDB) y el errór de alineación (en formato json).
Antes de usar gget alphafold por primera vez:
-
Instale openmm ejecutando el siguiente comando desde la línea de comando:
Para Python versiones < 3.10:
conda install -qy conda==4.13.0 && conda install -qy -c conda-forge openmm=7.5.1
Para Python versión 3.10:
conda install -qy conda==24.1.2 && conda install -qy -c conda-forge openmm=7.7.0
Para Python versión 3.11:
conda install -qy conda==24.11.1 && conda install -qy -c conda-forge openmm=8.0.0Recomendación: siga con
conda update -qy condapara actualizar conda a la última versión. -
Corre
gget setup alphafold/gget.setup("alphafold")(ver tambiéngget setup). Al ejecutargget setup alphafold/gget.setup("alphafold")se descargará e instalará la última versión de AlphaFold2 alojada en el AlphaFold GitHub Repo. Puede volver a ejecutar este comando en cualquier momento para actualizar el software cuando hay una nueva versión de AlphaFold.
Parámetro posicional
sequence
Secuencia de aminoácidos (str), o una lista de secuencias (gget alphafold automaticamente usa el algoritmo del multímero si múltiples secuencias son ingresadas), o una ruta a un archivo formato FASTA.
Parámetros optionales
-mr --multimer_recycles
El algoritmo de multímero se reciclara hasta que las predicciones dejen de cambiar, el limite de ciclos esta indicado aqui. Por defecto: 3
Para obtener más exactitud, ajusta este limite a 20 (al costo de ejecuciones mas tardadas).
-o --out
Ruta a la carpeta para guardar los resultados de la predicción (str). Por defecto: "./[fecha_tiempo]_gget_alphafold_prediction".
Banderas
-mfm --multimer_for_monomer
Usa el algoritmo de multímero para un monómero.
-r --relax
Relaja el mejor modelo con el algoritmo AMBER.
-q --quiet
Uso limitado para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False.
plot
Solo para Python. plot=True provée una visualización interactiva de la predicción con el errór de alineación en 3D con py3Dmol y matplotlib (por defecto: True).
show_sidechains
Solo para Python. show_sidechains=True incluye las cadenas laterales de proteínas en el esquema (por defecto: True).
Ejemplo
# Predice la estructura de una proteína derivada de su secuencia de aminoácidos
gget alphafold MAAHKGAEHHHKAAEHHEQAAKHHHAAAEHHEKGEHEQAAHHADTAYAHHKHAEEHAAQAAKHDAEHHAPKPH
# Encuentra secuencias similares previamente depositadas en el PDB para análisis comparativo
gget blast --database pdbaa MAAHKGAEHHHKAAEHHEQAAKHHHAAAEHHEKGEHEQAAHHADTAYAHHKHAEEHAAQAAKHDAEHHAPKPH
# Busca los archivos PDB de estructuras similares resultantes de gget blast para comparar y obtener una medida de calidad del modelo predecido.
gget pdb 3UQ3 -o 3UQ3.pdb
gget pdb 2K42 -o 2K42.pdb
# Python
# Predice la estructura de una proteína derivada de su secuencia de aminoácidos
gget.alphafold("MAAHKGAEHHHKAAEHHEQAAKHHHAAAEHHEKGEHEQAAHHADTAYAHHKHAEEHAAQAAKHDAEHHAPKPH")
# Encuentra secuencias similares previamente depositadas en el PDB para análisis comparativo
gget.blast("MAAHKGAEHHHKAAEHHEQAAKHHHAAAEHHEKGEHEQAAHHADTAYAHHKHAEEHAAQAAKHDAEHHAPKPH", database="pdbaa")
# Busca los archivos PDB de estructuras similares resultantes de gget blast para comparar y obtener una medida de calidad del modelo predecido.
gget.pdb("3UQ3", save=True)
gget.pdb("2K42", save=True)
→ gget alphafold produce la estructura predecida (en formato PDB) y el errór de alineación (en formato json) en una nueva carpeta ("./[fecha_tiempo]_gget_alphafold_prediction"). Este ejemplo demuestra como usar gget blast y gget pdb para correr un análisis comparativo. Los archivos PDB se pueden ver en 3D con RCSB 3D view, o usando programas como PyMOL o Blender. Para comparar múltiples archivos PDB, use RCSB alignment. Python también produce esquemas interactivos, los cuales se pueden generar de los archivos PDB y JSON, como es describido en gget alphafold FAQ Q4.
Tutoriales
🔗 Google Colab tutorial
🔗 Predicción de la estructura de proteínas con comparación con estructuras cristalinas relacionadas
🔗 gget alphafold - preguntas más frecuentes
Citar
Si utiliza gget alphafold en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Jumper, J., Evans, R., Pritzel, A. et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596, 583–589 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2
Y, si corresponde:
- Evans, R. et al. Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. bioRxiv 2021.10.04.463034; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.04.463034
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no es especificado de otra manera. Las banderas son designadas como cierto o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede obtener desde Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget archs4 🐁
Encuentra los genes más correlacionados a un gen de interés, o bién, encuentra los tejidos donde un gen se expresa usando la base de datos ARCHS4.
Produce: Resultados en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV (Python).
Parámetro posicional
gene
Nombre corto (símbolo del gen) del gen de interés, p. ej. STAT4.
Alternativamente: usa la bandera --ensembl para ingresar un ID tipo Ensembl, p. ej. ENSG00000138378.
Parámetros optionales
-w --which
'correlation' (correlación; se usa por defecto) o 'tissue' (tejido).
'correlation' produce una tabla que contiene los 100 genes más correlacionados con el gen de interés. La correlación de Pearson se calcula de todas las muestras y tejidos en ARCHS4.
'tissue' produce un atlas de expresión tisular calculado de todas las muestras humanas o de ratón (según lo definido usando el parámetro --species (especies)) en ARCHS4.
-s --species
'human' (humano; se usa por defecto) o 'mouse' (ratón).
Define si se usan muestras humanas o de ratón de ARCHS4.
(Solo aplica para el atlas de expresión tisular.)
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.csv (o .json). Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, use save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Banderas
-e --ensembl
Usa esta bandera si gene se ingresa como ID tipo Ensembl.
-csv --csv
Solo para Terminal. Produce los resultados en formato CSV.
Para Python, usa json=True para obtener los resultados en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para impedir la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Ejemplo
gget archs4 ACE2
# Python
gget.archs4("ACE2")
→ Produce los 100 genes más correlacionados con el gen ACE2:
| gene_symbol | pearson_correlation |
|---|---|
| SLC5A1 | 0.579634 |
| CYP2C18 | 0.576577 |
| . . . | . . . |
gget archs4 -w tissue ACE2
# Python
gget.archs4("ACE2", which="tissue")
→ Produce la expresión tisular de ACE2 (por defecto, se utilizan datos humanos):
| id | min | q1 | median | q3 | max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System.Urogenital/Reproductive System.Kidney.RENAL CORTEX | 0.113644 | 8.274060 | 9.695840 | 10.51670 | 11.21970 |
| System.Digestive System.Intestine.INTESTINAL EPITHELIAL CELL | 0.113644 | 5.905560 | 9.570450 | 13.26470 | 13.83590 |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . |
Consulte este tutorial de Dave Tang, quien escribió un script R para crear esta visualización con los resultados de gget archs4 en formato JSON:
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget archs4 en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Lachmann A, Torre D, Keenan AB, Jagodnik KM, Lee HJ, Wang L, Silverstein MC, Ma’ayan A. Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse. Nature Communications 9. Article number: 1366 (2018), doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03751-6
-
Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P and Pachter L, Near optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification, Nature Biotechnology 34, p 525--527 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3519
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget bgee 🐝
Obtenga datos de ortología y expresión genética de Bgee utilizando IDs de Ensembl.
Resultado: JSON/CSV (línea de comandos) o marco de datos (Python).
Si estás interesado específicamente en datos de expresión génica humana, considera usar gget opentargets o gget archs4 en su lugar. gget bgee tiene menos datos, pero admite más especies.
Este módulo fue escrito por Sam Wagenaar con ediciones de Kateřina Večerková.
Argumento posicional
ens_id
ID de gen Ensembl, por ejemplo, ENSG00000169194 o ENSSSCG00000014725.
Cuando type=expression también puedes pasar una lista de múltiples ID de Ensembl.
NOTA: Algunas de las especies en Bgee no están en Ensembl, y para ellas puede utilizar los ID de genes del NCBI, p. 118215821 (un gen en Anguilla anguilla).
Argumentos requeridos
-t --type
Tipo de datos a obtener. Opciones: orthologs, expression.
Argumentos opcionales
-o --out
Ruta al archivo JSON donde se guardarán los resultados, por ejemplo, path/to/directory/results.json. Por defecto: Salida estándar.
Banderas
-csv --csv
Solo en línea de comandos. Devuelve la salida en formato CSV, en lugar de formato JSON.
Python: Usa json=True para devolver la salida en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo en línea de comandos. Evita que se muestre la información de progreso.
Python: Usa verbose=False para evitar que se muestre la información de progreso.
Ejemplos
Obtener ortólogos para un gen
gget bgee ENSSSCG00000014725 -t orthologs
import gget
gget.bgee("ENSSSCG00000014725", type="orthologs")
→ Devuelve ortólogos para el gen con el ID de Ensembl ENSSSCG00000014725.
| gene_id | gene_name | species_id | genus | species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 734881 | hbb1 | 8355 | Xenopus | laevis |
| ENSFCAG00000038029 | LOC101098159 | 9685 | Felis | catus |
| ENSBTAG00000047356 | LOC107131172 | 9913 | Bos | taurus |
| ENSOARG00000019163 | LOC101105437 | 9940 | Ovis | aries |
| ENSXETG00000025667 | hbg1 | 8364 | Xenopus | tropicalis |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Obtener datos de expresión génica para un gen
gget bgee ENSSSCG00000014725 -t expression
import gget
gget.bgee("ENSSSCG00000014725", type="expression")
→ Devuelve datos de expresión génica para el gen con el ID de Ensembl ENSSSCG00000014725.
| anat_entity_id | anat_entity_name | score | score_confidence | expression_state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBERON:0000178 | blood | 99.98 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0002106 | spleen | 99.96 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0002190 | subcutaneous adipose tissue | 99.70 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0005316 | endocardial endothelium | 99.61 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0002107 | liver | 99.27 | high | expressed |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Obtener datos de expresión génica para múltiples genes
gget bgee ENSBTAG00000047356 ENSBTAG00000018317 -t expression
import gget
gget.bgee(["ENSBTAG00000047356", "ENSBTAG00000018317"], type="expression")
→ Devuelve datos de expresión génica para los genes ENSBTAG00000047356 y ENSBTAG00000018317:
| anat_entity_id | anat_entity_name | score | score_confidence | expression_state |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBERON:0001017 | central nervous system | 92.15 | high | expressed |
| UBERON:0002616 | regional part of brain | 79.01 | high | expressed |
| BGEE:0000000 | anatomical entity and cellular component | 89.12 | high | expressed |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget bgee en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Frederic B Bastian, Julien Roux, Anne Niknejad, Aurélie Comte, Sara S Fonseca Costa, Tarcisio Mendes de Farias, Sébastien Moretti, Gilles Parmentier, Valentine Rech de Laval, Marta Rosikiewicz, Julien Wollbrett, Amina Echchiki, Angélique Escoriza, Walid H Gharib, Mar Gonzales-Porta, Yohan Jarosz, Balazs Laurenczy, Philippe Moret, Emilie Person, Patrick Roelli, Komal Sanjeev, Mathieu Seppey, Marc Robinson-Rechavi (2021). The Bgee suite: integrated curated expression atlas and comparative transcriptomics in animals. Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D831–D847, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa793
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Las banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget blast 💥
BLAST una secuencia de nucleótidos o aminoácidos a cualquier base de datos BLAST.
Produce: Resultados en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV (Python).
Parámetro posicional
sequence
Secuencia de nucleótidos o aminoácidos, o una ruta a un archivo tipo FASTA o .txt.
Parámetros optionales
-p --program
'blastn', 'blastp', 'blastx', 'tblastn', o 'tblastx'.
Por defecto: 'blastn' para secuencias de nucleótidos; 'blastp' para secuencias de aminoácidos.
-db --database
'nt', 'nr', 'refseq_rna', 'refseq_protein', 'swissprot', 'pdbaa', o 'pdbnt'.
Por defecto: 'nt' para secuencias de nucleótidos; 'nr' para secuencias de aminoácidos.
Más información sobre los bases de datos BLAST
-l --limit
Limita el número de resultados producidos. Por defecto: 50.
-e --expect
Define el umbral de 'expect value'. Por defecto: 10.0.
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.csv (o .json). Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Banderas
-lcf --low_comp_filt
Activa el 'low complexity filter' (filtro de baja complejidad).
-mbo --megablast_off
Desactiva el algoritmo MegaBLAST. Por defecto: MegaBLAST esta activado (solo aplicable para blastn).
-csv --csv
Solo para Terminal. Produce los resultados en formato CSV.
Para Python, usa json=True para producir los resultados en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para imipidir la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
wrap_text
Solo para Python. wrap_text=True muestra los resultados con texto envuelto para facilitar la lectura (por defecto: False).
Por ejemplo
gget blast MKWMFKEDHSLEHRCVESAKIRAKYPDRVPVIVEKVSGSQIVDIDKRKYLVPSDITVAQFMWIIRKRIQLPSEKAIFLFVDKTVPQSR
# Python
gget.blast("MKWMFKEDHSLEHRCVESAKIRAKYPDRVPVIVEKVSGSQIVDIDKRKYLVPSDITVAQFMWIIRKRIQLPSEKAIFLFVDKTVPQSR")
→ Produce los resultados BLAST de la secuencia de interés. gget blast automáticamente detecta esta secuencia como una secuencia de aminoácidos y, por lo tanto, establece el programa BLAST en blastp con la base de datos nr.
| Description | Scientific Name | Common Name | Taxid | Max Score | Total Score | Query Cover | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PREDICTED: gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-as... | Colobus angolensis palliatus | NaN | 336983 | 180 | 180 | 100% | ... |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | ... |
BLAST desde un archivo .fa o .txt:
gget blast fasta.fa
# Python
gget.blast("fasta.fa")
→ Produce los resultados BLAST de la primera secuencia contenida en el archivo 'fasta.fa'.
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget blast en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403-10. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. PMID: 2231712.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget blat 🎯
Encuentra la ubicación genómica de una secuencia de nucleótidos o aminoácidos usando BLAT.
Produce: Resultados en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV (Python).
Parámetro posicional
sequence
Secuencia de nucleótidos o aminoácidos, o una ruta a un archivo tipo FASTA o .txt.
Parámetros optionales
-st --seqtype
'DNA', 'protein', 'translated%20RNA', o 'translated%20DNA'.
Por defecto: 'DNA' para secuencias de nucleótidos; 'protein' para secuencias de aminoácidos.
-a --assembly
Ensamblaje del genoma. 'human' (hg38) (se usa por defecto), 'mouse' (mm39) (ratón), 'zebrafish' (taeGut2) (pinzón cebra),
o cualquiera de los ensamblajes de especies disponibles aquí (use el nombre corto del ensamblado, p. ej. 'hg38').
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.csv (o .json). Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Banderas
-csv --csv
Solo para Terminal. Produce los resultados en formato CSV.
Para Python, usa json=True para producir los resultados en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para impedir la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Ejemplo
gget blat -a taeGut2 MKWMFKEDHSLEHRCVESAKIRAKYPDRVPVIVEKVSGSQIVDIDKRKYLVPSDITVAQFMWIIRKRIQLPSEKAIFLFVDKTVPQSR
# Python
gget.blat("MKWMFKEDHSLEHRCVESAKIRAKYPDRVPVIVEKVSGSQIVDIDKRKYLVPSDITVAQFMWIIRKRIQLPSEKAIFLFVDKTVPQSR", assembly="taeGut2")
→ Produce los resultados de BLAT para el ensamblaje taeGut2 (pinzón cebra). En este ejemplo, gget blat automáticamente detecta esta secuencia como una secuencia de aminoácidos y, por lo tanto, establece el tipo de secuencia (--seqtype) como proteína.
| genome | query_size | aligned_start | aligned_end | matches | mismatches | %_aligned | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| taeGut2 | 88 | 12 | 88 | 77 | 0 | 87.5 | ... |
Màs ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget blat en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Kent WJ. BLAT--the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002 Apr;12(4):656-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.229202. PMID: 11932250; PMCID: PMC187518.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget cbio 📖
Trazar mapas de calor de la genómica del cáncer utilizando datos de cBioPortal con IDs de Ensembl o nombres de genes.
Este módulo fue escrito por Sam Wagenaar.
Argumento posicional
subcommand
O bien search o plot
Subcomando search (Python: gget.cbio_search)
Buscar IDs de estudios de cBioPortal por palabra clave.
Formato de retorno: JSON (línea de comandos) o lista de cadenas (Python).
Nota: Esto no devuelve estudios con tipos de cáncer mixtos.
Argumento posicional
keywords
Lista de palabras clave separadas por espacios para buscar, por ejemplo breast lung.
Python: Pasa palabras clave como una lista de cadenas.
Subcomando plot (Python: gget.cbio_plot)
Graficar mapas de calor de genómica del cáncer utilizando datos de cBioPortal.
Formato de retorno: PNG (línea de comandos y Python).
Argumentos requeridos
-s --study_ids
Lista separada por espacios de IDs de estudios de cBioPortal, por ejemplo, msk_impact_2017 egc_msk_2023.
-g --genes
Lista separada por espacios de nombres de genes o IDs de Ensembl, por ejemplo, NOTCH3 ENSG00000108375.
Argumentos opcionales
-st --stratification
Columna por la cual estratificar los datos. Predeterminado: tissue.
Opciones:
- tissue
- cancer_type
- cancer_type_detailed
- study_id
- sample
-vt --variation_type
Tipo de variación a graficar. Predeterminado: mutation_occurrences.
Opciones:
- mutation_occurrences
- cna_nonbinary (Nota: la
stratificationdebe ser 'sample' para esta opción) - sv_occurrences
- cna_occurrences
- Consequence (Nota: la
stratificationdebe ser 'sample' para esta opción)
-f --filter
Filtrar los datos por un valor específico en una columna específica, por ejemplo, study_id:msk_impact_2017.
Python: filter=(column, value)
-dd --data_dir
Directorio para almacenar los archivos de datos. Predeterminado: ./gget_cbio_cache.
-fd --figure_dir
Directorio para las figuras de salida. Predeterminado: ./gget_cbio_figures.
-fn --filename
Nombre del archivo de salida, relativo a figure_dir. Predeterminado: auto-generado.
Python: figure_filename.
-t --title
Título para la figura de salida. Predeterminado: auto-generado.
Python: figure_title.
-dpi --dpi
DPI de la figura de salida. Predeterminado: 100.
Banderas
-q --quiet
Solo en línea de comandos. Evita que se muestre la información de progreso.
Python: Usa verbose=False para evitar que se muestre la información de progreso.
-nc --no_confirm
Solo en línea de comandos. Omitir las confirmaciones de descarga.
Python: Usa confirm_download=True para habilitar las confirmaciones de descarga.
-sh --show
Mostrar la gráfica en una ventana (automático en notebooks de Jupyter).
Ejemplos
Encontrar todos los estudios de cBioPortal con tipos de cáncer que coinciden con palabras clave específicas:
gget cbio search esophag ovary ovarian
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_search(['esophag', 'ovary', 'ovarian'])
→ Devuelve una lista de estudios con tipos de cáncer que coinciden con las palabras clave esophag, ovary, o ovarian.
['egc_tmucih_2015', 'egc_msk_2017', ..., 'msk_spectrum_tme_2022']
Graficar un mapa de calor de ocurrencias de mutaciones para genes específicos en un estudio específico:
gget cbio plot \
-s msk_impact_2017 \
-g AKT1 ALK FLT4 MAP3K1 MLL2 MLL3 NOTCH3 NOTCH4 PDCD1 RNF43 \
-st tissue \
-vt mutation_occurrences \
-dpi 200
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_plot(
['msk_impact_2017'],
['AKT1', 'ALK', 'FLT4', 'MAP3K1', 'MLL2', 'MLL3', 'NOTCH3', 'NOTCH4', 'PDCD1', 'RNF43'],
stratification='tissue',
variation_type='mutation_occurrences',
dpi=200
)
→ Guarda un mapa de calor de ocurrencias de mutaciones para los genes especificados en el estudio especificado en ./gget_cbio_figures/Heatmap_tissue.png.

Graficar un mapa de calor de tipos de mutaciones para genes específicos en un estudio específico:
gget cbio plot \
-s msk_impact_2017 \
-g AKT1 ALK FLT4 MAP3K1 MLL2 MLL3 NOTCH3 NOTCH4 PDCD1 RNF43 \
-st sample \
-vt Consequence \
-dpi 200
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_plot(
['msk_impact_2017'],
['AKT1', 'ALK', 'FLT4', 'MAP3K1', 'MLL2', 'MLL3', 'NOTCH3', 'NOTCH4', 'PDCD1', 'RNF43'],
stratification='sample',
variation_type='Consequence',
dpi=200,
)
→ Guarda un mapa de calor de tipos de mutaciones para los genes especificados en el estudio especificado en ./gget_cbio_figures/Heatmap_sample.png.

Graficar un mapa de calor de tipos de mutaciones para genes específicos en un estudio específico, filtrando por tejido::
gget cbio plot \
-s msk_impact_2017 \
-g AKT1 ALK FLT4 MAP3K1 MLL2 MLL3 NOTCH3 NOTCH4 PDCD1 RNF43 \
-st sample \
-vt Consequence \
-f tissue:intestine \
-dpi 200
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_plot(
['msk_impact_2017'],
['AKT1', 'ALK', 'FLT4', 'MAP3K1', 'MLL2', 'MLL3', 'NOTCH3', 'NOTCH4', 'PDCD1', 'RNF43'],
stratification='sample',
variation_type='Consequence',
filter=('tissue', 'intestine'),
dpi=200,
)
→ Guarda un mapa de calor de tipos de mutaciones para los genes especificados en el estudio especificado, filtrado por tejido, en ./gget_cbio_figures/Heatmap_sample_intestine.png.

Graficar un mapa de calor con un título y nombre de archivo personalizados::
gget cbio plot \
-s msk_impact_2017 \
-g AKT1 ALK FLT4 MAP3K1 MLL2 MLL3 NOTCH3 NOTCH4 PDCD1 RNF43 \
-st sample \
-vt Consequence \
-f tissue:intestine \
-dpi 200 \
-t "Intestinal Mutations" \
-fn intestinal_mutations.png
# Python
import gget
gget.cbio_plot(
['msk_impact_2017'],
['AKT1', 'ALK', 'FLT4', 'MAP3K1', 'MLL2', 'MLL3', 'NOTCH3', 'NOTCH4', 'PDCD1', 'RNF43'],
stratification='sample',
variation_type='Consequence',
filter=('tissue', 'intestine'),
dpi=200,
figure_title='Intestinal Mutations',
figure_filename='intestinal_mutations.png'
)
→ Guarda un mapa de calor de los tipos de mutaciones para los genes especificados en el estudio especificado, filtrado por tejido, con el título "Mutaciones intestinales" en ./gget_cbio_figures/intestinal_mutations.png.

Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget cbio en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, Antipin Y, Reva B, Goldberg AP, Sander C, Schultz N. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012 May;2(5):401-4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095. Erratum in: Cancer Discov. 2012 Oct;2(10):960. PMID: 22588877; PMCID: PMC3956037.
-
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, Cerami E, Sander C, Schultz N. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013 Apr 2;6(269):pl1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004088. PMID: 23550210; PMCID: PMC4160307.
-
de Bruijn I, Kundra R, Mastrogiacomo B, Tran TN, Sikina L, Mazor T, Li X, Ochoa A, Zhao G, Lai B, Abeshouse A, Baiceanu D, Ciftci E, Dogrusoz U, Dufilie A, Erkoc Z, Garcia Lara E, Fu Z, Gross B, Haynes C, Heath A, Higgins D, Jagannathan P, Kalletla K, Kumari P, Lindsay J, Lisman A, Leenknegt B, Lukasse P, Madela D, Madupuri R, van Nierop P, Plantalech O, Quach J, Resnick AC, Rodenburg SYA, Satravada BA, Schaeffer F, Sheridan R, Singh J, Sirohi R, Sumer SO, van Hagen S, Wang A, Wilson M, Zhang H, Zhu K, Rusk N, Brown S, Lavery JA, Panageas KS, Rudolph JE, LeNoue-Newton ML, Warner JL, Guo X, Hunter-Zinck H, Yu TV, Pilai S, Nichols C, Gardos SM, Philip J; AACR Project GENIE BPC Core Team, AACR Project GENIE Consortium; Kehl KL, Riely GJ, Schrag D, Lee J, Fiandalo MV, Sweeney SM, Pugh TJ, Sander C, Cerami E, Gao J, Schultz N. Analysis and Visualization of Longitudinal Genomic and Clinical Data from the AACR Project GENIE Biopharma Collaborative in cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 1;83(23):3861-3867. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0816. PMID: 37668528; PMCID: PMC10690089.
-
Please also cite the source of the data if you are using a publicly available dataset.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Las banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget cellxgene 🍱
Query data de la base de datos CZ CELLxGENE Discover usando CZ CELLxGENE Discover Census.
Produce: Un objeto AnnData que contiene la matriz de recuentos de genes y los metadatos de resultados de single cell RNA-seq de los tejidos/genes/etcetera previamente definidos.
Antes de usar gget cellxgene por primera vez, corre gget setup cellxgene / gget.setup("cellxgene") (ver también gget setup).
Parámetros opcionales
-s --species
'homo_sapiens' o 'mus_musculus'. Por defecto: 'homo_sapiens'.
-g --gene
Str o lista de genes de interés o ID(s) tipo Ensembl. Por defecto: None (ninguno).
Atención: Utilice la bandera -e / --ensembl (Python: ensembl=True) cuando ingrese ID(s) tipo Ensembl.
Atención: ¡Los símbolos de genes distinguen mayúsculas y minúsculas! Usa la capitalización canónica al pasar símbolos de genes; p. ej., ‘PAX7’ (humano), ‘Pax7’ (ratón).
Ver https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/gene-expression para ejemplos de genes.
-cv --census_version
Versión del CZ CELLxGENE Discover Census (str), p. ej. "2023-05-15", o "latest" (ultima) o "stable" (estable). Por defecto: "stable" (estable).
-cn --column_names
Lista de columnas de metadatos a obtener (almacenadas en AnnData.obs).
Por defecto: ['dataset_id', 'assay', 'suspension_type', 'sex', 'tissue_general', 'tissue', 'cell_type']
Para más opciones, ver: https://api.cellxgene.cziscience.com/curation/ui/#/ -> 'Schemas' -> 'dataset'
-o --out
Ruta al archivo para guardar el objeto AnnData formato .h5ad (o .csv con bandera -mo / --meta_only).
¡Requerido cuando se usa desde Terminal!
Banderas
-e --ensembl
Usa esta bandera si gene se ingresa como ID tipo Ensembl.
-mo --meta_only
Solo produce la tabla (Dataframe) con metadatos (corresponde a AnnData.obs).
-q --quiet
Solo para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para impedir la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Parámetros opcionales correspondientes a los atributos de metadatos de CZ CELLxGENE Discover
--tissue
Str o lista de tejido(s), p. ej. ['lung', 'blood']. Por defecto: None.
Ver https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/gene-expression para ejemplos de tejidos.
--cell_type
Str o lista de tipo(s) de célula(s), p. ej. ['mucus secreting cell', 'neuroendocrine cell']. Por defecto: None.
Ver https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/gene-expression y seleccione un tejido para ejemplos de tipos de células.
--development_stage
Str o lista de etapa(s) de desarrollo. Por defecto: None.
--disease
Str o lista de enfermedad(es). Por defecto: None.
--sex
Str o lista de sexo(s), p. ej. 'female' (femenina). Por defecto: None.
--dataset_id
Str o lista de CELLxGENE ID(s). Por defecto: None.
--tissue_general_ontology_term_id
Str o lista de tejido(s) del tipo high-level UBERON ID. Por defecto: None.
Tejidos y sus IDs tipo UBERON se enumeran aquí.
--tissue_general
Str o lista de tejido(s) del tipo high-level. Por defecto: None.
Tejidos y sus IDs de UBERON se enumeran aquí.
--tissue_ontology_term_id
Str o lista de ID(s) de 'tissue ontology term' como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--assay_ontology_term_id
Str o lista de ID(s) de 'assay ontology term' como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--assay
Str o lista de 'assays' (métodos) como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--cell_type_ontology_term_id
Str o lista de ID(s) de 'celltype ontology term' como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--development_stage_ontology_term_id
Str o lista de ID(s) de 'development stage ontology term' como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--disease_ontology_term_id
Str o lista de ID(s) de 'disease ontology term' como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--donor_id
Str o lista de ID(s) de 'donor' (donador) como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--self_reported_ethnicity_ontology_term_id
Str o lista de ID(s) de 'self-reported ethnicity ontology' como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--self_reported_ethnicity
Str o lista de etnias autoinformadas como están definidas en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--sex_ontology_term_id
Str o lista de ID(s) de 'sex ontology' como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
--suspension_type
Str o lista de tipo(s) de suspensión como están definidos en el esquema de datos del CELLxGENE. Por defecto: None.
Ejemplo
gget cellxgene --gene ACE2 ABCA1 SLC5A1 --tissue lung --cell_type 'mucus secreting cell' 'neuroendocrine cell' -o example_adata.h5ad
# Python
adata = gget.cellxgene(
gene = ["ACE2", "ABCA1", "SLC5A1"],
tissue = "lung",
cell_type = ["mucus secreting cell", "neuroendocrine cell"]
)
adata
→ Produce un objeto AnnData que contiene la matriz de recuentos de scRNAseq de los genes ACE2, ABCA1 y SLC5A1 en 3322 células secretoras de mucosidad y neuroendocrinas pulmonares humanas y sus metadatos correspondientes.
Obtiene solo los metadatos (corresponde a AnnData.obs):
gget cellxgene --meta_only --gene ENSMUSG00000015405 --ensembl --tissue lung --species mus_musculus -o example_meta.csv
# Python
df = gget.cellxgene(
meta_only = True,
gene = "ENSMUSG00000015405",
ensembl = True,
tissue = "lung",
species = "mus_musculus"
)
df
→ Produce solo los metadatos de los conjuntos de datos de ENSMUSG00000015405 (ACE2), los cuales corresponden a células pulmonares murinas.
Ver también: https://chanzuckerberg.github.io/cellxgene-census/notebooks/api_demo/census_gget_demo.html
Citar
Si utiliza gget cellxgene en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Chanzuckerberg Initiative. (n.d.). CZ CELLxGENE Discover. Retrieved [insert date here], from https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Las banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget cosmic 🪐
Busca genes, mutaciones y otros factores asociados con el cáncer utilizando la base de datos COSMIC (Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer).
Formato de retorno: JSON (línea de comandos) o data frame/CSV (Python) cuando download_cosmic=False. Cuando download_cosmic=True, se descarga la base de datos solicitada en la carpeta especificada.
Este módulo fue escrito originalmente en parte por @AubakirovArman (consultas de información) y @josephrich98 (descarga de bases de datos).
NOTA: Se aplican tarifas de licencia para el uso comercial de COSMIC. Puedes leer más sobre la licencia de los datos de COSMIC aquí.
NOTA: Al utilizar este módulo por primera vez, primero descarga una base de datos de COSMIC para obtener cosmic_tsv_path (ver ejemplos abajo).
Argumento posicional (para consultar información)
searchterm
Término de búsqueda, que puede ser una mutación, un nombre de gen (o ID de Ensembl), una muestra, etc.
Ejemplos: 'EGFR', 'ENST00000275493', 'c.650A>T', 'p.Q217L', 'COSV51765119', 'BT2012100223LNCTB' (ID de muestra)
NOTA: (solo en Python) Establecer en None al descargar bases de datos de COSMIC con download_cosmic=True.
Argumento obligatorio (para consultar información)
-ctp --cosmic_tsv_path
Ruta al archivo tsv de la base de datos de COSMIC, por ejemplo: 'path/to/CancerMutationCensus_AllData_v101_GRCh37.tsv'.
Este archivo se descarga al usar los argumentos descritos debajo para descargar bases de datos.
NOTA: Este argumento es obligatorio cuando download_cosmic=False.
Argumentos opcionales (para consultar información)
-l --limit
Límite en la cantidad de resultados a devolver. Valor por defecto: 100.
-csv --csv
Solo para línea de comandos. Devuelve los resultados en formato CSV.
Python: usa json=True para obtener la salida en formato JSON.
Banderas (para descargar bases de datos de COSMIC)
-d --download_cosmic
Activa el modo de descarga de base de datos.
-gm --gget_mutate
Crea una versión modificada de la base de datos COSMIC para usar con gget mutate.
Argumentos opcionales (para descargar bases de datos de COSMIC)
-cp --cosmic_project
'cancer' (por defecto), 'cancer_example', 'census', 'resistance', 'cell_line', 'genome_screen', o 'targeted_screen'
Tipo de base de datos COSMIC a descargar:
| cosmic_project | Descripción | Notas | Tamaño |
|---|---|---|---|
| cancer | Cancer Mutation Census (CMC) (conjunto más comúnmente usado de COSMIC) | Solo disponible para GRCh37. Esquema más completo (requiere más tiempo para buscar). | 2 GB |
| cancer_example | Subconjunto de CMC de ejemplo para pruebas y demostración | Descargable sin cuenta COSMIC. Conjunto de datos mínimo. | 2.5 MB |
| census | Censo de mutaciones somáticas en genes conocidos relacionado al cáncer | Conjunto curado más pequeño de genes impulsores del cáncer. | 630 MB |
| resistance | Mutaciones asociadas con resistencia a fármacos | Útil para investigación en farmacogenómica. | 1.6 MB |
| cell_line | Datos de mutaciones del proyecto de líneas celulares | A menudo incluye metadatos de muestras. | 2.7 GB |
| genome_screen | Mutaciones de estudios de cribado genómico | Incluye datos menos curados, útiles para estudios a gran escala. | |
| targeted_screen | Mutaciones de paneles de cribado dirigido | Datos centrados, útiles en contextos clínicos. |
-cv --cosmic_version
Versión de la base de datos COSMIC. Valor por defecto: None → se usa la versión más reciente.
-gv --grch_version
Versión del genoma de referencia humano GRCh en el que se basa la base de datos COSMIC (37 o 38). Por defecto: 37
--email
Correo electrónico para iniciar sesión en COSMIC. Útil para evitar la entrada manual al ejecutar gget COSMIC. Por defecto: None
--password
Contraseña para iniciar sesión en COSMIC. Útil para evitar la entrada manual al ejecutar gget COSMIC, pero se almacenará en texto plano en el script. Por defecto: None
Argumentos adicionales para la bandera --gget_mutate
--keep_genome_info
Indica si se debe conservar la información genómica en la base modificada para usar con gget mutate. Por defecto: False
--remove_duplicates
Indica si se deben eliminar filas duplicadas de la base modificada para usar con gget mutate. Por defecto: False
--seq_id_column
(str) Nombre de la columna de ID de secuencia en el archivo CSV creado por gget_mutate. Por defecto: "seq_ID"
--mutation_column
(str) Nombre de la columna de mutaciones en el archivo CSV creado por gget_mutate. Por defecto: "mutation"
--mut_id_column
(str) Nombre de la columna de ID de mutación en el archivo CSV creado por gget_mutate. Por defecto: "mutation_id"
Argumentos opcionales (generales)
-o --out
Ruta del archivo (o carpeta cuando se descargan bases de datos con la bandera download_cosmic) donde se guardarán los resultados, por ejemplo: 'path/to/results.json'.
Valores por defecto:
→ Cuando download_cosmic=False: los resultados se devuelven por la salida estándar
→ Cuando download_cosmic=True: la base de datos se descarga en el directorio de trabajo actual
Banderas (generales)
-q --quiet
Solo en línea de comandos. Evita que se muestren mensajes de progreso.
Python: usa verbose=False para evitar mensajes de progreso.
Ejemplos
Descargar la base de datos "cancer" de COSMIC y consultar información
# The download_cosmic command will ask for your COSMIC email and password and only needs to be run once
gget cosmic --download_cosmic --cosmic_project cancer
gget cosmic EGFR --cosmic_tsv_path 'CancerMutationCensus_AllData_Tsv_v101_GRCh37/CancerMutationCensus_AllData_v101_GRCh37.tsv'
# Python
# The download_cosmic command will ask for your COSMIC email and password and only needs to be run once
gget.cosmic(searchterm=None, download_cosmic=True, cosmic_project="cancer")
gget.cosmic("EGFR", cosmic_tsv_path="CancerMutationCensus_AllData_Tsv_v101_GRCh37/CancerMutationCensus_AllData_v101_GRCh37.tsv")
→ El primer comando descarga la base de datos solicitada de la última versión de COSMIC en el directorio de trabajo actual. El segundo comando busca en la base de datos las mutaciones asociadas al gen 'EGFR' y devuelve los resultados en el siguiente formato:
| GENE_NAME | ACCESSION_NUMBER | ONC_TSG | Mutation_CDS | Mutation_AA | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | ENST00000275493.2 | oncogene | c.650A>T | p.Q217L | ... |
| EGFR | ENST00000275493.2 | oncogene | c.966C>T | p.G322= | ... |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Descargar la base de datos "census" de COSMIC y consultar información
# The download_cosmic command will ask for your COSMIC email and password and only needs to be run once
gget cosmic --download_cosmic --cosmic_project census
gget cosmic EGFR --cosmic_tsv_path 'Cosmic_MutantCensus_Tsv_v101_GRCh37/Cosmic_MutantCensus_v101_GRCh37.tsv'
# Python
# The download_cosmic command will ask for your COSMIC email and password and only needs to be run once
gget.cosmic(searchterm=None, download_cosmic=True, cosmic_project="cancer")
gget.cosmic("EGFR", cosmic_tsv_path="Cosmic_MutantCensus_Tsv_v101_GRCh37/Cosmic_MutantCensus_v101_GRCh37.tsv")
→ El primer comando descarga la base de datos solicitada de la última versión de COSMIC en el directorio de trabajo actual. El segundo comando busca en la base de datos las mutaciones asociadas al gen 'EGFR' y devuelve los resultados en el siguiente formato:
| GENE_SYMBOL | COSMIC_GENE_ID | MUTATION_DESCRIPTION | MUTATION_CDS | Mutation_AA | MUTATION_SOMATIC_STATUS | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | COSG35617 | inframe_deletion | c.2235_2249del | p.E746_A750del | Reported in another cancer sample as somatic | ... |
| EGFR | COSG35617 | missense_variant | c.2573T>G | p.L858R | Reported in another cancer sample as somatic | ... |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
Citar
Si utiliza gget cosmic en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, Sondka Z, Beare DM, Bindal N, Boutselakis H, Cole CG, Creatore C, Dawson E, Fish P, Harsha B, Hathaway C, Jupe SC, Kok CY, Noble K, Ponting L, Ramshaw CC, Rye CE, Speedy HE, Stefancsik R, Thompson SL, Wang S, Ward S, Campbell PJ, Forbes SA. COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 8;47(D1):D941-D947. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1015. PMID: 30371878; PMCID: PMC6323903.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Las banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget diamond 💎
Alinee múltiples proteínas o secuencias de ADN traducidas usando DIAMOND (DIAMOND es similar a BLAST, pero este es un cálculo local).
Produce: Resultados en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV (Python).
Parámetro posicional
query
Secuencia(s) (str o lista) de aminoácidos, o una ruta a un archivo tipo FASTA.
Parámetro requerido
-ref --reference
Secuencias de aminoácidos de referencia (str o lista), o una ruta a un archivo tipo FASTA.
Parámetros optionales
-db --diamond_db
Ruta para guardar la base de datos DIAMOND creada a partir de reference (str).
Por defecto: None -> El archivo de base de datos DIAMOND temporal se eliminará después de la alineación o se guardará en out si se proporciona out.
-s --sensitivity
Sensibilidad de la alineación (str). Por defecto: "very-sensitive" (muy sensible).
Uno de los siguientes: fast, mid-sensitive, sensitive, more-sensitive, very-sensitive, or ultra-sensitive.
-t --threads
Número de hilos de procesamiento utilizados (int). Por defecto: 1.
-db --diamond_binary
Ruta al binario DIAMOND (str). Por defecto: None -> Utiliza el binario DIAMOND instalado automáticamente con gget.
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados (str), p. ej. "ruta/al/directorio". Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT); los archivos temporales se eliminan.
Banderas
-u --uniprot
Use esta bandera cuando sequence es un ID de Uniprot en lugar de una secuencia de aminoácidos.
-csv --csv
Solo para Terminal. Produce los resultados en formato CSV.
Para Python, usa json=True para producir los resultados en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para impedir la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Ejemplo
# !!! Asegúrese de enumerar primero el argumento posicional aquí para que no se agregue como secuencia de referencia
gget diamond GGETISAWESQME ELVISISALIVE LQVEFRANKLIN PACHTERLABRQCKS -ref GGETISAWESQMEELVISISALIVELQVEFRANKLIN PACHTERLABRQCKS
# Python
gget.diamond(["GGETISAWESQME", "ELVISISALIVE", "LQVEFRANKLIN", "PACHTERLABRQCKS"], reference=["GGETISAWESQMEELVISISALIVELQVEFRANKLIN", "PACHTERLABRQCKS"])
→ Produce los resultados de la alineación en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV:
| query_accession | subject_accession | identity_percentage | query_seq_length | subject_seq_length | length | mismatches | gap_openings | query_start | query_end | subject_start | subject_end | e-value | bit_score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seq0 | Seq0 | 100 | 13 | 37 | 13 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 13 | 1 | 13 | 2.82e-09 | 30.8 |
| Seq2 | Seq0 | 100 | 12 | 37 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 12 | 26 | 37 | 4.35e-08 | 27.7 |
| Seq3 | Seq1 | 100 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 15 | 1 | 15 | 2.01e-11 | 36.2 |
Màs ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget diamond en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Buchfink, B., Xie, C. & Huson, D. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12, 59–60 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3176
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget elm 🎭
Prediga localmente motivos lineales eucarióticos (ELMs) a partir de una secuencia de aminoácidos o UniProt Acc utilizando datos de la base de datos ELM.
Produce: Resultados en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV (Python). Este módulo devuelve dos tipos de resultados (ver ejemplos).
Los datos de ELM se pueden descargar y distribuir para uso no comercial de acuerdo con el acuerdo de licencia de software de ELM.
Antes de usar gget elm por primera vez, ejecute gget setup elm / gget.setup("elm") una vez (consulte también gget setup).
Parámetro posicional
sequence
Secuencia de aminoácidos o Uniprot Acc (str).
Al proporcionar una Uniprot Acc, use la bandera --uniprot (Python: uniprot=True).
Parámetros optionales
-s sensitivity
Sensibilidad de la alineación DIAMOND (str). Por defecto: "very-sensitive" (muy sensible).
Uno de los siguientes: fast, mid-sensitive, sensitive, more-sensitive, very-sensitive, or ultra-sensitive.
-t threads
Número de hilos de procesamiento utilizados en la alineación de secuencias con DIAMOND (int). Por defecto: 1.
-bin diamond_binary
Ruta al binario DIAMOND (str). Por defecto: None -> Utiliza el binario DIAMOND instalado automáticamente con gget.
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados (str), p. ej. "ruta/al/directorio". Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT); los archivos temporales se eliminan.
Banderas
-u --uniprot
Use esta bandera cuando sequence es una Uniprot Acc en lugar de una secuencia de aminoácidos.
-e --expand
Amplíe la información devuelta en el marco de datos de expresiones regulares para incluir los nombres de proteínas, los organismos y las referencias en las que se validó originalmente el motivo.
-csv --csv
Solo para Terminal. Produce los resultados en formato CSV.
Para Python, usa json=True para producir los resultados en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para impedir la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Ejemplo
Encuentre ELM en una secuencia de aminoácidos:
gget setup elm # Descarga/actualiza la base de datos ELM local
gget elm -o gget_elm_results LIAQSIGQASFV
# Python
gget.setup(“elm”) # Descarga/actualiza la base de datos ELM local
ortholog_df, regex_df = gget.elm("LIAQSIGQASFV")
Encuentre ELM que proporcionen a una UniProt Acc:
gget setup elm # Descarga/actualiza la base de datos ELM local
gget elm -o gget_elm_results --uniprot Q02410 -e
# Python
gget.setup(“elm”) # Descarga/actualiza la base de datos ELM local
ortholog_df, regex_df = gget.elm("Q02410", uniprot=True, expand=True)
→ Produce dos resultados con información extensa sobre ELMs asociados con proteínas ortólogas y motivos encontrados en la secuencia de entrada directamente en función de sus expresiones regex:
ortholog_df:
| Ortholog_UniProt_Acc | ProteinName | class_accession | ELMIdentifier | FunctionalSiteName | Description | Organism | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q02410 | APBA1_HUMAN | ELME000357 | LIG_CaMK_CASK_1 | CASK CaMK domain binding ligand motif | Motif that mediates binding to the calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK) domain of the peripheral plasma membrane protein CASK/Lin2. | Homo sapiens | … |
| Q02410 | APBA1_HUMAN | ELME000091 | LIG_PDZ_Class_2 | PDZ domain ligands | The C-terminal class 2 PDZ-binding motif is classically represented by a pattern such as | Homo sapiens | … |
regex_df:
| Instance_accession | ELMIdentifier | FunctionalSiteName | ELMType | Description | Instances (Matched Sequence) | Organism | … |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELME000321 | CLV_C14_Caspase3-7 | Caspase cleavage motif | CLV | Caspase-3 and Caspase-7 cleavage site. | ERSDG | Mus musculus | … |
| ELME000102 | CLV_NRD_NRD_1 | NRD cleavage site | CLV | N-Arg dibasic convertase (NRD/Nardilysin) cleavage site. | RRA | Rattus norvegicus | … |
| ELME000100 | CLV_PCSK_PC1ET2_1 | PCSK cleavage site | CLV | NEC1/NEC2 cleavage site. | KRD | Mus musculus | … |
| ELME000146 | CLV_PCSK_SKI1_1 | PCSK cleavage site | CLV | Subtilisin/kexin isozyme-1 (SKI1) cleavage site. | RLLTA | Homo sapiens | … |
| ELME000231 | DEG_APCC_DBOX_1 | APCC-binding Destruction motifs | DEG | An RxxL-based motif that binds to the Cdh1 and Cdc20 components of APC/C thereby targeting the protein for destruction in a cell cycle dependent manner | SRVKLNIVR | Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c | … |
| … | … | … | … | … | … | … | … |
(Los motivos que aparecen en muchas especies diferentes pueden parecer repetidos, pero todas las filas deben ser únicas.)
Màs ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget elm en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Laura Luebbert, Chi Hoang, Manjeet Kumar, Lior Pachter, Fast and scalable querying of eukaryotic linear motifs with gget elm, Bioinformatics, 2024, btae095, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btae095
-
Manjeet Kumar, Sushama Michael, Jesús Alvarado-Valverde, Bálint Mészáros, Hugo Sámano‐Sánchez, András Zeke, Laszlo Dobson, Tamas Lazar, Mihkel Örd, Anurag Nagpal, Nazanin Farahi, Melanie Käser, Ramya Kraleti, Norman E Davey, Rita Pancsa, Lucía B Chemes, Toby J Gibson, The Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource: 2022 release, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 50, Issue D1, 7 January 2022, Pages D497–D508, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab975
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Las banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget enrichr 💰
Realice un análisis de enriquecimiento de una lista de genes utilizando Enrichr.
Produce: Resultados en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV (Python).
Parámetro posicional
genes
Lista de nombres cortos (símbolos) de los genes de interés para realizar el análisis de enriquecimiento, p. PHF14 RBM3 MSL1 PHF21A.
Alternativamente: use la bandera --ensembl para ingresar IDs tipo Ensembl, p. ENSG00000106443 ENSG00000102317 ENSG00000188895.
Otros parámetros requeridos
-db --database
Base de datos que será utilizada como referencia para el análisis de enriquecimiento.
Admite cualquier base de datos enumerada aquí o uno de los siguientes accesos directos:
'pathway' (KEGG_2021_Human)
'transcription' (ChEA_2016)
'ontology' (GO_Biological_Process_2021)
'diseases_drugs' (GWAS_Catalog_2019)
'celltypes' (PanglaoDB_Augmented_2021)
'kinase_interactions' (KEA_2015)
Parámetros opcionales
-s --species
Especies a utilizar como referencia para el análisis de enriquecimiento. (Por defecto: human)
Opciones:
| Species | Database list |
|---|---|
human | Enrichr |
mouse | Equivalente al humano |
fly | FlyEnrichr |
yeast | YeastEnrichr |
worm | WormEnrichr |
fish | FishEnrichr |
-bkg_l --background_list
Lista de nombres cortos (símbolos) de genes de 'background' (de fondo/control), p. NSUN3 POLRMT NLRX1.
Alternativamente: usa la bandera --ensembl_background para ingresar IDs tipo Ensembl.
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.csv (o .json). Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
-ko --kegg_out
Ruta al archivo png en el que se guardará la imágen de la vía de señalización celular KEGG, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/KEGG.png. (Por defecto: None)
-kr --kegg_rank
Rango de la ruta KEGG que se va a trazar. (Por defecto: 1)
figsize
Solo para Python. (ancho, alto) de la visualización en pulgadas. (Por defecto: (10,10))
ax
Solo para Python. Ingresa un objeto de ejes matplotlib para personalizar la visualización.(Por defecto: None)
Banderas
-e --ensembl
Usa esta bandera si genes se ingresa como una lista de IDs tipo Ensembl.
-e_b --ensembl_bkg
Usa esta bandera si background_list se ingresa como una lista de IDs tipo Ensembl.
-bkg --background
Use un conjunto de 20,625 genes 'background'
listados aquí.
-csv --csv
Solo para Terminal. Produce los resultados en formato CSV.
Para Python, usa json=True produce los resultados en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para imipidir la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
plot
Solo para Python. plot=True provée la visualización de los primeros 15 resultados (por defecto: False).
Ejemplo
gget enrichr -db ontology ACE2 AGT AGTR1
# Python
gget.enrichr(["ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1"], database="ontology", plot=True)
→ Produce vías/funciones celulares relacionadas con los genes ACE2, AGT y AGTR1 de la base de datos GO Biological Process 2021. En Python, plot=True provee la visualización de resultados:

Use gget enrichr con una lista de genes 'background':
# Aquí, primero ingresamos los genes de interés (parámetro posicional 'genes'), para que no se agreguen a la lista de genes 'background' detrás del parámetro '-bkgr_l'
gget enrichr \
PHF14 RBM3 MSL1 PHF21A ARL10 INSR JADE2 P2RX7 LINC00662 CCDC101 PPM1B KANSL1L CRYZL1 ANAPC16 TMCC1 CDH8 RBM11 CNPY2 HSPA1L CUL2 PLBD2 LARP7 TECPR2 ZNF302 CUX1 MOB2 CYTH2 SEC22C EIF4E3 ROBO2 ADAMTS9-AS2 CXXC1 LINC01314 ATF7 ATP5F1 \
-db ChEA_2022 \
-bkg_l NSUN3 POLRMT NLRX1 SFXN5 ZC3H12C SLC25A39 ARSG DEFB29 PCMTD2 ACAA1A LRRC1 2810432D09RIK SEPHS2 SAC3D1 TMLHE LOC623451 TSR2 PLEKHA7 GYS2 ARHGEF12 HIBCH LYRM2 ZBTB44 ENTPD5 RAB11FIP2 LIPT1 INTU ANXA13 KLF12 SAT2 GAL3ST2 VAMP8 FKBPL AQP11 TRAP1 PMPCB TM7SF3 RBM39 BRI3 KDR ZFP748 NAP1L1 DHRS1 LRRC56 WDR20A STXBP2 KLF1 UFC1 CCDC16 9230114K14RIK RWDD3 2610528K11RIK ACO1 CABLES1 LOC100047214 YARS2 LYPLA1 KALRN GYK ZFP787 ZFP655 RABEPK ZFP650 4732466D17RIK EXOSC4 WDR42A GPHN 2610528J11RIK 1110003E01RIK MDH1 1200014M14RIK AW209491 MUT 1700123L14RIK 2610036D13RIK PHF14 RBM3 MSL1 PHF21A ARL10 INSR JADE2 P2RX7 LINC00662 CCDC101 PPM1B KANSL1L CRYZL1 ANAPC16 TMCC1 CDH8 RBM11 CNPY2 HSPA1L CUL2 PLBD2 LARP7 TECPR2 ZNF302 CUX1 MOB2 CYTH2 SEC22C EIF4E3 ROBO2 ADAMTS9-AS2 CXXC1 LINC01314 ATF7 ATP5F1COX15 TMEM30A NSMCE4A TM2D2 RHBDD3 ATXN2 NFS1 3110001I20RIK BC038156 C330002I19RIK ZFYVE20 POLI TOMM70A LOC100047782 2410012H22RIK RILP A230062G08RIK PTTG1IP RAB1 AFAP1L1 LYRM5 2310026E23RIK SLC7A6OS MAT2B 4932438A13RIK LRRC8A SMO NUPL2
# Python
gget.enrichr(
genes = [
"PHF14", "RBM3", "MSL1", "PHF21A", "ARL10", "INSR", "JADE2", "P2RX7",
"LINC00662", "CCDC101", "PPM1B", "KANSL1L", "CRYZL1", "ANAPC16", "TMCC1",
"CDH8", "RBM11", "CNPY2", "HSPA1L", "CUL2", "PLBD2", "LARP7", "TECPR2",
"ZNF302", "CUX1", "MOB2", "CYTH2", "SEC22C", "EIF4E3", "ROBO2",
"ADAMTS9-AS2", "CXXC1", "LINC01314", "ATF7", "ATP5F1"
],
database = "ChEA_2022",
background_list = [
"NSUN3","POLRMT","NLRX1","SFXN5","ZC3H12C","SLC25A39","ARSG",
"DEFB29","PCMTD2","ACAA1A","LRRC1","2810432D09RIK","SEPHS2",
"SAC3D1","TMLHE","LOC623451","TSR2","PLEKHA7","GYS2","ARHGEF12",
"HIBCH","LYRM2","ZBTB44","ENTPD5","RAB11FIP2","LIPT1",
"INTU","ANXA13","KLF12","SAT2","GAL3ST2","VAMP8","FKBPL",
"AQP11","TRAP1","PMPCB","TM7SF3","RBM39","BRI3","KDR","ZFP748",
"NAP1L1","DHRS1","LRRC56","WDR20A","STXBP2","KLF1","UFC1",
"CCDC16","9230114K14RIK","RWDD3","2610528K11RIK","ACO1",
"CABLES1", "LOC100047214","YARS2","LYPLA1","KALRN","GYK",
"ZFP787","ZFP655","RABEPK","ZFP650","4732466D17RIK","EXOSC4",
"WDR42A","GPHN","2610528J11RIK","1110003E01RIK","MDH1","1200014M14RIK",
"AW209491","MUT","1700123L14RIK","2610036D13RIK",
"PHF14", "RBM3", "MSL1", "PHF21A", "ARL10", "INSR", "JADE2",
"P2RX7", "LINC00662", "CCDC101", "PPM1B", "KANSL1L", "CRYZL1",
"ANAPC16", "TMCC1","CDH8", "RBM11", "CNPY2", "HSPA1L", "CUL2",
"PLBD2", "LARP7", "TECPR2", "ZNF302", "CUX1", "MOB2", "CYTH2",
"SEC22C", "EIF4E3", "ROBO2", "ADAMTS9-AS2", "CXXC1", "LINC01314", "ATF7",
"ATP5F1""COX15","TMEM30A","NSMCE4A","TM2D2","RHBDD3","ATXN2","NFS1",
"3110001I20RIK","BC038156","C330002I19RIK","ZFYVE20","POLI","TOMM70A",
"LOC100047782","2410012H22RIK","RILP","A230062G08RIK",
"PTTG1IP","RAB1","AFAP1L1", "LYRM5","2310026E23RIK",
"SLC7A6OS","MAT2B","4932438A13RIK","LRRC8A","SMO","NUPL2"
],
plot=True
)
→ Provée factores de transcripción relacionados a los genes de interés y controlados con la lista de genes background de la base de datos ChEA 2022. En Python, plot=True permite la visualización de resultados:

Genere una imagen de la vía de señalización de células KEGG con los genes del análisis de enriquecimiento resaltados:
Esta función está disponible gracias a un PR de Noriaki Sato.
gget enrichr -db pathway --kegg_out kegg.png --kegg_rank 1 ZBP1 IRF3 RIPK1
# Python
gget.enrichr(["ZBP1", "IRF3", "RIPK1"], database="pathway", kegg_out="kegg.png", kegg_rank=1)
→ Además de los resultados estándar gget enrichr, el argumento kegg_out guarda una imagen con los genes del análisis de enriquecimiento resaltados guardado como kegg.png:
El siguiente ejemplo fue enviado por Dylan Lawless a través de un PR (con ajustes de Laura Luebbert):
Use gget enrichr en R y cree unq visualización similar usando ggplot.
TENGA EN CUENTA el cambio de ejes en comparación con la visualización en Python.
system("pip install gget")
install.packages("reticulate")
library(reticulate)
gget <- import("gget")
# Perform enrichment analysis on a list of genes
df <- gget$enrichr(list("ACE2", "AGT", "AGTR1"), database = "ontology")
# Count number of overlapping genes
df$overlapping_genes_count <- lapply(df$overlapping_genes, length) |> as.numeric()
# Only keep the top 15 results
df <- df[1:15, ]
# Plot
library(ggplot2)
df |>
ggplot() +
geom_bar(aes(
x = -log10(adj_p_val),
y = reorder(path_name, -adj_p_val)
),
stat = "identity",
fill = "lightgrey",
width = 0.5,
color = "black") +
geom_text(
aes(
y = path_name,
x = (-log10(adj_p_val)),
label = overlapping_genes_count
),
nudge_x = 0.75,
show.legend = NA,
color = "red"
) +
geom_text(
aes(
y = Inf,
x = Inf,
hjust = 1,
vjust = 1,
label = "# of overlapping genes"
),
show.legend = NA,
color = "red"
) +
geom_vline(linetype = "dotted", linewidth = 1, xintercept = -log10(0.05)) +
ylab("Pathway name") +
xlab("-log10(adjusted P value)")
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget enrichr en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z, Meirelles GV, Clark NR, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013; 128(14). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-128
-
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM, Lachmann A, McDermott MG, Monteiro CD, Gundersen GW, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016; gkw377. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw377
-
Xie Z, Bailey A, Kuleshov MV, Clarke DJB., Evangelista JE, Jenkins SL, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML, Kropiwnicki E, Jagodnik KM, Jeon M, & Ma’ayan A. Gene set knowledge discovery with Enrichr. Current Protocols, 1, e90. 2021. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.90.
Si trabaja con conjuntos de datos no humanos/ratón, cite también:
- Kuleshov MV, Diaz JEL, Flamholz ZN, Keenan AB, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML, Cagan RL, Ma'ayan A. modEnrichr: a suite of gene set enrichment analysis tools for model organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 2;47(W1):W183-W190. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz347. PMID: 31069376; PMCID: PMC6602483.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget gpt 💬
Genera texto en lenguaje natural basado en mensaje de entrada. gget gpt use la API 'openai.ChatCompletion.create' de OpenAI.
Este módulo, incluido su código, documentación y pruebas unitarias, fue escrito en parte por Chat-GTP3 de OpenAI.
TENGA EN CUENTA:
Las llamadas a la API de OpenAI solo son 'gratuitas' durante los primeros tres meses después de generar su cuenta de OpenAI (OpenAI proporciona un crédito de $5 que vence).
Puede definir un límite de facturación mensual estricto (por ejemplo, $1) aquí.
Vea sus precios y preguntas frecuentes aquí.
Obtenga su clave API de OpenAI aquí.
Regresa: El texto generado (str).
Antes de usar gget gpt por primera vez, corre gget setup gpt / gget.setup("gpt") (ver también gget setup).
Parámetros posicionales
prompt
Mensaje de entrada basado en el cual generar texto (str).
api_key
Su clave API de OpenAI (str) (obtenga su clave API).
Parámetros optionales
-m --model
El nombre del algoritmo GPT que se usará para generar el texto (str). Por defecto: "gpt-3.5-turbo".
See https://platform.openai.com/docs/models/gpt-4 for more information on the available models.
-temp --temperature
Valor entre 0 y 2 que controla el nivel de aleatoriedad y creatividad en el texto generado (float).
Los valores más altos resultan en un texto más creativo y variado. Por defecto: 1.
-tp --top_p
Controla la diversidad del texto generado como alternativa al muestreo con --temperature (float).
Los valores más altos resultan en un texto más diverso e inesperado. Por defecto: 1.
Tenga en cuenta que OpenAI recomienda modificar --top_p o el parámetro --temperature, pero no ambas.
-s --stop
Una secuencia de tokens para marcar el final del texto generado (str). Por defecto: None.
-mt --max_tokens
Controla la longitud máxima del texto generado, en tokens (int). Por defecto: 200.
-pp --presence_penalty
Número entre -2.0 y 2.0. Los valores más altos aumentan la probabilidad de que el modelo hable sobre temas nuevos (float). Por defecto: 0.
-fp --frequency_penalty
Número entre -2.0 y 2.0. Los valores más altos reducen la probabilidad de que el modelo repita la misma línea palabra por palabra (float). Por defecto: 0.
-lb --logit_bias
Un diccionario que especifica un sesgo hacia ciertos tokens en el texto generado (dict). Por defecto: None.
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.txt. Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Por ejemplo
gget gpt "Cómo estás hoy GPT?" su_clave_api
# Python
print(gget.gpt("Cómo estás hoy GPT?", "su_clave_api"))

Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget info 💡
Obtenga información detallada sobre genes y transcripciones de Ensembl, UniProt y NCBI utilizando sus IDs del tipo Ensembl.
Regresa: Resultados en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV (Python).
Parámetro posicional
ens_ids
Uno o más ID del tipo Ensembl.
NOTA: Proporcionar una lista de más de 1000 ID de Ensembl a la vez puede provocar un error del servidor (para procesar más de 1000 ID, divida la lista de ID en fragmentos de 1000 ID y ejecútelos por separado).
Parámetros optionales
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.csv (o .json). Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Banderas
-n --ncbi
DESACTIVA los resultados de NCBI.
Para Python: ncbi=False evita la incluida de datos de NCBI (por defecto: True).
-u --uniprot
DESACTIVA los resultados de UniProt.
Para Python: uniprot=False evita la incluida de datos de UniProt (por defecto: True).
-pdb --pdb
INCLUYE PDB IDs en los resultados (podría aumentar el tiempo de ejecución).
Para Python: pdb=True incluye IDs de PDB en los resultados (por defecto: False).
-csv --csv
Solo para la Terminal. Regresa los resultados en formato CSV.
Para Python, usa json=True para regresar los resultados en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo para la Terminal. Impide la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para imipidir la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
wrap_text
Solo para Python. wrap_text=True muestra los resultados con texto envuelto para facilitar la lectura (por defecto: False).
Por ejemplo
gget info ENSG00000034713 ENSG00000104853 ENSG00000170296
# Python
gget.info(["ENSG00000034713", "ENSG00000104853", "ENSG00000170296"])
→ Regresa información detallada sobre cada ID de Ensembl ingresada:
| uniprot_id | ncbi_gene_id | primary_gene_name | synonyms | protein_names | ensembl_description | uniprot_description | ncbi_description | biotype | canonical_transcript | ... | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000034713 | P60520 | 11345 | GABARAPL2 | [ATG8, ATG8C, FLC3A, GABARAPL2, GATE-16, GATE16, GEF-2, GEF2] | Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein like 2 (GABA(A) receptor-associated protein-like 2)... | GABA type A receptor associated protein like 2 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:13291] | FUNCTION: Ubiquitin-like modifier involved in intra- Golgi traffic (By similarity). Modulates intra-Golgi transport through coupling between NSF activity and ... | Enables ubiquitin protein ligase binding activity. Involved in negative regulation of proteasomal protein catabolic process and protein... | protein_coding | ENST00000037243.7 | ... |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | ... |
More examples
Citar
Si utiliza gget info en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
-
Sayers EW, Beck J, Bolton EE, Brister JR, Chan J, Comeau DC, Connor R, DiCuccio M, Farrell CM, Feldgarden M, Fine AM, Funk K, Hatcher E, Hoeppner M, Kane M, Kannan S, Katz KS, Kelly C, Klimke W, Kim S, Kimchi A, Landrum M, Lathrop S, Lu Z, Malheiro A, Marchler-Bauer A, Murphy TD, Phan L, Prasad AB, Pujar S, Sawyer A, Schmieder E, Schneider VA, Schoch CL, Sharma S, Thibaud-Nissen F, Trawick BW, Venkatapathi T, Wang J, Pruitt KD, Sherry ST. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D33-D43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1044. PMID: 37994677; PMCID: PMC10767890.
-
The UniProt Consortium , UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D523–D531, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1052
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget muscle 🦾
Alinea múltiples secuencias de nucleótidos o aminoácidos usando el algoritmo Muscle5.
Regresa: Salida estándar (STDOUT) en formato ClustalW o archivo de tipo 'aligned FASTA' (.afa).
Parámetro posicional
fasta
Lista de secuencias o ruta al archivo FASTA o .txt que contiene las secuencias de nucleótidos o aminoácidos que se van a alinear.
Parámetros optionales
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.afa. Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Banderas
-s5 --super5
Alinea las secuencies usando el algoritmo Super5 en lugar del algoritmo Parallel Perturbed Probcons (PPP) para disminuir el tiempo y la memoria usada durante la corrida.
Use para ingresos grandes (unos cientos secuencias).
-q --quiet
Solo para la Terminal. Impide la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para imipidir la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
Por ejemplo
gget muscle MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS
# Python
gget.muscle(["MSSSSWLLLSLVAVTAAQSTIEEQAKTFLDKFNHEAEDLFYQSSLAS", "MSSSSWLLLSLVEVTAAQSTIEQQAKTFLDKFHEAEDLFYQSLLAS"])
gget muscle fasta.fa
# Python
gget.muscle("fasta.fa")
→ Regresa las secuencias alineadas con coloración ClustalW. (Para devolver un archivo FASTA alineado (.afa), use el argumento --out (o save=True en Python).) En este ejemplo, el archivo 'fasta.fa' incluye varias secuencias para alineación (por ejemplo, isoformas devueltas desde gget seq).

También puede ver archivos FASTA alineados devueltos por gget.muscle usando programas como alv:
# Python
!pip install biopython
!pip install alv
from Bio import AlignIO
import alv
gget.muscle("fasta.fa", out="fasta_aligned.afa")
msa = AlignIO.read("fasta_aligned.afa", "fasta")
alv.view(msa)
More examples
Citar
Si utiliza gget muscle en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Edgar RC (2021), MUSCLE v5 enables improved estimates of phylogenetic tree confidence by ensemble bootstrapping, bioRxiv 2021.06.20.449169. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.20.449169
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget mutate 🧟
Recibe secuencias de nucleótidos y mutaciones (en anotación de mutación estándar) y devuelve versiones mutadas de las secuencias según las mutaciones proporcionadas.
Resultado: Guarda las secuencias mutadas en formato FASTA (o devuelve una lista que contiene las secuencias mutadas si out=None).
Este módulo fue coescrito por Joseph Rich.
Argumento posicional
sequences
Ruta al archivo FASTA que contiene las secuencias a ser mutadas, por ejemplo, 'path/to/seqs.fa'.
Los identificadores de las secuencias que siguen al carácter '>' deben corresponder a los identificadores en la columna seq_ID de mutations.
Formato de ejemplo del archivo FASTA:
>seq1 (or ENSG00000106443)
ACTGCGATAGACT
>seq2
AGATCGCTAG
Alternativamente: Secuencia(s) de entrada como una cadena o lista, por ejemplo, 'AGCTAGCT'.
NOTA: Solo se utilizarán las letras hasta el primer espacio o punto como identificadores de secuencias; se ignorarán los números de versión de los IDs de Ensembl.
NOTA: Cuando la entrada sequences es un archivo fasta de genoma, consulte también el argumento gtf a continuación.
Argumentos requeridos
-m --mutations
Ruta al archivo csv o tsv (por ejemplo, 'path/to/mutations.csv') o marco de datos (objeto DataFrame) que contiene información sobre las mutaciones en el siguiente formato (las columnas 'notes' y 'mut_ID' son opcionales):
| mutation | mut_ID | seq_ID | notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| c.2C>T | mut1 | seq1 | -> Aplicar mutación 1 a la secuencia 1 |
| c.9_13inv | mut2 | seq2 | -> Aplicar mutación 2 a la secuencia 2 |
| c.9_13inv | mut2 | seq4 | -> Aplicar mutación 2 a la secuencia 4 |
| c.9_13delinsAAT | mut3 | seq4 | -> Aplicar mutación 3 a la secuencia 4 |
| ... | ... | ... |
'mutation' = Columna que contiene las mutaciones a realizar escritas en la anotación estándar de mutaciones
'mut_ID' = Columna que contiene el identificador para cada mutación
'seq_ID' = Columna que contiene los identificadores de las secuencias a ser mutadas (deben corresponder a la cadena que sigue al carácter '>' en el archivo FASTA 'sequences'; NO incluya espacios ni puntos)
Alternativamente: Mutación(es) de entrada como una cadena o lista, por ejemplo, 'c.2C>T'.
Si se proporciona una lista, el número de mutaciones debe ser igual al número de secuencias de entrada.
Para usar desde la terminal (bash): Enciérrale las anotaciones de mutación individuales entre comillas para evitar errores de análisis.
Argumentos opcionales relacionados con la entrada
-mc --mut_column
Nombre de la columna que contiene las mutaciones a realizar en mutations. Predeterminado: 'mutation'.
-sic --seq_id_column
Nombre de la columna que contiene los ID de las secuencias a ser mutadas en mutations. Predeterminado: 'seq_ID'.
-mic --mut_id_column
Nombre de la columna que contiene los IDs de cada mutación en mutations. Predeterminado: Igual que mut_column.
-gtf --gtf
Ruta a un archivo .gtf. Al proporcionar un archivo fasta de genoma como entrada para 'sequences', puede proporcionar un archivo .gtf aquí y las secuencias de entrada se definirán de acuerdo con los límites de los transcritos, por ejemplo, 'path/to/genome_annotation.gtf'. Predeterminado: Ninguno
-gtic --gtf_transcript_id_column
Nombre de la columna en el archivo de entrada mutations que contiene el ID del transcrito. En este caso, la columna seq_id_column debe contener el número de cromosoma.
Requerido cuando se proporciona gtf. Predeterminado: Ninguno
Argumentos opcionales para la generación/filtrado de secuencias mutantes
-k --k
Longitud de las secuencias que flanquean la mutación. Predeterminado: 30.
Si k > longitud total de la secuencia, se mantendrá toda la secuencia.
-msl --min_seq_len
Longitud mínima de la secuencia de salida mutante, por ejemplo, 100. Las secuencias mutantes más pequeñas que esto serán descartadas. Predeterminado: Ninguno
-ma --max_ambiguous
Número máximo de caracteres 'N' (o 'n') permitidos en la secuencia de salida, por ejemplo, 10. Predeterminado: Ninguno (no se aplicará filtro de caracteres ambiguos)
Banderas opcionales para la generación/filtrado de secuencias mutantes
-ofr --optimize_flanking_regions
Elimina nucleótidos de cualquiera de los extremos de la secuencia mutante para asegurar (cuando sea posible) que la secuencia mutante no contenga ningún k-mer que también se encuentre en la secuencia de tipo salvaje/entrada.
-rswk --remove_seqs_with_wt_kmers
Elimina las secuencias de salida donde al menos un k-mer también está presente en la secuencia de tipo salvaje/entrada en la misma región.
Cuando se utiliza con --optimize_flanking_regions, solo se eliminarán las secuencias para las cuales un k-mer de tipo salvaje aún está presente después de la optimización.
-mio --merge_identical_off
No fusionar secuencias mutantes idénticas en la salida (por defecto, las secuencias idénticas se fusionarán concatenando los encabezados de secuencia para todas las secuencias idénticas).
Argumentos opcionales para generar salida adicional
Esta salida se activa utilizando la bandera --update_df y se almacenará en una copia del DataFrame mutations.
-udf_o --update_df_out
Ruta al archivo csv de salida que contiene el DataFrame actualizado, por ejemplo, 'path/to/mutations_updated.csv'. Solo válido cuando se usa con --update_df.
Predeterminado: Ninguno -> el nuevo archivo csv se guardará en el mismo directorio que el DataFrame mutations con el apéndice '_updated'
-ts --translate_start
(int o str) La posición en la secuencia de nucleótidos de entrada para comenzar a traducir, por ejemplo, 5. Si se proporciona una cadena, debe corresponder a un nombre de columna en mutations que contenga las posiciones de inicio del marco de lectura abierto para cada secuencia/mutación. Solo válido cuando se usa con --translate.
Predeterminado: traduce desde el principio de cada secuencia
-te --translate_end
(int o str) La posición en la secuencia de nucleótidos de entrada para finalizar la traducción, por ejemplo, 35. Si se proporciona una cadena, debe corresponder a un nombre de columna en mutations que contenga las posiciones de fin del marco de lectura abierto para cada secuencia/mutación. Solo válido cuando se usa con --translate.
Predeterminado: traduce hasta el final de cada secuencia
Banderas opcionales para modificar salida adicional
-udf --update_df
Actualiza el DataFrame de entrada mutations para incluir columnas adicionales con el tipo de mutación, la secuencia de nucleótidos de tipo salvaje y la secuencia de nucleótidos mutante (solo válido si mutations es un archivo .csv o .tsv).
-sfs --store_full_sequences
Incluye las secuencias completas de tipo salvaje y mutantes en el DataFrame actualizado mutations (no solo la sub-secuencia con flancos de longitud k). Solo válido cuando se usa con --update_df.
-tr --translate
Agrega columnas adicionales al DataFrame actualizado mutations que contienen las secuencias de aminoácidos de tipo salvaje y mutantes. Solo válido cuando se usa con --store_full_sequences.
Argumentos generales opcionales
-o --out
Ruta al archivo FASTA de salida que contiene las secuencias mutadas, por ejemplo, 'path/to/output_fasta.fa'.
Predeterminado: Ninguno -> devuelve una lista de las secuencias mutadas a la salida estándar.
Los identificadores (que siguen al '>') de las secuencias mutadas en el FASTA de salida serán '>[seq_ID]_[mut_ID]'.
Banderas generales opcionales
-q --quiet
Solo en línea de comandos. Previene que se muestre información de progreso.
Python: Usa verbose=False para prevenir que se muestre información de progreso.
Ejemplos
gget mutate ATCGCTAAGCT -m 'c.4G>T'
# Python
gget.mutate("ATCGCTAAGCT", "c.4G>T")
→ Devuelve ATCTCTAAGCT.
Lista de secuencias con una mutación para cada secuencia proporcionada en una lista:
gget mutate ATCGCTAAGCT TAGCTA -m 'c.4G>T' 'c.1_3inv' -o mut_fasta.fa
# Python
gget.mutate(["ATCGCTAAGCT", "TAGCTA"], ["c.4G>T", "c.1_3inv"], out="mut_fasta.fa")
→ Guarda el archivo 'mut_fasta.fa' que contiene:
>seq1_mut1
ATCTCTAAGCT
>seq2_mut2
GATCTA
Una mutación aplicada a varias secuencias con k ajustado:
gget mutate ATCGCTAAGCT TAGCTA -m 'c.1_3inv' -k 3
# Python
gget.mutate(["ATCGCTAAGCT", "TAGCTA"], "c.1_3inv", k=3)
→ Devuelve ['CTAGCT', 'GATCTA'].
Agregar mutaciones a un genoma completo con salida extendida
Entrada principal:
- información de mutación como un CSV de
mutations(teniendoseq_id_columnque contenga información de cromosoma, ymut_columnque contenga información de mutación con respecto a las coordenadas del genoma) - el genoma como el archivo
sequences
Dado que estamos pasando la ruta a un archivo gtf al argumento gtf, se respetarán los límites de los transcritos (el genoma se dividirá en transcritos). gtf_transcript_id_column especifica el nombre de la columna en mutations que contiene los IDs de los transcritos correspondientes a los IDs de transcritos en el archivo gtf.
El argumento optimize_flanking_regions maximiza la longitud de las secuencias resultantes que contienen la mutación manteniendo la especificidad (ningún k-mer de tipo salvaje se mantendrá).
update_df activa la creación de un nuevo archivo CSV con información actualizada sobre cada secuencia de entrada y salida. Este nuevo archivo CSV se guardará como update_df_out. Dado que store_full_sequences está activado, este nuevo archivo CSV no solo contendrá las secuencias de salida (restringidas en tamaño por las regiones flanqueantes de tamaño k), sino también las secuencias completas de entrada y salida. Esto nos permite observar la mutación en el contexto de la secuencia completa. Por último, también estamos agregando las versiones traducidas de las secuencias completas mediante la activación de la bandera translate, para que podamos observar cómo cambia la secuencia de aminoácidos resultante. Los argumentos translate_start y translate_end especifican los nombres de las columnas en mutations que contienen las posiciones de inicio y fin del marco de lectura abierto (posiciones de inicio y fin para traducir la secuencia de nucleótidos a una secuencia de aminoácidos), respectivamente.
gget mutate \
-m mutations_input.csv \
-o mut_fasta.fa \
-k 4 \
-sic Chromosome \
-mic Mutation \
-gtf genome_annotation.gtf \
-gtic Ensembl_Transcript_ID \
-ofr \
-update_df \
-udf_o mutations_updated.csv \
-sfs \
-tr \
-ts Translate_Start \
-te Translate_End \
genome_reference.fa
# Python
gget.mutate(
sequences="genome_reference.fa",
mutations="mutations_input.csv",
out="mut_fasta.fa",
k=4,
seq_id_column="Chromosome",
mut_column="Mutation",
gtf="genome_annotation.gtf",
gtf_transcript_id_column="Ensembl_Transcript_ID",
optimize_flanking_regions=True,
update_df=True,
update_df_out="mutations_updated.csv",
store_full_sequences=True,
translate=True,
translate_start="Translate_Start",
translate_end="Translate_End"
)
→ Toma un genoma fasta ('genome_reference.fa') y un archivo gtf ('genome_annotation.gtf') (estos se pueden descargar usando gget ref), así como un archivo 'mutations_input.csv' que contiene:
| Chromosome | Mutation | Ensembl_Transcript_ID | Translate_Start | Translate_End |
|------------|-------------------|------------------------|-----------------|---------------|
| 1 | g.224411A>C | ENST00000193812 | 0 | 100 |
| 8 | g.25111del | ENST00000174411 | 0 | 294 |
| X | g.1011_1012insAA | ENST00000421914 | 9 | 1211 |
→ Guarda el archivo 'mut_fasta.fa' que contiene:
>1:g.224411A>C
TGCTCTGCT
>8:g.25111del
GAGTCGAT
>X:g.1011_1012insAA
TTAGAACTT
→ Guarda el archivo 'mutations_updated.csv' que contiene:
| Chromosome | Mutation | Ensembl_Transcript_ID | mutation_type | wt_sequence | mutant_sequence | wt_sequence_full | mutant_sequence_full | wt_sequence_aa_full | mutant_sequence_aa_full |
|------------|-------------------|------------------------|---------------|-------------|-----------------|-------------------|----------------------|---------------------|-------------------------|
| 1 | g.224411A>C | ENSMUST00000193812 | Substitution | TGCTATGCT | TGCTCTGCT | ...TGCTATGCT... | ...TGCTCTGCT... | ...CYA... | ...CSA... |
| 8 | g.25111del | ENST00000174411 | Deletion | GAGTCCGAT | GAGTCGAT | ...GAGTCCGAT... | ...GAGTCGAT... | ...ESD... | ...ES... |
| X | g.1011_1012insAA | ENST00000421914 | Insertion | TTAGCTT | TTAGAACTT | ...TTAGCTT... | ...TTAGAACTT... | ...A... | ...EL... |
Citar
Si utiliza gget mutate en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
- Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget opentargets 🎯
Obtenga enfermedades o fármacos asociados con ciertos genes desde OpenTargets.
Formato de salida: JSON/CSV (línea de comandos) o marco de datos (Python).
Este módulo fue escrito por Sam Wagenaar.
Argumento posicional
ens_id
ID de gen Ensembl, por ejemplo, ENSG00000169194.
Argumentos opcionales
-r --resource
Define el tipo de información a devolver en la salida. Predeterminado: 'diseases' (enfermedades).
Los recursos posibles son:
| Recurso | Valor devuelto | Filtros válidos | Fuentes |
|---|---|---|---|
diseases | Enfermedades asociadas | Ninguno | Varias:etc. |
drugs | Fármacos asociados | disease_id | ChEMBL |
tractability | Datos de tractabilidad | Ninguno | Open Targets |
pharmacogenetics | Respuestas farmacogenéticas | drug_id | PharmGKB |
expression | Datos de expresión génica (por tejidos, órganos y sistemas anatómicos) | tissue_idanatomical_systemorgan | |
depmap | Datos de efecto gen→enfermedad en DepMap. | tissue_id | DepMap Portal |
interactions | Interacciones proteína⇄proteína | protein_a_idprotein_b_idgene_b_id |
-l --limit
Limitar el número de resultados, por ejemplo, 10. Predeterminado: Sin límite.
Nota: No es compatible con los recursos tractability y depmap.
-o --out
Ruta al archivo JSON donde se guardarán los resultados, por ejemplo, path/to/directory/results.json. Predeterminado: Salida estándar.
Python: save=True guardará la salida en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Argumentos opcionales de filtrado
-fd --filter_disease disease_id
Filtrar por ID de enfermedad, por ejemplo, 'EFO_0000274'. Válido solo para el recurso drugs.
-fc --filter_drug drug_id
Filtrar por ID de fármaco, por ejemplo, 'CHEMBL1743081'. Válido solo para el recurso pharmacogenetics.
-ft --filter_tissue tissue_id
Filtrar por ID de tejido, por ejemplo, 'UBERON_0000473'. Válido solo para los recursos expression y depmap.
-fa --filter_anat_sys
Filtrar por sistema anatómico, por ejemplo, 'sistema nervioso'. Válido solo para el recurso expression.
-fo --filter_organ anatomical_system
Filtrar por órgano, por ejemplo, 'cerebro'. Válido solo para el recurso expression.
-fpa --filter_protein_a protein_a_id
Filtrar por ID de la primera proteína en la interacción, por ejemplo, 'ENSP00000304915'. Válido solo para el recurso interactions.
-fpb --filter_protein_b protein_b_id
Filtrar por ID de la segunda proteína en la interacción, por ejemplo, 'ENSP00000379111'. Válido solo para el recurso interactions.
-fgb --filter_gene_b gene_b_id
Filtrar por ID de gen de la segunda proteína en la interacción, por ejemplo, 'ENSG00000077238'. Válido solo para el recurso interactions.
filters
Solo para Python. Un diccionario de filtros, por ejemplo:
{'disease_id': ['EFO_0000274', 'HP_0000964']}
`filter_mode`
Solo para Python. `filter_mode='or'` combina filtros de diferentes IDs con lógica OR.
`filter_mode='and'` combina filtros de diferentes IDs con lógica AND (predeterminado).
**Banderas**
`-csv` `--csv`
Solo en línea de comandos. Devuelve la salida en formato CSV, en lugar de formato JSON.
Python: Use `json=True` para devolver la salida en formato JSON.
`-q` `--quiet`
Solo en línea de comandos. Evita que se muestre la información de progreso.
Python: Use `verbose=False` para evitar que se muestre la información de progreso.
`-or` `--or`
Solo en línea de comandos. Los filtros se combinan con lógica OR. Predeterminado: lógica AND.
`wrap_text`
Solo para Python. `wrap_text=True` muestra el marco de datos con texto ajustado para facilitar la lectura (predeterminado: False).
### Ejemplos
**Obtenga enfermedades asociadas a un gen específico:**
```bash
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r diseases -l 1
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='diseases', limit=1)
→ Devuelve la principal enfermedad asociada con el gen ENSG00000169194.
| id | name | description | score |
|---|---|---|---|
| EFO_0000274 | atopic eczema | A chronic inflammatory genetically determined disease of the skin ... | 0.66364347241831 |
Obtener medicamentos asociados para un gen específico:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r drugs -l 2
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='drugs', limit=2)
→ Devuelve los 2 principales medicamentos asociados con el gen ENSG00000169194.
| id | name | type | action_mechanism | description | synonyms | trade_names | disease_id | disease_name | trial_phase | trial_status | trial_ids | approved |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHEMBL1743081 | TRALOKINUMAB | Antibody | Interleukin‑13 inhibitor | Antibody drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of IV ... | ['CAT-354', 'Tralokinumab'] | ['Adbry', 'Adtralza'] | EFO_0000274 | atopic eczema | 4 | [] | True | |
| CHEMBL4297864 | CENDAKIMAB | Antibody | Interleukin‑13 inhibitor | Antibody drug with a maximum clinical trial phase of III ... | [ABT-308, Abt-308, CC-93538, Cendakimab, RPC-4046] | [] | EFO_0004232 | eosinophilic esophagitis | 3 | Recruiting | [NCT04991935] | False |
Note: Los trial_ids devueltos son identificadores de ClinicalTrials.gov
Obtenga datos de trazabilidad para un gen específico:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r tractability
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='tractability')
→ Devuelve datos de trazabilidad para el gen ENSG00000169194.
| label | modality |
|---|---|
| High-Quality Pocket | Small molecule |
| Approved Drug | Antibody |
| GO CC high conf | Antibody |
| UniProt loc med conf | Antibody |
| UniProt SigP or TMHMM | Antibody |
Obtenga respuestas farmacogenéticas para un gen específico:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r pharmacogenetics -l 1
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='pharmacogenetics', limit=1)
→ Devuelve respuestas farmacogenéticas para el gen ENSG00000169194.
| rs_id | genotype_id | genotype | variant_consequence_id | variant_consequence_label | drugs | phenotype | genotype_annotation | response_category | direct_target | evidence_level | source | literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1295686 | 5_132660151_T_T,T | TT | SO:0002073 | no_sequence_alteration | id name 0 None hepatitis vaccines | increased risk for non‑immune response to the hepatitis B vaccine | Patients with the TT genotype may be at increased risk for non-immune response to the hepatitis B vaccine... | efficacy | False | 3 | pharmgkb | [21111021] |
Note: Los identificadores de literature devueltos son identificadores de PMC de Europa
Obtenga tejidos donde un gen se expresa más:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r expression -l 2
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='expression', limit=2)
→ Devuelve los 2 tejidos principales donde se expresa más el gen ENSG00000169194.
| tissue_id | tissue_name | rna_zscore | rna_value | rna_unit | rna_level | anatomical_systems | organs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBERON_0000473 | testis | 5 | 1026 | 3 | [reproductive system] | [reproductive organ, reproductive structure] | |
| CL_0000542 | EBV‑transformed lymphocyte | 1 | 54 | 2 | [hemolymphoid system, immune system, lymphoid system] | [immune organ] |
Obtenga datos sobre el efecto de la enfermedad genética de DepMap para un gen específico:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r depmap
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='depmap')
→ Devuelve datos del efecto de la enfermedad del gen DepMap para el gen ENSG00000169194.
| depmap_id | expression | effect | tissue_id | tissue_name | cell_line_name | disease_cell_line_id | disease_name | mutation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACH‑001532 | 0.176323 | 0.054950 | UBERON_0002113 | kidney | JMU-RTK-2 | None | Rhabdoid Cancer | None |
Obtener interacciones proteína-proteína para un gen específico:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r interactions -l 2
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='interactions', limit=2)
→ Devuelve las 2 interacciones proteína-proteína principales para el gen ENSG00000169194.
| evidence_score | evidence_count | source_db | protein_a_id | gene_a_id | gene_a_symbol | role_a | taxon_a | protein_b_id | gene_b_id | gene_b_symbol | role_b | taxon_b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.999 | 3 | string | ENSP00000304915 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | ENSP00000379111 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | unspecified role | 9606 |
| 0.999 | 3 | string | ENSP00000304915 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | ENSP00000360730 | ENSG00000131724 | IL13RA1 | unspecified role | 9606 |
Obtenga interacciones proteína-proteína para un gen específico, filtrando por ID de proteínas y genes:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r interactions -fpa P35225 --filter_gene_b ENSG00000077238
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets('ENSG00000169194', resource='interactions', filters={'protein_a_id': 'P35225', 'gene_b_id': 'ENSG00000077238'})
→ Devuelve interacciones proteína-proteína para el gen ENSG00000169194, donde la primera proteína es P35225 y el segundo gen es ENSG00000077238:
| evidence_score | evidence_count | source_db | protein_a_id | gene_a_id | gene_a_symbol | role_a | taxon_a | protein_b_id | gene_b_id | gene_b_symbol | role_b | taxon_b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | 3 | reactome | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | P24394 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | unspecified role | 9606 |
| None | 2 | signor | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | regulator | 9606 | P24394 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | regulator target | 9606 |
Obtenga interacciones proteína-proteína para un gen específico, filtrando por ID de proteína o gen:
gget opentargets ENSG00000169194 -r interactions -fpa P35225 --filter_gene_b ENSG00000077238 ENSG00000111537 --or -l 5
# Python
import gget
gget.opentargets(
'ENSG00000169194',
resource='interactions',
filters={'protein_a_id': 'P35225', 'gene_b_id': ['ENSG00000077238', 'ENSG00000111537']},
filter_mode='or',
limit=5
)
→ Devuelve interacciones proteína-proteína para el gen ENSG00000169194, donde la primera proteína es P35225 o el segundo gen es ENSG00000077238 o ENSG00000111537. | evidence_score | evidence_count | source_db | protein_a_id | gene_a_id | gene_a_symbol | role_a | taxon_a | protein_b_id | gene_b_id | gene_b_symbol | role_b | taxon_b | |----------------|----------------|-----------|-----------------|-----------------|---------------|-----------------------|---------|-----------------|-----------------|---------------|-----------------------|---------| | 0.999 | 3 | string | ENSP00000304915 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | ENSP00000379111 | ENSG00000077238 | IL4R | unspecified role | 9606 | | 0.961 | 2 | string | ENSP00000304915 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | ENSP00000229135 | ENSG00000111537 | IFNG | unspecified role | 9606 | | 0.800 | 9 | intact | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | Q14627 | ENSG00000123496 | IL13RA2 | unspecified role | 9606 | | 0.740 | 6 | intact | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | P78552 | ENSG00000131724 | IL13RA1 | unspecified role | 9606 | | 0.400 | 1 | intact | P35225 | ENSG00000169194 | IL13 | unspecified role | 9606 | Q86XT9 | ENSG00000149932 | TMEM219 | stimulator | 9606 |
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget opentargets en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Ochoa D, Hercules A, Carmona M, Suveges D, Baker J, Malangone C, Lopez I, Miranda A, Cruz-Castillo C, Fumis L, Bernal-Llinares M, Tsukanov K, Cornu H, Tsirigos K, Razuvayevskaya O, Buniello A, Schwartzentruber J, Karim M, Ariano B, Martinez Osorio RE, Ferrer J, Ge X, Machlitt-Northen S, Gonzalez-Uriarte A, Saha S, Tirunagari S, Mehta C, Roldán-Romero JM, Horswell S, Young S, Ghoussaini M, Hulcoop DG, Dunham I, McDonagh EM. The next-generation Open Targets Platform: reimagined, redesigned, rebuilt. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D1353-D1359. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1046. PMID: 36399499; PMCID: PMC9825572.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget pdb 🔮
Obtenga la estructura o los metadatos de una proteína usando data de RCSB Protein Data Bank (PDB).
Regresa: El archivo 'pdb' se regresa en formato PDB. Todos los demás datos se regresan en formato JSON.
Parámetro posicional
pdb_id
ID del tipo PDB, p. ej. '7S7U'.
Parámetros optionales
-r --resource
Define el tipo de información a regresar. Uno de los siguientes:
'pdb': Regresa la estructura de la proteína en formato PDB (regresa por defecto).
'entry': Regresa información sobre las estructuras PDB en el nivel superior de la organización de datos PDB jerárquicos.
'pubmed': Regresa anotaciones de PubMed (datos integrados de PubMed) para la cita principal de un ID PDB.
'assembly': Regresa información sobre estructuras PDB en el nivel de estructura cuaternaria.
'branched_entity': Regresa la descripción de la entidad ramificada (defina el ID de la entidad como identifier).
'nonpolymer_entity': Regresa datos de entidades no poliméricas (defina el ID de la entidad como identifier).
'polymer_entity': Regresa datos de entidades poliméricas (defina el ID de la entidad como identifier).
'uniprot': Regresa anotaciones UniProt para una entidad macromolecular (defina el ID de la entidad como identifier).
'branched_entity_instance': Regresa la descripción de instancia de entidad ramificada (defina el ID de cadena como identifier).
'polymer_entity_instance': Regresa datos de instancia de entidad polimérica (también conocida como cadena) (defina el ID de cadena como identifier).
'nonpolymer_entity_instance': Regresa datos de instancia de entidad no polimérica (defina el ID de cadena como identifier).
-i --identifier
Este parámetro se puede utilizar para definir el ID de ensamblaje, entidad o cadena (po defecto: None). Los IDs de ensamblaje/entidad son números (p. ej., 1) y los IDs de cadena son letras (p. ej., 'A').
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/7S7U.pdb (o 7S7U_entry.json). Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Por ejemplo
gget pdb 7S7U -o 7S7U.pdb
# Python
gget.pdb("7S7U", save=True)
→ Guarda la estructura de 7S7U en formato PDB como '7S7U.pdb' en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Encuentre estructuras cristalinas de PDB para un análisis comparativo de la estructura de proteínas:
# Encuentre IDs de PDB asociados con un ID de Ensembl
gget info ENSG00000130234
# Alternativamente: como que muchas entradas en el PDB no tienen ID de Ensembl vinculados,
# es probable que encuentre más entradas de PDB BLASTing la secuencia contra el PDB:
# Obtenga la secuencia de aminoácidos
gget seq --translate ENSG00000130234 -o gget_seq_results.fa
# BLAST la secuencia de aminoácidos para encontrar estructuras similares en el PDB
gget blast --database pdbaa gget_seq_results.fa
# Obtenga archivos PDB de los IDs de PDB regresados por gget blast para un análisis comparativo
gget pdb 7DQA -o 7DQA.pdb
gget pdb 7CT5 -o 7CT5.pdb
# Encuentre IDs de PDB asociados con un ID de Ensembl
gget.info("ENSG00000130234")
# Alternativamente: como que muchas entradas en el PDB no tienen ID de Ensembl vinculados,
# es probable que encuentre más entradas de PDB BLASTing la secuencia contra el PDB:
# Obtenga la secuencia de aminoácidos
gget.seq("ENSG00000130234", translate=True, save=True)
# BLAST la secuencia de aminoácidos para encontrar estructuras similares en el PDB
gget.blast("gget_seq_results.fa", database="pdbaa")
# Obtenga archivos PDB de los IDs de PDB regresados por gget blast para un análisis comparativo
gget.pdb("7DQA", save=True)
gget.pdb("7CT5", save=True)
→ Este caso de uso ejemplifica cómo encontrar archivos PDB para un análisis comparativo de la estructura de las proteínas asociado con IDs de Ensembl o secuencias de aminoácidos. Los archivos PDB obtenidos también se pueden comparar con las estructuras predichas generadas por gget alphafold. Los archivos PDB se pueden ver de forma interactiva en 3D aquí, o usando programas como PyMOL o Blender. Múltiple archivos PDB se pueden visualizar para comparación aquí.
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget pdb en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.235. PMID: 10592235; PMCID: PMC102472.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget ref 📖
Obtenga enlaces de descarga y metadatos para los genomas de referencia de Ensembl.
Regresa: Resultados en formato JSON.
Parámetro posicional
species
La especie por la cual que se buscará los FTP en el formato género_especies, p. ej. homo_sapiens.
Nota: No se requiere cuando se llama a la bandera --list_species.
Accesos directos: 'human', 'mouse', 'human_grch37' (accede al ensamblaje del genoma GRCh37)
Parámetros optionales
-w --which
Define qué resultados devolver. Por defecto: 'all' -> Regresa todos los resultados disponibles.
Las entradas posibles son uno solo o una combinación de las siguientes (como lista separada por comas):
'gtf' - Regresa la anotación (GTF).
'cdna' - Regresa el transcriptoma (cDNA).
'dna' - Regresa el genoma (DNA).
'cds' - Regresa las secuencias codificantes correspondientes a los genes Ensembl. (No contiene UTR ni secuencia intrónica).
'cdrna' - Regresa secuencias de transcripción correspondientes a genes de ARN no codificantes (ncRNA).
'pep' - Regresa las traducciones de proteínas de los genes Ensembl.
-r --release
Define el número de versión de Ensembl desde el que se obtienen los archivos, p. ej. 104. Default: latest Ensembl release.
-od --out_dir
Ruta al directorio donde se guardarán los archivos FTP, p. ruta/al/directorio/. Por defecto: directorio de trabajo actual.
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.json. Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Banderas
-l --list_species
Enumera todas las especies disponibles. (Para Python: combina con species=None.)
-ftp --ftp
Regresa solo los enlaces FTP solicitados.
-d --download
Solo para Terminal. Descarga los FTP solicitados al directorio actual (requiere curl para ser instalado).
-q --quiet
Solo para la Terminal. Impide la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para imipidir la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
Por ejemplo
Use gget ref en combinación con kallisto | bustools para construir un índice de referencia:
kb ref -i INDEX -g T2G -f1 FASTA $(gget ref --ftp -w dna,gtf homo_sapiens)
→ kb ref crea un índice de referencia utilizando los últimos archivos de ADN y GTF de especies Homo sapiens que le ha pasado gget ref.
Enumere todos los genomas disponibles de la versión 103 de Ensembl:
gget ref --list_species -r 103
# Python
gget.ref(species=None, list_species=True, release=103)
→ Regresa una lista con todos los genomas disponibles (gget ref verifica si GTF y FASTA están disponibles) de la versión 103 de Ensembl.
(Si no se especifica ninguna versión, gget ref siempre devolverá información de la última versión de Ensembl).
Obtenga la referencia del genoma para una especie específica:
gget ref -w gtf,dna homo_sapiens
# Python
gget.ref("homo_sapiens", which=["gtf", "dna"])
→ Regresa un JSON con los últimos FTP humanos GTF y FASTA, y sus respectivos metadatos, en el formato:
{
"homo_sapiens": {
"annotation_gtf": {
"ftp": "http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-106/gtf/homo_sapiens/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.106.gtf.gz",
"ensembl_release": 106,
"release_date": "28-Feb-2022",
"release_time": "23:27",
"bytes": "51379459"
},
"genome_dna": {
"ftp": "http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/release-106/fasta/homo_sapiens/dna/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.dna.primary_assembly.fa.gz",
"ensembl_release": 106,
"release_date": "21-Feb-2022",
"release_time": "09:35",
"bytes": "881211416"
}
}
}
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget ref en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget search 🔎
Obtenga genes y transcripciones de Ensembl usando términos de búsqueda de forma libre.
Los resultados se comparan según las secciones "nombre del gen" y "descripción" en la base de datos de Ensembl. gget versión >= 0.27.9 también incluye resultados que coinciden con la sección "sinónimo" de Ensembl.
Regresa: Resultados en formato JSON (Terminal) o Dataframe/CSV (Python).
Parámetro posicional
searchwords
Una o más palabras de búsqueda de forma libre, p. ej. gaba nmda. (Nota: la búsqueda no distingue entre mayúsculas y minúsculas).
Otros parámetros requeridos
-s --species
Especies o base de datos a buscar.
Una especie se puede pasar en el formato 'género_especie', p. ej. 'homo_sapiens' o 'arabidopsis_thaliana'.
Para pasar una base de datos específica, pase el nombre de la base de datos CORE, p. ej. 'mus_musculus_dba2j_core_105_1'.
Todas las bases de datos disponibles para cada versión de Ensembl se pueden encontrar aquí:
Vertebrados: http://ftp.ensembl.org/pub/current/mysql/
Invertebrados: http://ftp.ensemblgenomes.org/pub/current/ + selecciona reino animal + selecciona mysql/
Accesos directos: 'human', 'mouse'
Parámetros optionales
-r --release
Define el número de versión de Ensembl desde el que se obtienen los archivos, p. ej. 104. Por defecto: None -> se usa la última versión de Ensembl.
Nota: No se aplica a las especies invertebrados (en su lugar, puede pasar una base de datos de una especies específica (incluyen un número de versión) al argumento species). Para especies de invertebrados, Ensembl solo almacena bases de datos de 10 versiones anteriores a la versión actual.
Este argumento se sobrescribe si se pasa una base de datos específica (que incluye un número de publicación) al argumento species.
-t --id_type
'gene' (esto se use por defecto) o 'transcript'
Regesa genes o transcripciones, respectivamente.
-ao --andor
'or' (esto se use por defecto) o 'and'
'or' ('o'): Regresa todos los genes que INCLUYEN AL MENOS UNA de las palabras de búsqueda en su nombre/descripción.
'and' ('y'): Regresa solo los genes que INCLUYEN TODAS las palabras de búsqueda en su nombre/descripción.
-l --limit
Limita el número de resultados de búsqueda, p. ej. 10. Por defecto: None.
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ej. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.csv (o .json). Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Banderas
-csv --csv
Solo para la Terminal. Regresa los resultados en formato CSV.
Para Python, usa json=True para regresar los resultados en formato JSON.
-q --quiet
Solo para la Terminal. Impide la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para imipidir la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
wrap_text
Solo para Python. wrap_text=True muestra los resultados con texto envuelto para facilitar la lectura (por defecto: False).
Por ejemplo
gget search -s human gaba gamma-aminobutyric
# Python
gget.search(["gaba", "gamma-aminobutyric"], "homo_sapiens")
→ Regresa todos los genes que contienen al menos una de las palabras de búsqueda en su nombre o descripción de Ensembl/referencia externa:
| ensembl_id | gene_name | ensembl_description | ext_ref_description | biotype | url |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSG00000034713 | GABARAPL2 | GABA type A receptor associated protein like 2 [Source:HGNC Symbol;Acc:HGNC:13291] | GABA type A receptor associated protein like 2 | protein_coding | https://uswest.ensembl.org/homo_sapiens/Gene/Summary?g=ENSG00000034713 |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . |
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget search en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget setup 🔧
Función para instalar/descargar dependencias de terceros para un módulo de gget.
Nota: Algunas dependencias (por ejemplo,
cellxgene-census) pueden no ser compatibles con las versiones más recientes de Python. Si encuentras errores durante la instalación, intenta usar un entorno con una versión anterior de Python.
Parámetro posicional
module
Módulo gget para el que se deben instalar las dependencias.
Por ejemplo
gget setup alphafold
# Python
gget.setup("alphafold")
→ Instala todas las dependencias de terceros (modificadas) y descarga los parámetros del algoritmo (~4 GB) necesarios para ejecutar gget alphafold.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget seq 🧬
Obtenga la(s) secuencia(s) nucleótidos o aminoácidos de un gen (y todas sus isoformas) con su ID de Ensembl.
Regresa: Archivo de tipo FASTA.
Parámetro posicional
ens_ids
One or more Ensembl IDs.
Parámetros optionales
-o --out
Ruta al archivo en el que se guardarán los resultados, p. ruta/al/directorio/resultados.fa. Por defecto: salida estándar (STDOUT).
Para Python, usa save=True para guardar los resultados en el directorio de trabajo actual.
Banderas
-t --translate
Regresa secuencias de aminoácidos (en lugar de nucleótidos).
Las secuencias de nucleótidos se obtienen de Ensembl.
Las secuencias de aminoácidos se obtienen de UniProt.
-iso --isoforms
Regresa las secuencias de todas las transcripciones conocidas.
(Solo para IDs de genes).
-q --quiet
Solo para la Terminal. Impide la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
Para Python, usa verbose=False para imipidir la informacion de progreso de ser exhibida durante la corrida.
Por ejemplo
gget seq ENSG00000034713 ENSG00000104853 ENSG00000170296
# Python
gget.seq(["ENSG00000034713", "ENSG00000104853", "ENSG00000170296"])
→ Regresa las secuencias de nucleótidos de ENSG00000034713, ENSG00000104853, y ENSG00000170296 en formato FASTA.
gget seq -t -iso ENSG00000034713
# Python
gget.seq("ENSG00000034713", translate=True, isoforms=True)
→ Regresa las secuencias de aminoácidos de todas las transcripciones conocidas de ENSG00000034713 en formato FASTA.
Más ejemplos
Citar
Si utiliza gget seq en una publicación, favor de citar los siguientes artículos:
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606
-
The UniProt Consortium , UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D523–D531, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1052
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Parámetros de Python són iguales a los parámetros largos (
--parámetro) de Terminal, si no especificado de otra manera. Banderas son parámetros de verdadero o falso (True/False) en Python. El manuál para cualquier modulo de gget se puede llamar desde la Terminal con la bandera-h--help.
gget virus 🦠
Descargue secuencias nucleotídicas virales, junto con metadatos ricos y vinculados, de toda la International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC), incluyendo NCBI, ENA y DDBJ (a través de NCBI Virus), con la opción de enriquecer adicionalmente los resultados usando metadatos de NCBI GenBank (por ejemplo, anotaciones de genes y proteínas, secuencias de aminoácidos y más). gget virus aplica filtros secuenciales tanto del lado del servidor como locales para descargar de forma eficiente conjuntos de datos personalizados.
Formato de salida: archivos FASTA, CSV y JSONL guardados en una carpeta de salida.
Este módulo fue escrito por Ferdous Nasri.
Nota: Para consultas de SARS-CoV-2 y Alphainfluenza (Influenza A), gget virus utiliza los paquetes de datos optimizados en caché de NCBI mediante la NCBI datasets CLI. El binario de la CLI de datasets se incluye con gget para las principales plataformas—no se requiere instalación adicional. Si ya tienes la CLI datasets instalada en tu sistema, gget usará automáticamente tu instalación existente.
Argumento posicional
virus
Nombre del taxón del virus (p. ej. 'Zika virus'), ID taxonómico (p. ej. 2697049), número de acceso (p. ej. 'NC_045512.2'), lista de accesiones separadas por espacios (p. ej. 'NC_045512.2 MN908947.3 MT020781.1'), o ruta a un archivo de texto que contiene números de acceso (uno por línea, cuando se combina con --is_accession).
Use la bandera --download_all_accessions para aplicar filtros sin buscar un virus específico.
Argumentos opcionales
Filtros de hospedador
--host
Filtra por nombre del organismo hospedador o ID de Taxonomía de NCBI (p. ej. 'human', 'Aedes aegypti', 1335626).
--lab_passaged
'true' o 'false'. Filtra a favor o en contra de muestras pasadas por laboratorio (lab-passaged).
Línea de comandos: --lab_passaged true para obtener únicamente muestras pasadas por laboratorio, o --lab_passaged false para excluirlas.
Python: lab_passaged=True o lab_passaged=False (lab_passaged=None para no aplicar ningún filtro).
Filtros de Secuencia y Gen
--nuc_completeness
Filtrar por integridad del nucleótido. Una de las siguientes opciones: 'complete' o 'partial'.
Establezca 'complete' para devolver únicamente secuencias de nucleótidos marcadas como completas; establezca 'partial' para devolver únicamente secuencias marcadas como parciales.
--min_seq_length
Filtra por longitud mínima de secuencia.
--max_seq_length
Filtra por longitud máxima de secuencia.
--min_gene_count
Filtra por número mínimo de genes.
--max_gene_count
Filtra por número máximo de genes.
--min_protein_count
Filtra por número mínimo de proteínas.
--max_protein_count
Filtra por número máximo de proteínas.
--min_mature_peptide_count
Filtra por número mínimo de péptidos maduros.
--max_mature_peptide_count
Filtra por número máximo de péptidos maduros.
--max_ambiguous_chars
Filtra por número máximo de caracteres nucleotídicos ambiguos (N).
--has_proteins
Filtra por secuencias que contengan proteínas o genes específicos (p. ej. 'spike', 'ORF1ab'). Puede ser un solo nombre de proteína o una lista de nombres de proteínas.
Python: has_proteins="spike" o has_proteins=["spike", "ORF1ab"]
--annotated
'true' o 'false'. Filtra por secuencias que han sido anotadas con información de genes/proteínas.
Línea de comandos: --annotated true para obtener únicamente secuencias anotadas con información de genes/proteínas, o --annotated false para excluirlas.
Python: annotated=True o annotated=False (annotated=None para no aplicar ningún filtro).
Filtros de fecha
--min_collection_date
Filtra por fecha mínima de recolección de la muestra (YYYY-MM-DD).
--max_collection_date
Filtra por fecha máxima de recolección de la muestra (YYYY-MM-DD).
--min_release_date
Filtra por fecha mínima de liberación de la secuencia (YYYY-MM-DD).
--max_release_date
Filtra por fecha máxima de liberación de la secuencia (YYYY-MM-DD).
Filtros de ubicación y remitente
--geographic_location
Filtra por ubicación geográfica de la recolección de la muestra (p. ej. 'USA', 'Asia').
--submitter_country
Filtra por el país del remitente de la secuencia.
Filtros específicos de SARS-CoV-2
--lineage
Filtra por linaje de SARS-CoV-2 (p. ej. 'B.1.1.7', 'P.1').
Configuración del pipeline
--genbank_batch_size
Tamaño de lote para solicitudes a la API de metadatos de GenBank. Por defecto: 200. Lotes más grandes son más rápidos pero pueden ser más propensos a timeouts.
-o --out
Ruta a la carpeta donde se guardarán los resultados. Por defecto: directorio de trabajo actual.
Python: outfolder="path/to/folder"
Banderas
-a --is_accession
Bandera para indicar que el argumento posicional virus es un número de acceso, una lista de accesiones separadas por espacios, o una ruta a un archivo de texto que contiene números de acceso (uno por línea). Para descargas en caché de SARS-CoV-2 y Alphainfluenza, soporta:
- Acceso único:
NC_045512.2 - Lista separada por espacios:
NC_045512.2 MN908947.3 MT020781.1 - Ruta de archivo de texto:
accessions.txt(uno por línea)
--download_all_accessions
Use esta bandera al aplicar filtros sin buscar un virus específico (deje el argumento virus vacío).
⚠️ ADVERTENCIA: Si no especifica filtros adicionales, esta bandera descargará TODAS las secuencias virales disponibles de NCBI (toda la taxonomía de Virus, taxon ID 10239). Este es un conjunto de datos extremadamente grande que puede tardar muchas horas en descargarse y requerir un espacio considerable en disco. Úsela con precaución y asegúrese de contar con suficiente almacenamiento y ancho de banda. Cuando esta bandera está activada, el argumento virus se ignora.
--refseq_only
Bandera para limitar la búsqueda solo a genomas RefSeq (secuencias de mayor calidad, curadas).
--is_sars_cov2
Usa los paquetes de datos optimizados en caché de NCBI para una consulta de SARS-CoV-2. Esto proporciona descargas más rápidas y confiables. El sistema puede detectar automáticamente consultas por nombre de taxón de SARS-CoV-2, pero para consultas basadas en accesiones debes establecer esta bandera explícitamente.
--is_alphainfluenza
Usa los paquetes de datos optimizados en caché de NCBI para una consulta de Alphainfluenza (virus de la Influenza A). Esto proporciona descargas más rápidas y confiables para grandes conjuntos de datos de Influenza A. El sistema puede detectar automáticamente consultas por nombre de taxón de Alphainfluenza, pero para consultas basadas en accesiones debes establecer esta bandera explícitamente.
-g --genbank_metadata
Obtiene y guarda metadatos adicionales detallados desde GenBank, incluyendo fechas de recolección, detalles del hospedador y referencias de publicaciones, en un archivo separado {virus}_genbank_metadata.csv (además de volcados completos XML/CSV dumps).
--proteins_complete
Bandera para incluir solo secuencias donde todas las proteínas anotadas estén completas.
-kt --keep_temp
Bandera para conservar todos los archivos intermedios/temporales generados durante el procesamiento. Por defecto, solo se conservan los archivos de salida finales.
-q --quiet
Uso limitado para Terminal. Impide la información de progreso de ser exhibida durante la ejecución del programa.
Para Python, usa verbose=False.
Ejemplo
gget virus "Zika virus" --nuc_completeness complete --host human --out zika_data
# Python
import gget
gget.virus(
"Zika virus",
nuc_completeness="complete",
host="human",
outfolder="zika_data"
)
→ Descarga genomas completos de Zika virus de hospedadores humanos. Los resultados se guardan en la carpeta zika_data como Zika_virus_sequences.fasta, Zika_virus_metadata.csv, Zika_virus_metadata.jsonl y command_summary.txt.
El archivo CSV de metadatos se verá así:
| accession | Organism Name | GenBank/RefSeq | Release date | Length | Nuc Completeness | Geographic Location | Host | ... |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KX198135.1 | Zika virus | GenBank | 2016-05-18 | 10807 | complete | Americas:Haiti | Homo sapiens | ... |
| . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | . . . | ... |
El archivo de resumen del comando (command_summary.txt) contendrá, por ejemplo:
================================================================================
GGET VIRUS COMMAND SUMMARY
================================================================================
Execution Date: 2025-12-15 13:33:39
Output Folder: zika_data
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
COMMAND LINE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
gget virus "Zika virus" --nuc_completeness complete --host human --out zika_data
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
EXECUTION STATUS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
✓ Command completed successfully
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SEQUENCE STATISTICS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total records from API: 234
After metadata filtering: 234
Final sequences (after all filters): 234
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DETAILED STATISTICS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Unique hosts: 1
- Homo sapiens
Unique geographic locations: 15
- Americas:Brazil
- Americas:Colombia
- ... (showing top 20)
Sequence length range: 10272 - 11155 bp
Average sequence length: 10742 bp
Completeness breakdown:
- complete: 234
Source database breakdown:
- GenBank: 233
- RefSeq: 1
Unique submitter countries: 12
- USA
- Brazil
- ... (showing top 20)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
OUTPUT FILES
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FASTA Sequences: Zika_virus_sequences.fasta (2.45 MB)
JSONL Metadata: Zika_virus_metadata.jsonl (0.53 MB)
CSV Metadata: Zika_virus_metadata.csv (0.42 MB)
================================================================================
END OF SUMMARY
================================================================================
Nota: Si alguna operación falla durante la ejecución (timeouts de API, fallos de descarga de secuencias, fallos de metadatos de GenBank), el resumen incluirá una sección "FAILED OPERATIONS - RETRY COMMANDS" con comandos y URLs exactas que pueden ejecutarse manualmente para reintentar las operaciones fallidas. Por ejemplo:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FAILED OPERATIONS - RETRY COMMANDS
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Some operations failed during execution. You can retry them manually:
[Failed Sequence Download Batches]
Total failed batches: 2
Batch 15: 200 sequences
Error: HTTPError: 500 Server Error
Accessions: NC_045512.2, MN908947.3, MT020781.1 ... and 197 more
Retry URL: https://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/efetch.fcgi?db=nucleotide&id=NC_045512.2,MN908947.3,...&rettype=fasta&retmode=text
[Failed GenBank Metadata Batches]
Total failed batches: 1
See detailed log file: genbank_failed_batches.log
Accessions: NC_045512.2, MN908947.3, MT020781.1 ... and 2 more
Retry URL: https://eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/efetch.fcgi?db=nucleotide&id=NC_045512.2,MN908947.3,...&rettype=gb&retmode=xml
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Descargar un genoma de referencia específico de SARS-CoV-2 usando su número de acceso:
gget virus NC_045512.2 --is_accession --is_sars_cov2
# Python
import gget
gget.virus("NC_045512.2", is_accession=True, is_sars_cov2=True)
→ Uses the optimized download method for SARS-CoV-2 to fetch the reference genome and its metadata.
Descargar secuencias de SARS-CoV-2 con optimización en caché Y metadatos de GenBank:
gget virus "SARS-CoV-2" --host human --nuc_completeness complete --min_seq_length 29000 --genbank_metadata
# Python
import gget
gget.virus(
"SARS-CoV-2",
host="human",
nuc_completeness="complete",
min_seq_length=29000,
genbank_metadata=True,
is_sars_cov2=True,
outfolder="covid_data"
)
→ Uses cached download for speed (via NCBI's SARS-CoV-2 data packages when available), applies the sequence length filter post-download, and fetches detailed GenBank metadata for all filtered sequences.
Descargar secuencias del virus de la Influenza A con caché optimizada y filtrado posterior a la descarga:
gget virus "Influenza A virus" --host human --nuc_completeness complete --max_seq_length 15000 --genbank_metadata --is_alphainfluenza
# Python
import gget
gget.virus(
"Influenza A virus",
host="human",
nuc_completeness="complete",
max_seq_length=15000,
genbank_metadata=True,
is_alphainfluenza=True,
outfolder="influenza_a_data"
)
→ Uses NCBI's cached data packages for Alphainfluenza to download complete Influenza A genomes from human hosts much faster than the standard API method, then applies the sequence length filter and fetches GenBank metadata.
Citar
Si utilizas gget virus en una publicación, por favor cita los siguientes artículos:
-
Nasri, F. et al (2026). En preparación.
-
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
O’Leary, N.A., Cox, E., Holmes, J.B. et al (2024). Exploring and retrieving sequence and metadata for species across the tree of life with NCBI Datasets. Sci Data 11, 732. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-024-03571-y
Detalles Adicionales: Flujo de trabajo de recuperación de virus
Visión general
La función gget.virus() implementa un flujo de trabajo optimizado de 10 pasos para recuperar secuencias virales y metadatos asociados desde NCBI. El sistema está diseñado para minimizar la sobrecarga de descarga filtrando primero los metadatos y luego descargando solo las secuencias que pasan los filtros iniciales, con recuperación opcional de metadatos detallados de GenBank. Para consultas de SARS-CoV-2 y Alphainfluenza, el flujo de trabajo puede usar paquetes de datos optimizados en caché mientras sigue aplicando todos los filtros y obteniendo metadatos de GenBank.
Arquitectura
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Usuarios │
│ │
│ • Consulta de virus │
│ (Taxón/Acc) │
│ • Criterios de filtrado │
│ (Hospedador, fechas, │
│ longitud...) │
│ • Banderas de salida │
│ (`--genbank_metadata`) │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Verificación de descarga │
│ en caché │
│ (SARS-CoV-2/Alphainfluenza)│
│ │
│ • Autodetección o banderas │
│ • Descarga de paquetes │
│ en caché │
│ • Aplicar filtros básicos │
│ (host, complete, lineage)│
│ • Guardar para el pipeline │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ API y prefiltrado │
│ (o usar metadatos en │
│ caché) │
│ │
│ • Llama a NCBI Datasets API│
│ O usa metadatos en caché │
│ • Aplica filtros del lado │
│ del servidor (host, │
│ refseq) │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐
│ Filtrado local de metadatos │
│ y manejo de secuencias │
│ │
│ • Aplica TODOS los filtros │
│ locales restantes │
│ (fechas, recuentos de │
│ genes, etc.) │
│ • Genera la lista final de │
│ números de acceso │
│ • Usa secuencias en caché │
│ O descarga vía │
│ E-utilities │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘
│
┌───────────┴──────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────────────────┐ ┌───────────────────────────────────┐
│ Procesamiento final │ │ Metadatos de GenBank (Opcional) │
│ │ │ │
│ • Aplica filtros a nivel │ │ • Se obtienen incluso para │
│ de secuencia (p. ej., │ │ descargas en caché cuando │
│ max N's) │ │ se solicita │
│ • Formatea metadatos │ │ • Usa la lista final de │
│ estándar │ │ números de acceso │
└──────────────┬──────────────┘ │ • Se obtienen vía E-utilities API │
│ └──────────────────┬────────────────┘
│ │
└──────────────────┬─────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ Guardar archivos de salida │
│ finales │
│ │
│ • _sequences.fasta │
│ • _metadata.csv & .jsonl │
│ • _genbank_metadata.csv │
│ (si se solicita) │
└──────────────┬────────────────┘
│
▼
┌───────────────────────────────┐
│ Resumen y limpieza │
│ │
│ • command_summary.txt │
│ • Mostrar resultados al │
│ usuario │
│ • Limpiar archivos temporales│
└───────────────────────────────┘
Pasos del flujo de trabajo
Paso 1: Validación de entrada y configuración
-
Función: función principal
virus() -
Propósito: Validar todos los parámetros del usuario y configurar el logging
-
Operaciones clave:
- Validar el formato del taxón/accesión del virus
- Verificar rangos y formatos de los parámetros de filtrado
- Configurar la estructura del directorio de salida
- Configurar el logging según el nivel de verbosidad
- Verificar oportunidades de optimización para SARS-CoV-2 o Alphainfluenza
Paso 2: Descarga optimizada en caché (SARS-CoV-2 y Alphainfluenza)
-
Funciones:
download_sars_cov2_optimized(),download_alphainfluenza_optimized() -
Propósito: Usar los paquetes de datos en caché precomputados por NCBI para descargas más rápidas
-
NCBI datasets CLI: gget incluye el binario de la CLI de NCBI datasets para las principales plataformas (macOS, Linux, Windows). Si ya tienes la CLI
datasetsinstalada en tu sistema, gget usará automáticamente la instalación del sistema. -
Operaciones clave:
- Autodetectar o usar banderas explícitas para consultas de SARS-CoV-2/Alphainfluenza
- Descargar paquetes comprimidos en caché mediante NCBI datasets CLI
- Aplicar filtros básicos soportados por descargas en caché (host, complete_only, annotated, lineage)
- Extraer secuencias y metadatos básicos
- Guardar datos para continuar el pipeline (no retorna temprano)
- Retroceso jerárquico a la API estándar si falla la descarga en caché
-
Filtros aplicados:
- ✅
host- Aplicado durante la descarga - ✅
complete_only- Aplicado durante la descarga - ✅
annotated- Aplicado durante la descarga - ✅
lineage(solo COVID) - Aplicado durante la descarga - ⏭️ Todos los demás filtros se aplican en pasos posteriores
- ✅
Paso 3: Recuperación de metadatos
-
Función:
fetch_virus_metadata() -
Propósito: Recuperar metadatos desde NCBI Datasets API con filtrado del lado del servidor, o usar metadatos en caché
-
Operaciones clave:
- Si se usa descarga en caché: Omitir llamada a la API, usar metadatos en caché
- De lo contrario: Llamar a NCBI Datasets API con filtros del lado del servidor
- Aplicar filtros del lado del servidor (host, ubicación geográfica, fecha de liberación, completitud)
- Manejar paginación de la API con connection pooling
- Implementar exponential backoff con jitter para reintentos
- Parsear respuestas JSON con streaming para conjuntos de datos grandes
- Almacenar metadatos en un formato estructurado con validación
Paso 4: Filtrado solo de metadatos
-
Función:
filter_metadata_only() -
Propósito: Aplicar TODOS los filtros locales que no requieren datos de secuencia
-
Operaciones clave:
- Filtrar por rangos de fechas con análisis inteligente de fechas
- Filtrar por completitud del genoma e indicadores de calidad
- Aplicar filtros de rango numérico (recuentos de genes/proteínas, longitud de secuencia)
- Manejar metadatos faltantes o malformados de forma robusta
- Generar lista optimizada de accesiones para procesamiento dirigido
- Nota: Los filtros no aplicados durante la descarga en caché se aplican aquí
Paso 5: Manejo de secuencias
-
Función:
download_sequences_by_accessions() -
Propósito: Usar secuencias en caché o descargar secuencias FASTA para accesiones filtradas
-
Operaciones clave:
- Si se usa descarga en caché: Filtrar secuencias en caché por la lista de accesiones del Paso 4
- De lo contrario: Descargar mediante la API de E-utilities con optimización por lotes
- Implementar tamaños de lote configurables (por defecto: 200)
- Hacer streaming de respuestas grandes para gestionar memoria
- Manejar reintentos de descarga con exponential backoff
- Devolver la ruta al archivo FASTA para procesamiento
Paso 6: Filtrado dependiente de la secuencia
-
Función:
filter_sequences() -
Propósito: Aplicar filtros finales que requieren análisis de secuencia
-
Operaciones clave:
- Parsear secuencias FASTA y calcular métricas de secuencia
- Filtrar por recuento de caracteres ambiguos (
max_ambiguous_chars) - Filtrar por presencia de proteína/gen (
has_proteins) - Filtrar por indicadores de completitud de proteínas (
proteins_complete) - Devolver secuencias filtradas y metadatos actualizados
Paso 7: Guardar los archivos de salida finales
-
Funciones:
save_metadata_to_csv(),FastaIO.write() -
Propósito: Guardar secuencias filtradas y metadatos en archivos de salida
-
Operaciones clave:
- Escribir secuencias filtradas en un archivo FASTA
- Guardar metadatos en formatos CSV y JSONL
- Registrar tamaños de archivos de salida para el resumen
- Validar que los archivos se hayan creado correctamente
Paso 8: Recuperación de metadatos de GenBank (Opcional)
-
Función:
fetch_genbank_metadata() -
Propósito: Obtener registros detallados de GenBank para el conjunto final de secuencias
-
Operaciones clave:
- Disponible tanto para descargas en caché como sin caché
- Recuperar registros completos de GenBank
- Extraer 23+ campos de metadatos por registro
- Procesar en tamaños de lote configurables
- Implementar rate limiting y reintentos
- Parsear y validar XML de GenBank
- Combinar con metadatos existentes
Paso 9: Resumen final y generación del resumen del comando
-
Función:
save_command_summary() -
Propósito: Crear un resumen detallado de la ejecución y mostrar resultados
-
Operaciones clave:
- Registrar la línea de comandos y parámetros
- Seguir estadísticas de filtrado en cada etapa
- Listar archivos de salida con tamaños
- Documentar operaciones fallidas con comandos de reintento
- Mostrar un resumen de resultados completo al usuario
Paso 10: Limpieza
-
Propósito: Limpiar archivos temporales y finalizar la ejecución
-
Operaciones clave:
- Eliminar el directorio temporal de procesamiento (a menos que
keep_temp=True) - Eliminar archivos de metadatos intermedios
- Conservar el CSV de metadatos de GenBank cuando se recupera con éxito
- Registrar el estado de finalización
- Eliminar el directorio temporal de procesamiento (a menos que
Dependencias de funciones
virus()
├── check_min_max() [Paso 1: Validación de entrada]
│ └── Valida pares de parámetros min/max
├── is_sars_cov2_query() [Paso 2: Detección de SARS-CoV-2]
│ └── Autodetecta consultas de SARS-CoV-2
├── download_sars_cov2_optimized() [Paso 2: Descarga en caché]
│ ├── _get_datasets_path()
│ ├── Llamadas a NCBI datasets CLI
│ └── Descarga de paquetes en caché
├── is_alphainfluenza_query() [Paso 2b: Detección de Alphainfluenza]
│ └── Autodetecta consultas de Alphainfluenza
├── download_alphainfluenza_optimized() [Paso 2b: Descarga en caché]
│ ├── _get_datasets_path()
│ ├── Llamadas a NCBI datasets CLI
│ └── Descarga de paquetes en caché
├── unzip_file() [Paso 2/2b: Extraer datos en caché]
│ └── Utilidades de extracción ZIP
├── fetch_virus_metadata() [Paso 3: Recuperación de metadatos API]
│ ├── Cliente de NCBI Datasets API
│ ├── Manejo de paginación
│ ├── Lógica de reintento con backoff
│ └── _get_modified_virus_name() para reintento
├── fetch_virus_metadata_chunked() [Paso 3: Fallback para conjuntos grandes]
│ └── Estrategia de descarga por bloques de fecha
├── load_metadata_from_api_reports() [Paso 3: Conversión de metadatos]
│ └── Convierte el formato de la API al formato interno
├── filter_metadata_only() [Paso 4: Filtrado de metadatos]
│ ├── parse_date() para comparaciones de fecha
│ ├── Validación numérica
│ └── Manejo de datos faltantes
├── download_sequences_by_accessions() [Paso 5: Descarga de secuencias]
│ ├── Cliente de la API de E-utilities
│ ├── Procesamiento por lotes (por defecto: 200)
│ └── Manejo de streaming
├── filter_sequences() [Paso 6: Filtrado de secuencias]
│ ├── Parser FastaIO
│ └── Validación de secuencias
├── save_metadata_to_csv() [Paso 7: Guardar salidas]
│ └── Formateo y escritura CSV
├── fetch_genbank_metadata() [Paso 8: Datos opcionales de GenBank]
│ ├── _fetch_genbank_batch()
│ ├── _clean_xml_declarations()
│ ├── Utilidades de parseo XML
│ └── Rate limiting
├── save_genbank_metadata_to_csv() [Paso 8: Guardar datos de GenBank]
│ └── Combina con metadatos del virus
└── save_command_summary() [Paso 9: Resumen de ejecución]
└── Seguimiento de operaciones fallidas
Características de optimización
1. Filtrado del lado del servidor
- Aplica filtros a nivel de la API de NCBI para reducir la transferencia de datos
- Filtros soportados: host, ubicación geográfica, fecha de liberación, completitud del genoma
- Validación automática de compatibilidad y valores de filtros
2. Filtrado en múltiples etapas
- Etapa 1: Filtros solo de metadatos (rápido, sin descarga de secuencias)
- Etapa 2: Filtros dependientes de la secuencia (conjunto prefiltrado)
- Etapa 3: Integración y filtrado de metadatos de GenBank
- Etapa 4: Validación final y controles de calidad
3. Descargas optimizadas
- Tamaños de lote configurables para diferentes tipos de datos
- Connection pooling para mejorar el rendimiento
- Manejo de streaming para descargas grandes
- Mecanismos de rate limiting y reintento
4. Descargas optimizadas en caché
-
Manejo especial para consultas de SARS-CoV-2 y Alphainfluenza usando paquetes de datos en caché de NCBI
-
Detección automática o banderas explícitas (
--is_sars_cov2,--is_alphainfluenza) -
Estrategias de fallback jerárquicas a la API estándar si falla la descarga en caché
-
Descargas significativamente más rápidas para conjuntos de datos grandes
-
Continuación del pipeline: Las descargas en caché ahora continúan por todos los pasos del flujo de trabajo
-
Filtrado posterior a la descarga: Los filtros no aplicados durante la descarga en caché se aplican después
-
Metadatos de GenBank: Disponible para descargas en caché cuando se usa la bandera
--genbank_metadata -
Categorías de filtros:
- Aplicados durante la descarga:
host,complete_only,annotated,lineage(COVID) - Aplicados después: todos los demás filtros (longitud de secuencia, recuentos de genes, fechas, etc.)
- Aplicados durante la descarga:
5. Estructuras de datos eficientes
- Diccionarios basados en accesión para búsquedas O(1)
- Parsers en streaming para JSON y XML
- Manejo de FASTA eficiente en memoria
- Combinación de metadatos optimizada
Archivos de salida
1. Secuencias FASTA ({virus}_sequences.fasta)
- Contiene secuencias de nucleótidos para resultados filtrados
- Formato FASTA estándar con encabezados detallados
- Se conserva la orientación original de NCBI
- Anotaciones opcionales de proteínas/segmentos en los encabezados
2. Metadatos CSV ({virus}_metadata.csv)
- Formato tabular para análisis en hojas de cálculo
- Estructura de columnas estandarizada
- Información geográfica y taxonómica
- Detalles de recolección y envío
- Métricas de calidad y anotaciones
3. Metadatos de GenBank ({virus}_genbank_metadata.csv) [Opcional]
- 23+ columnas detalladas de metadatos
- Referencias de publicaciones
- Anotaciones de características
- Referencias cruzadas a otras bases de datos
- Detalles de cepa e aislamiento
4. Metadatos JSONL ({virus}_metadata.jsonl)
- Formato JSON Lines para metadatos de virus después del filtrado solo de metadatos
- Formato amigable para streaming y acceso programático
- Un objeto JSON por secuencia con los mismos campos que el CSV de metadatos
- Los campos específicos de GenBank se almacenan por separado en
{virus}_genbank_metadata.csvcuando se utiliza--genbank_metadata
5. Resumen del comando (command_summary.txt)
-
Resumen generado automáticamente de la ejecución del comando
-
Registra la línea de comandos exacta que se ejecutó
-
Estado de ejecución (éxito/fallo con mensajes de error)
-
Estadísticas de filtrado en cada etapa:
- Registros totales desde la API
- Registros después del filtrado de metadatos
- Secuencias finales después de todos los filtros
-
Estadísticas detalladas:
- Hospedadores únicos con recuentos (hasta 20 principales)
- Ubicaciones geográficas únicas con recuentos (hasta 20 principales)
- Rango de longitudes de secuencia y promedio
- Desglose de completitud (complete vs partial)
- Desglose de base de datos de origen (GenBank vs RefSeq)
- Países de remitentes únicos con recuentos (hasta 20 principales)
-
Lista de todos los archivos de salida generados con tamaños
-
Seguimiento de operaciones fallidas (cuando aplica):
- Fallos por timeout de API: URL exacta que expiró con sugerencias alternativas
- Lotes de descarga de secuencias fallidos: números de lote, listas de accesiones y URLs de reintento
- Lotes de metadatos de GenBank fallidos: listas de accesiones con URLs de reintento individuales
- Todas las operaciones fallidas incluyen comandos/URLs exactos que pueden ejecutarse manualmente para reintentar
Características de rendimiento
Escalabilidad
- Conjuntos pequeños (< 1,000 secuencias): procesamiento casi instantáneo
- Conjuntos medianos (1,000 - 10,000 secuencias): minutos para completarse
- Conjuntos grandes (> 10,000 secuencias): paginación y filtrado optimizados
Uso de memoria
- El procesamiento en streaming minimiza el uso de memoria
- Metadatos cacheados en memoria para operaciones de filtrado
- Archivos FASTA grandes procesados en bloques
Eficiencia de red
- Mínimas llamadas a la API gracias al filtrado del lado del servidor
- Descargas dirigidas reducen el uso de ancho de banda
- Reintento automático con exponential backoff
Manejo de errores
Fallos de API
-
Estrategia de reintento inteligente con exponential backoff y jitter
-
Detección de errores del lado del servidor con guía específica:
- Manejo de timeouts para conjuntos grandes
- Sugerencias para optimizar filtros geográficos
- Ajustes de tamaño de lote para metadatos de GenBank
-
Connection pooling y gestión de sesiones
-
Registro detallado de errores con pasos de troubleshooting
Validación de datos
-
Validación integral de parámetros de entrada:
- Verificación de tipos para todos los parámetros
- Validación de rangos para valores numéricos
- Validación de formato y rango de fechas
- Normalización de parámetros booleanos
-
Verificación de integridad de secuencias:
- Validación de formato FASTA
- Detección de caracteres ambiguos
- Chequeos de completitud de proteínas/genes
-
Validación de consistencia de metadatos:
- Verificación de presencia de campos requeridos
- Validación de tipo de datos
- Validación de referencias cruzadas
- Validación de registros de GenBank
Mecanismos de recuperación
-
Limpieza automática de archivos temporales
-
Preservación parcial de resultados:
- Guardado de metadatos intermedios
- Guardado progresivo del estado de filtrado
- Caché de metadatos de GenBank
-
Estrategias de fallback jerárquicas:
- Paquetes optimizados de SARS-CoV-2
- Fallback a datos en caché
- Fallback a recuperación basada en API
-
Reporte detallado de errores:
- Análisis de causa raíz
- Sugerencias de comandos alternativos
- Recomendaciones para relajar filtros
- Consejos de optimización de rendimiento
Ejemplos de uso
Ejemplos de línea de comandos
# Get help and see all available parameters
$ gget virus --help
$ gget virus "Nipah virus"
# Download Zika virus sequences with basic filtering (API + metadata filtering)
$ gget virus "Zika virus" --host human --min_seq_length 10000 --max_seq_length 11000
# Download with metadata and sequence filtering
$ gget virus "Ebolavirus" --max_seq_length 20000 --genbank_metadata -o ./ebola_data
# Download SARS-CoV-2 with cached optimization
$ gget virus "SARS-CoV-2" --host dog --nuc_completeness complete
# Download Influenza A with post-download sequence filtering (warning: big data size)
$ gget virus "Influenza A virus" --host human --max_ambiguous_chars 50 --has_proteins spike
# Using accession ID to get data
$ gget virus -a "MK947457" --host deer --min_collection_date "2020-01-01"
Ejemplos en Python
import gget
import pandas as pd
from Bio import SeqIO
# Basic download with GenBank metadata
gget.virus(
"Zika virus",
host="human",
genbank_metadata=True,
outfolder="zika_data"
)
# Access different data types from output files
sequences = list(SeqIO.parse("zika_data/Zika_virus_sequences.fasta", "fasta"))
virus_metadata = pd.read_csv("zika_data/Zika_virus_metadata.csv")
genbank_metadata = pd.read_csv("zika_data/Zika_virus_genbank_metadata.csv")
# Print GenBank metadata summary
for _, row in genbank_metadata.head().iterrows():
print(f"Sequence: {row['accession']}")
print(f" Length: {row['sequence_length']} bp")
print(f" Host: {row.get('host', 'Unknown')}")
print(f" Location: {row.get('geographic_location', 'Unknown')}")
print(f" Collection date: {row.get('collection_date', 'Unknown')}")
# Advanced filtering with GenBank data
gget.virus(
"SARS-CoV-2",
host="human",
min_seq_length=29000,
max_seq_length=30000,
min_collection_date="2020-03-01",
max_collection_date="2020-03-31",
geographic_location="North America",
genbank_metadata=True,
genbank_batch_size=200,
outfolder="covid_march2020"
)
# Process and analyze results
# Read virus metadata
virus_df = pd.read_csv("covid_march2020/SARS-CoV-2_metadata.csv")
print(f"Total sequences: {len(virus_df)}")
print(f"Unique hosts: {virus_df['Host'].nunique()}")
print(f"Date range: {virus_df['Collection Date'].min()} to {virus_df['Collection Date'].max()}")
# Read GenBank metadata for detailed analysis
genbank_df = pd.read_csv("covid_march2020/SARS-CoV-2_genbank_metadata.csv")
print(f"Sequences with GenBank data: {len(genbank_df)}")
print("\nPublication summary:")
print(genbank_df['reference_count'].describe())
# Custom sequence analysis
sequences = list(SeqIO.parse("covid_march2020/SARS-CoV-2_sequences.fasta", "fasta"))
for record in sequences:
gc_content = (str(record.seq).count('G') + str(record.seq).count('C')) / len(record.seq)
print(f"{record.id}: GC content = {gc_content:.2%}")
# Merge metadata sources
merged_df = pd.merge(
virus_df,
genbank_df,
on='accession',
how='left',
suffixes=('_virus', '_genbank')
)
# Save merged analysis
merged_df.to_csv("covid_march2020/combined_analysis.csv", index=False)
Ejemplos de estrategia de análisis
Los ejemplos anteriores demuestran diferentes enfoques de análisis:
- Integración básica de GenBank: Obtener secuencias con metadatos de GenBank para un análisis completo
- Filtrado avanzado: Combinar metadatos de virus y datos de GenBank con filtros personalizados
- Análisis personalizado: Procesar secuencias y metadatos usando BioPython y Pandas
- Integración de datos: Unir metadatos de virus y GenBank para un análisis detallado
Acceso programático
# Access filtered metadata and sequences
metadata_file = "covid_data/SARS-CoV-2_metadata.jsonl"
sequences_file = "covid_data/SARS-CoV-2_sequences.fasta"
# Process results with custom analysis
import json
with open(metadata_file) as f:
for line in f:
record = json.loads(line)
# Custom analysis here
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Bienvenido a la guía de contribución de gget
¡Gracias por invertir su tiempo en contribuir con nuestro proyecto! Cualquier contribución que hagas se verá reflejada en el repositorio de GitHub de gget. ✨
Lea nuestro Código de conducta para mantener nuestra comunidad accesible y respetable.
En esta guía, obtendrá una descripción general del flujo de trabajo de contribución desde la creación de un GitHub Issue (asunto) o la creación de un GitHub Pull Request (PR) hasta la revisión y fusión de un PR.
Issues (asuntos)
Crear un nuevo Issue
Si detecta un problema con gget o tiene una idea para una nueva función, comproba si ya existe un Issue para este problema/sugerencia. Si no existe un Issue relacionado, puede abrir un nuevo Issue utilizando el formulario correspondiente.
Resolver un Issue
Explore nuestros Issues existentes para encontrar uno que le interese. Puede restringir la búsqueda utilizando "labels" como filtros. Si encuentra un Issue en el que desea trabajar, puede abrir un PR con una solución.
Contribuir a través de Pull Requests (PRs)
Empezar
- Bifurcar ("fork") el repositorio de GitHub de gget.
-
Usando GitHub Desktop:
- "Getting started with GitHub Desktop" lo guiará a través de la configuración de Desktop.
- Una vez que GitHub Desktop está configurado, puede usarlo para bifurcar el repositorio!
-
Usando la Terminal:
- Bifurca el repositorio para que pueda realizar sus cambios sin afectando el proyecto original hasta que esté listo para fusionarlos.
- ¡Cree una rama de trabajo y comience con sus cambios!
Confirma sus actualizaciones
Confirme sus cambios una vez que esté satisfecho con ellos.
‼️ Auto-revisa lo siguiente antes de crear un PR ‼️
- Revise el contenido para mantener precisión técnica.
- Edite los cambios/comentarios de gramática, ortografía y adherencia al estilo general del código de gget existente.
- Formatee su código usando "black".
- Asegúrese de que las pruebas unitarias pasen:
- Las dependencias de desarrollador se pueden instalar con
pip install -r dev-requirements.txt - Ejecute pruebas unitarias existentes desde la carpeta de gget con
coverage run -m pytest -ra -v tests && coverage report --omit=main.py,tests*
- Las dependencias de desarrollador se pueden instalar con
- Agregue nuevas pruebas unitarias si corresponde:
- Los parámetros y los resultados esperados se pueden encontrar en archivos json en ./tests/fixtures/
- Las pruebas unitarias se pueden agregar a ./tests/test_*.py y serán detectado automáticamente
- Asegúrese de que las ediciones sean compatibles tanto con Python como con la Terminal
- Los parámetros para la Terminal se definen en ./gget/main.py
- Agregue módulos/argumentos nuevos a la documentación, si corresponde:
- El manual de cada módulo se puede editar/añadir como ./docs/src/*.md
Si tiene alguna pregunta, no dude en iniciar una discusión o crear un Issue como se describe anteriormente.
Crear un Pull Request (PR)
Cuando haya terminado con los cambios, cree un Pull Request, también conocido como "PR".
‼️ Realice todos los PRs contra la rama dev del repositorio gget
- No olvide de vincular su PR con un Issue si estás resolviendo uno.
- Habilite la casilla de verificación para permitir ediciones del mantenedor para que la rama se pueda actualizar para una fusión.
- Si se encuentra con problemas durante la fusión, consulte este tutorial de git para ayudarlo a resolver conflictos de fusión y otros problemas.
Una vez que envíe su PR, un miembro del equipo gget revisará su propuesta. Podemos hacer preguntas o solicitar información adicional.
¡Su PR está fusionado!
¡Felicidades! 🎉 El equipo de gget te lo agradece. ✨
Una vez que su PR se fusione, sus contribuciones serán visibles públicamente en el repositorio de gget.
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Código de Conducta convenido para Contribuyentes
Nuestro compromiso
Nosotros, como miembros, contribuyentes y administradores nos comprometemos a hacer de la participación en nuestra comunidad sea una experiencia libre de acoso para todo el mundo, independientemente de la edad, dimensión corporal, discapacidad visible o invisible, etnicidad, características sexuales, identidad y expresión de género, nivel de experiencia, educación, nivel socio-económico, nacionalidad, apariencia personal, raza, casta, color, religión, o identidad u orientación sexual.
Nos comprometemos a actuar e interactuar de maneras que contribuyan a una comunidad abierta, acogedora, diversa, inclusiva y sana.
Nuestros estándares
Ejemplos de comportamientos que contribuyen a crear un ambiente positivo para nuestra comunidad:
- Demostrar empatía y amabilidad ante otras personas
- Respeto a diferentes opiniones, puntos de vista y experiencias
- Dar y aceptar adecuadamente retroalimentación constructiva
- Aceptar la responsabilidad y disculparse ante quienes se vean afectados por nuestros errores, aprendiendo de la experiencia
- Centrarse en lo que sea mejor no sólo para nosotros como individuos, sino para la comunidad en general
Ejemplos de comportamiento inaceptable:
- El uso de lenguaje o imágenes sexualizadas, y aproximaciones o atenciones sexuales de cualquier tipo
- Comentarios despectivos (trolling), insultantes o derogatorios, y ataques personales o políticos
- El acoso en público o privado
- Publicar información privada de otras personas, tales como direcciones físicas o de correo electrónico, sin su permiso explícito
- Otras conductas que puedan ser razonablemente consideradas como inapropiadas en un entorno profesional
Aplicación de las responsabilidades
Los administradores de la comunidad son responsables de aclarar y hacer cumplir nuestros estándares de comportamiento aceptable y tomarán acciones apropiadas y correctivas de forma justa en respuesta a cualquier comportamiento que consideren inapropiado, amenazante, ofensivo o dañino.
Los administradores de la comunidad tendrán el derecho y la responsabilidad de eliminar, editar o rechazar comentarios, commits, código, ediciones de páginas de wiki, issues y otras contribuciones que no se alineen con este Código de Conducta, y comunicarán las razones para sus decisiones de moderación cuando sea apropiado.
Alcance
Este código de conducta aplica tanto a espacios del proyecto como a espacios públicos donde un individuo esté en representación del proyecto o comunidad. Ejemplos de esto incluyen el uso de la cuenta oficial de correo electrónico, publicaciones a través de las redes sociales oficiales, o presentaciones con personas designadas en eventos en línea o no.
Aplicación
Instancias de comportamiento abusivo, acosador o inaceptable de otro modo podrán ser reportadas a los administradores de la comunidad responsables del cumplimiento a través de lpachter@caltech.edu. Todas las quejas serán evaluadas e investigadas de una manera puntual y justa.
Todos los administradores de la comunidad están obligados a respetar la privacidad y la seguridad de quienes reporten incidentes.
Guías de Aplicación
Los administradores de la comunidad seguirán estas Guías de Impacto en la Comunidad para determinar las consecuencias de cualquier acción que juzguen como un incumplimiento de este Código de Conducta:
1. Corrección
Impacto en la Comunidad: El uso de lenguaje inapropiado u otro comportamiento considerado no profesional o no acogedor en la comunidad.
Consecuencia: Un aviso escrito y privado por parte de los administradores de la comunidad, proporcionando claridad alrededor de la naturaleza de este incumplimiento y una explicación de por qué el comportamiento es inaceptable. Una disculpa pública podría ser solicitada.
2. Aviso
Impacto en la Comunidad: Un incumplimiento causado por un único incidente o por una cadena de acciones.
Consecuencia: Un aviso con consecuencias por comportamiento prolongado. No se interactúa con las personas involucradas, incluyendo interacción no solicitada con quienes se encuentran aplicando el Código de Conducta, por un periodo especificado de tiempo. Esto incluye evitar las interacciones en espacios de la comunidad, así como a través de canales externos como las redes sociales. Incumplir estos términos puede conducir a una expulsión temporal o permanente.
3. Expulsión temporal
Impacto en la Comunidad: Una serie de incumplimientos de los estándares de la comunidad, incluyendo comportamiento inapropiado continuo.
Consecuencia: Una expulsión temporal de cualquier forma de interacción o comunicación pública con la comunidad durante un intervalo de tiempo especificado. No se permite interactuar de manera pública o privada con las personas involucradas, incluyendo interacciones no solicitadas con quienes se encuentran aplicando el Código de Conducta, durante este periodo. Incumplir estos términos puede conducir a una expulsión permanente.
4. Expulsión permanente
Impacto en la Comunidad: Demostrar un patrón sistemático de incumplimientos de los estándares de la comunidad, incluyendo conductas inapropiadas prolongadas en el tiempo, acoso de individuos, o agresiones o menosprecio a grupos de individuos.
Consecuencia: Una expulsión permanente de cualquier tipo de interacción pública con la comunidad del proyecto.
Atribución
Este Código de Conducta es una adaptación del Contributor Covenant, versión 2.1, disponible en https://www.contributor-covenant.org/es/version/2/1/code_of_conduct.html
Las Guías de Impacto en la Comunidad están inspiradas en la escalera de aplicación del código de conducta de Mozilla.
Para respuestas a las preguntas frecuentes de este código de conducta, consulta las FAQ en https://www.contributor-covenant.org/faq. Hay traducciones disponibles en https://www.contributor-covenant.org/translationshttps://www.contributor-covenant.org/translations
Ver el codigo fuente de la pagina en GitHub
Citar
Si utiliza gget en una publicación, favor de citar:
Luebbert, L., & Pachter, L. (2023). Efficient querying of genomic reference databases with gget. Bioinformatics. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btac836
-
Si utiliza
gget alphafold, favor de citar también:- Jumper, J., Evans, R., Pritzel, A. et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596, 583–589 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2
Y si aplica:
- Evans, R. et al. Protein complex prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. bioRxiv 2021.10.04.463034; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.04.463034
-
Si utiliza
gget archs4, favor de citar también:-
Lachmann A, Torre D, Keenan AB, Jagodnik KM, Lee HJ, Wang L, Silverstein MC, Ma’ayan A. Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse. Nature Communications 9. Article number: 1366 (2018), doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03751-6
-
Bray NL, Pimentel H, Melsted P and Pachter L, Near optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification, Nature Biotechnology 34, p 525--527 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3519
-
-
Si utiliza
gget bgee, favor de citar también:- Frederic B Bastian, Julien Roux, Anne Niknejad, Aurélie Comte, Sara S Fonseca Costa, Tarcisio Mendes de Farias, Sébastien Moretti, Gilles Parmentier, Valentine Rech de Laval, Marta Rosikiewicz, Julien Wollbrett, Amina Echchiki, Angélique Escoriza, Walid H Gharib, Mar Gonzales-Porta, Yohan Jarosz, Balazs Laurenczy, Philippe Moret, Emilie Person, Patrick Roelli, Komal Sanjeev, Mathieu Seppey, Marc Robinson-Rechavi (2021). The Bgee suite: integrated curated expression atlas and comparative transcriptomics in animals. Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 49, Issue D1, 8 January 2021, Pages D831–D847, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa793
-
Si utiliza
gget blast, favor de citar también:- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403-10. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. PMID: 2231712.
-
Si utiliza
gget blat, favor de citar también:- Kent WJ. BLAT--the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 2002 Apr;12(4):656-64. doi: 10.1101/gr.229202. PMID: 11932250; PMCID: PMC187518.
-
Si utiliza
gget cbio, favor de citar también:-
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, Antipin Y, Reva B, Goldberg AP, Sander C, Schultz N. The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012 May;2(5):401-4. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095. Erratum in: Cancer Discov. 2012 Oct;2(10):960. PMID: 22588877; PMCID: PMC3956037.
-
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, Cerami E, Sander C, Schultz N. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 2013 Apr 2;6(269):pl1. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004088. PMID: 23550210; PMCID: PMC4160307.
-
de Bruijn I, Kundra R, Mastrogiacomo B, Tran TN, Sikina L, Mazor T, Li X, Ochoa A, Zhao G, Lai B, Abeshouse A, Baiceanu D, Ciftci E, Dogrusoz U, Dufilie A, Erkoc Z, Garcia Lara E, Fu Z, Gross B, Haynes C, Heath A, Higgins D, Jagannathan P, Kalletla K, Kumari P, Lindsay J, Lisman A, Leenknegt B, Lukasse P, Madela D, Madupuri R, van Nierop P, Plantalech O, Quach J, Resnick AC, Rodenburg SYA, Satravada BA, Schaeffer F, Sheridan R, Singh J, Sirohi R, Sumer SO, van Hagen S, Wang A, Wilson M, Zhang H, Zhu K, Rusk N, Brown S, Lavery JA, Panageas KS, Rudolph JE, LeNoue-Newton ML, Warner JL, Guo X, Hunter-Zinck H, Yu TV, Pilai S, Nichols C, Gardos SM, Philip J; AACR Project GENIE BPC Core Team, AACR Project GENIE Consortium; Kehl KL, Riely GJ, Schrag D, Lee J, Fiandalo MV, Sweeney SM, Pugh TJ, Sander C, Cerami E, Gao J, Schultz N. Analysis and Visualization of Longitudinal Genomic and Clinical Data from the AACR Project GENIE Biopharma Collaborative in cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 2023 Dec 1;83(23):3861-3867. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-0816. PMID: 37668528; PMCID: PMC10690089.
-
Please also cite the source of the data if you are using a publicly available dataset.
-
-
Si utiliza
gget cellxgene, favor de citar también:- Chanzuckerberg Initiative. (n.d.). CZ CELLxGENE Discover. Retrieved [insert date here], from https://cellxgene.cziscience.com/
-
Si utiliza
gget cosmic, favor de citar también:- Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, Sondka Z, Beare DM, Bindal N, Boutselakis H, Cole CG, Creatore C, Dawson E, Fish P, Harsha B, Hathaway C, Jupe SC, Kok CY, Noble K, Ponting L, Ramshaw CC, Rye CE, Speedy HE, Stefancsik R, Thompson SL, Wang S, Ward S, Campbell PJ, Forbes SA. COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 8;47(D1):D941-D947. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1015. PMID: 30371878; PMCID: PMC6323903.
-
Si utiliza
gget diamond, favor de citar también:- Buchfink, B., Xie, C. & Huson, D. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat Methods 12, 59–60 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3176
-
Si utiliza
gget elm, favor de citar también:-
Laura Luebbert, Chi Hoang, Manjeet Kumar, Lior Pachter, Fast and scalable querying of eukaryotic linear motifs with gget elm, Bioinformatics, 2024, btae095, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btae095
-
Manjeet Kumar, Sushama Michael, Jesús Alvarado-Valverde, Bálint Mészáros, Hugo Sámano‐Sánchez, András Zeke, Laszlo Dobson, Tamas Lazar, Mihkel Örd, Anurag Nagpal, Nazanin Farahi, Melanie Käser, Ramya Kraleti, Norman E Davey, Rita Pancsa, Lucía B Chemes, Toby J Gibson, The Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource: 2022 release, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 50, Issue D1, 7 January 2022, Pages D497–D508, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkab975
-
-
Si utiliza
gget enrichr, favor de citar también:-
Chen EY, Tan CM, Kou Y, Duan Q, Wang Z, Meirelles GV, Clark NR, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013; 128(14). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-128
-
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD, Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM, Lachmann A, McDermott MG, Monteiro CD, Gundersen GW, Ma'ayan A. Enrichr: a comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016; gkw377. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw377
-
Xie Z, Bailey A, Kuleshov MV, Clarke DJB., Evangelista JE, Jenkins SL, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML, Kropiwnicki E, Jagodnik KM, Jeon M, & Ma’ayan A. Gene set knowledge discovery with Enrichr. Current Protocols, 1, e90. 2021. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.90.
Si trabaja con conjuntos de datos no humanos/ratón, cite también:
- Kuleshov MV, Diaz JEL, Flamholz ZN, Keenan AB, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML, Cagan RL, Ma'ayan A. modEnrichr: a suite of gene set enrichment analysis tools for model organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 2;47(W1):W183-W190. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz347. PMID: 31069376; PMCID: PMC6602483.
-
-
Si utiliza
gget info, favor de citar también:-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
-
Sayers EW, Beck J, Bolton EE, Brister JR, Chan J, Comeau DC, Connor R, DiCuccio M, Farrell CM, Feldgarden M, Fine AM, Funk K, Hatcher E, Hoeppner M, Kane M, Kannan S, Katz KS, Kelly C, Klimke W, Kim S, Kimchi A, Landrum M, Lathrop S, Lu Z, Malheiro A, Marchler-Bauer A, Murphy TD, Phan L, Prasad AB, Pujar S, Sawyer A, Schmieder E, Schneider VA, Schoch CL, Sharma S, Thibaud-Nissen F, Trawick BW, Venkatapathi T, Wang J, Pruitt KD, Sherry ST. Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jan 5;52(D1):D33-D43. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad1044. PMID: 37994677; PMCID: PMC10767890.
-
The UniProt Consortium , UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D523–D531, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1052
-
-
Si utiliza
gget muscle, favor de citar también:- Edgar RC (2021), MUSCLE v5 enables improved estimates of phylogenetic tree confidence by ensemble bootstrapping, bioRxiv 2021.06.20.449169. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.06.20.449169
-
Si utiliza
gget opentargets, favor de citar también:- Ochoa D, Hercules A, Carmona M, Suveges D, Baker J, Malangone C, Lopez I, Miranda A, Cruz-Castillo C, Fumis L, Bernal-Llinares M, Tsukanov K, Cornu H, Tsirigos K, Razuvayevskaya O, Buniello A, Schwartzentruber J, Karim M, Ariano B, Martinez Osorio RE, Ferrer J, Ge X, Machlitt-Northen S, Gonzalez-Uriarte A, Saha S, Tirunagari S, Mehta C, Roldán-Romero JM, Horswell S, Young S, Ghoussaini M, Hulcoop DG, Dunham I, McDonagh EM. The next-generation Open Targets Platform: reimagined, redesigned, rebuilt. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D1353-D1359. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1046. PMID: 36399499; PMCID: PMC9825572.
-
Si utiliza
gget pdb, favor de citar también:- Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000 Jan 1;28(1):235-42. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.235. PMID: 10592235; PMCID: PMC102472.
-
Si utiliza
gget refogget search, favor de citar también:- Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
-
Si utiliza
gget seq, favor de citar también:-
Martin FJ, Amode MR, Aneja A, Austine-Orimoloye O, Azov AG, Barnes I, Becker A, Bennett R, Berry A, Bhai J, Bhurji SK, Bignell A, Boddu S, Branco Lins PR, Brooks L, Ramaraju SB, Charkhchi M, Cockburn A, Da Rin Fiorretto L, Davidson C, Dodiya K, Donaldson S, El Houdaigui B, El Naboulsi T, Fatima R, Giron CG, Genez T, Ghattaoraya GS, Martinez JG, Guijarro C, Hardy M, Hollis Z, Hourlier T, Hunt T, Kay M, Kaykala V, Le T, Lemos D, Marques-Coelho D, Marugán JC, Merino GA, Mirabueno LP, Mushtaq A, Hossain SN, Ogeh DN, Sakthivel MP, Parker A, Perry M, Piližota I, Prosovetskaia I, Pérez-Silva JG, Salam AIA, Saraiva-Agostinho N, Schuilenburg H, Sheppard D, Sinha S, Sipos B, Stark W, Steed E, Sukumaran R, Sumathipala D, Suner MM, Surapaneni L, Sutinen K, Szpak M, Tricomi FF, Urbina-Gómez D, Veidenberg A, Walsh TA, Walts B, Wass E, Willhoft N, Allen J, Alvarez-Jarreta J, Chakiachvili M, Flint B, Giorgetti S, Haggerty L, Ilsley GR, Loveland JE, Moore B, Mudge JM, Tate J, Thybert D, Trevanion SJ, Winterbottom A, Frankish A, Hunt SE, Ruffier M, Cunningham F, Dyer S, Finn RD, Howe KL, Harrison PW, Yates AD, Flicek P. Ensembl 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6;51(D1):D933-D941. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac958. PMID: 36318249; PMCID: PMC9825606.
-
The UniProt Consortium , UniProt: the Universal Protein Knowledgebase in 2023, Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 51, Issue D1, 6 January 2023, Pages D523–D531, https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac1052
-
Descargo de responsabilidad
gget es tan preciso como la base de datos/servidores/APIs que utiliza. La exactitud o fiabilidad de los datos no es garantizada por ningún motivo. Los proveedores por ningún motivo seran responsables de (incluyendo, sin limite alguno) la calidad, ejecución, o comerciabilidad para cualquier propósito particular surgiendo del uso o la incapacidad de usar los datos.





